1. 分類 常見的游標可分為顯示游標、隱式游標、靜態游標和動態游標四大類: 1.1 顯示游標 顯式是相對與隱式cursor而言的,就是有一個明確的聲明的cursor。顯式游標的聲明類似如下: delcare 游標關鍵字cursor 游標名 is 數據集; 游標從declare、open、fetch、 ...
1. 分類
常見的游標可分為顯示游標、隱式游標、靜態游標和動態游標四大類:
1.1 顯示游標
顯式是相對與隱式cursor而言的,就是有一個明確的聲明的cursor。顯式游標的聲明類似如下:
delcare 游標關鍵字cursor 游標名 is 數據集;
游標從declare、open、fetch、close是一個完整的生命旅程。當然了一個這樣的游標是可以被多次open進行使用的,顯式cursor是靜態cursor,她的作用域是全局的,但也必須明白,靜態cursor也只有pl/sql代碼才可以使用她。下麵看一個簡單的靜態顯式cursor的示例:

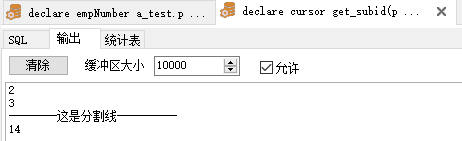
1 declare 2 cursor get_subid(pid a_test.parentid%type) is 3 select subid from a_test where parentid = pid; 4 v_subid a_test.subid%type; 5 begin 6 open get_subid(1); 7 loop 8 fetch get_subid 9 into v_subid; 10 exit when get_subid%notfound; 11 dbms_output.put_line(v_subid); 12 end loop; 13 close get_subid; 14 dbms_output.put_line('--------這是分割線----------'); 15 open get_subid(4); 16 loop 17 fetch get_subid 18 into v_subid; 19 exit when get_subid%notfound; 20 dbms_output.put_line(v_subid); 21 end loop; 22 close get_subid; 23 end;View Code
1.2 隱式游標
隱式cursor當然是相對於顯式而言的,就是沒有明確的cursor的declare。在Oracle的PL/SQL中,所有的DML操作都被Oracle內部解析為一個cursor名為SQL的隱式游標,只是對我們透明罷了。

begin for rec in (select user, sysdate from dual) loop dbms_output.put_line(rec.user || ':' || to_char(rec.sysdate, 'yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss')); end loop; end;View Code
1.3 靜態游標
靜態游標是相對於動態游標而言的,普通顯示定義的游標都是靜態游標。
1.4 動態游標
動態游標是相對於靜態游標而言的,要等到運行時才知道結果集查詢語句是什麼樣的。

1 declare 2 type atest_rec is record( 3 pid a_test.parentid%type, 4 subid a_test.subid%type); 5 6 type app_ref_cur_type is ref cursor return atest_rec; 7 my_cur app_ref_cur_type; 8 my_rec atest_rec; 9 begin 10 11 if (to_char(sysdate, 'dd') = 30) then 12 open my_cur for 13 select parentid, subid from a_test where parentid = 1; 14 else 15 open my_cur for 16 select parentid, subid from a_test where parentid = 2; 17 end if; 18 19 fetch my_cur 20 into my_rec; 21 while my_cur%found loop 22 --當前不是30號 執行else 結果: 23 --2#4 24 --2#5 25 dbms_output.put_line(my_rec.pid || '#' || my_rec.subid); 26 fetch my_cur 27 into my_rec; 28 end loop; 29 close my_cur; 30 31 end;View Code
【註】Record為記錄數據類型。它類似於C語言中的結構數據類型(STRUCTURE),PL/SQL提供了將幾個相關的、分離的、基本數據類型的變數組成一個整體的方法,即RECORD複合數據類型。在使用記錄數據類型變數時,需要在聲明部分先定義記錄的組成、記錄的變數,然後在執行部分引用該記錄變數本身或其中的成員。
定義記錄數據類型的語法如下:
1 TYPE RECORD_NAME IS RECORD( 2 V1 DATA_TYPE1 [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE], 3 V2 DATA_TYPE2 [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE], 4 VN DATA_TYPEN [NOT NULL][:=DEFAULT_VALUE]);
由上面的例子,可知cursor與REF cursor大致有以下幾點區別:
1)PL/SQL靜態游標不能返回到客戶端,只有PL/SQL才能利用它。動態游標能夠被返回到客戶端,這就是從Oracle的存儲過程返回結果集的方式。
2)PL/SQL靜態游標可以是全局的,而動態游標則不是,不能在包說明或包體中的過程或函數之外定義動態游標。
3)動態游標可以從子常式傳遞到子常式,而普通游標則不能。如果要共用靜態游標,必須在包說明或包體中把它定義為全局游標。 因為使用全局變數通常不是一種很好的編碼習慣,因此可以用動態游標來共用PL/SQL中的游標,無需混合使用全局變數。
4)靜態游標比動態游標標效率要高,所以在使用游標時首先考慮使用靜態游標,也有人建議儘量使用隱式游標,避免編寫附加的游標控制代碼(聲明,打開,獲取,關閉),也不需要聲明變數來保存從游標中獲取的數據。這個就因人因事而定吧。
另外,在oracle9i以後系統定義的一個refcursor, 這是一個弱類型的游標,相當於.Net中用戶var聲明的變數,主要用在過程中返回結果集。

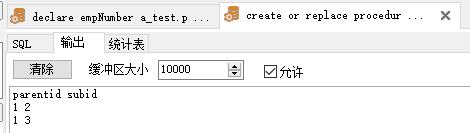
1 --創建存儲過程 2 create or replace procedure sp_get_subid(pid ina_test.parentid%type, 3 out_subid out SYS_REFCURSOR) as 4 begin 5 open out_subid for 6 SELECT * FROM a_test WHERE parentid = pid; 7 EXCEPTION 8 WHEN OTHERS THEN 9 RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR(-20101, 'Error in sp_get_subid' || SQLCODE); 10 end sp_get_subid; 11 12 --調用存儲過程 13 declare 14 v_rent_rows SYS_REFCURSOR; 15 v_rent_row a_test%rowType; 16 begin 17 sp_get_subid(1, v_rent_rows); 18 Dbms_output.put_line('parentid subid'); 19 loop 20 fetch v _rows 21 into v _row; 22 exit when v _rows%NOTFOUND; 23 Dbms_output.put_line(v _row.parentid || ' ' || v _row.subid); 24 end loop; 25 close v_rows; 26 end;View Code
2. 屬性
2.1 說明
1 %FOUND: bool - TRUE if >1 row returned 2 %NOTFOUND:bool - TRUE if 0 rows returned 3 %ISOPEN: bool - TRUE if cursor still open 4 %ROWCOUNT:int - number of rows affected by last SQL statement
【註】NO_DATA_FOUND和%NOTFOUND的用法是有區別的,小結如下:
1)SELECT . . . INTO 語句觸發 NO_DATA_FOUND;
2)當一個顯式游標的 where 子句未找到時觸發 %NOTFOUND;
3)當UPDATE或DELETE 語句的where 子句未找到時觸發 SQL%NOTFOUND;
4)在游標的提取(Fetch)迴圈中要用 %NOTFOUND 或%FOUND 來確定迴圈的退出條件,不要用NO_DATA_FOUND
2.2 示例
2.2.1 示例一:

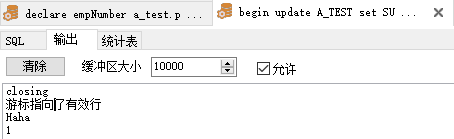
1 begin 2 3 update A_TEST set SUBID = '15' WHERE PARENTID = 4; 4 5 --SQL%ISOPEN是一個布爾值,如果游標打開,則為TRUE,如果游標關閉,則為FALSE. 6 7 if sql%isopen then 8 9 dbms_output.put_line('Openging'); 10 11 else 12 13 dbms_output.put_line('closing'); --對於隱式游標而言SQL%ISOPEN總是FALSE,這是因為隱式游標在DML語句執行時打開,結束時就立即關閉。 14 15 end if; 16 17 if sql%found then 18 19 dbms_output.put_line('游標指向了有效行'); --判斷游標是否指向有效行 20 21 else 22 23 dbms_output.put_line('Sorry'); 24 25 end if; 26 27 if sql%notfound then 28 29 dbms_output.put_line('Also Sorry'); 30 31 else 32 33 dbms_output.put_line('Haha'); 34 35 end if; 36 37 dbms_output.put_line(sql%rowcount); 38 39 exception 40 41 when no_data_found then 42 43 dbms_output.put_line('Sorry No data'); 44 45 when too_many_rows then 46 47 dbms_output.put_line('Too Many rows'); 48 49 end;View Code
【註】SQL語言分為DDL(Data Definition Language,數據定義語言,用來維護數據對象)和DML(Data Manipulation Language,數據操作語言,用於增刪改表中數據,DML是伴隨TCL事務控制的)。
2.2.2 示例二:

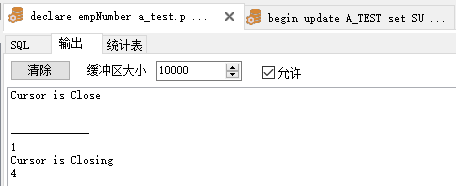
1 declare 2 3 empNumber a_test.parentid%TYPE; 4 5 empName a_test.subid%TYPE; 6 7 begin 8 9 if sql%isopen then 10 11 dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is opinging'); 12 13 else 14 15 dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is Close'); 16 17 end if; 18 19 if sql%notfound then 20 21 dbms_output.put_line('No Value'); 22 23 else 24 25 dbms_output.put_line(empNumber); --沒有賦值,輸出為空白 26 27 end if; 28 29 dbms_output.put_line(sql%rowcount); --沒有記錄,輸出為空白 30 31 dbms_output.put_line('-------------'); 32 33 34 35 select parentid, subid into empNumber, empName from a_test where parentid = 4; 36 37 dbms_output.put_line(sql%rowcount); 38 39 40 41 if sql%isopen then 42 43 dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is opinging'); 44 45 else 46 47 dbms_output.put_line('Cursor is Closing'); 48 49 end if; 50 51 if sql%notfound then 52 53 dbms_output.put_line('No Value'); 54 55 else 56 57 dbms_output.put_line(empNumber); 58 59 end if; 60 61 exception 62 63 when no_data_found then 64 65 dbms_output.put_line('No Value'); 66 67 when too_many_rows then 68 69 dbms_output.put_line('too many rows'); 70 71 end;View Code
【註】%Type是Oracle提供的一種數據定義方法,為的是使一個新定義的變數與另一個已經定義了的變數(通常是表的某一列)的數據類型保持一致,當被參照的那個變數的數據類型發生改變時,那麼這個新定義的變數的數據類型也會隨之發生改變。當不能確切的知道那個變數的類型是,就採用這種方法來定義變數的數據類型。
3. 操作
3.1 For迴圈游標
1 --聲明游標:delcare 游標關鍵字cursor 游標名 is 數據集; 2 3 declare 4 5 cursorc_list is 6 7 selectp.fid, max(t.exp) exp 8 9 from view_pilot p 10 11 left join IO_FMS_BILLOFHEALTH t 12 13 ont.phr = p.fjobnumber 14 15 group by p.fid; 16 17 18 --For迴圈,類似.Net中的foreach方法: 19 20 --begin 21 22 --for 元素名 in 游標名 迴圈關鍵字loop 23 24 --執行語句; 25 26 --endloop; 27 28 begin 29 30 for c_row in c_list loop 31 32 update alarm_pilotintelligence 33 34 set C = GetAlarmStateByExp(c_row.exp) 35 36 where isprimary = 0 37 38 and pid = c_row.fid; 39 40 end loop;
3.2 Fetch游標
1 --定義游標 2 3 declare 4 5 cursor c_job is 6 7 select * from a_test order by parentid; 8 9 --定義一個游標變數 10 11 c_row c_job%rowtype; 12 13 begin 14 15 --使用的時候必須要明確的打開游標 16 17 Open c_job; 18 19 --開始迴圈標記 20 21 loop 22 23 --提取一行數據到c_row,相當ADO.Net中的SqlDataReader.Read()方法 24 25 fetch c_job into c_row; 26 27 --判讀是否提取到值,沒取到值就退出 28 29 --取到值c_job%notfound 是false 30 31 --取不到值c_job%notfound 是true 32 33 exit when c_job%notfound; 34 35 dbms_output.put_line(c_row.parentid || '-' || c_row.subid); --用於輸出,這是oracle中最基礎的方法之一 36 37 --結束迴圈,並關閉游標 38 39 end loop; 40 41 close c_job; 42 43 end;
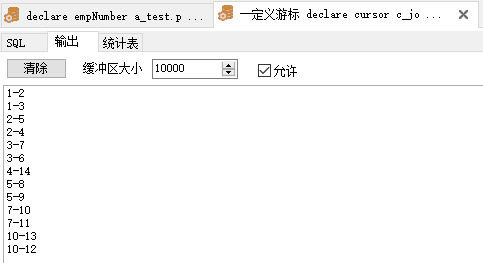
【註】如果一個表有較多的列,使用%ROWTYPE來定義一個表示表中一行記錄的變數,比分別使用%TYPE來定義表示表中各個列的變數要簡潔得多,並且不容易遺漏、出錯。這樣會增加程式的可維護性。當不能確切地知道被參照的那個表的結構及其數據類型時,可以採用這種方法定義變數的數據類型。
3.3 While迴圈游標
上面【示例二】中的結果還可以通過While迴圈與Fetch相結合來實現:
1 --定義游標 2 3 declare 4 5 cursor c_job is 6 7 select * from a_test order by parentid; 8 9 --定義一個游標變數 10 11 c_row c_job%rowtype; 12 13 begin 14 15 --使用的時候必須要明確的打開游標 16 17 Open c_job; 18 19 --開始迴圈標記 20 21 --提取一行數據到c_row,相當ADO.Net中的SqlDataReader.Read()方法 22 23 fetch c_job 24 25 into c_row; 26 27 --while迴圈 28 29 while c_job%found loop 30 31 dbms_output.put_line(c_row.parentid || '-' || c_row.subid); 32 33 fetch c_job 34 35 into c_row; 36 37 --結束迴圈,並關閉游標 38 39 end loop; 40 41 close c_job; 42 43 end;
參考資料:
2.游標屬性SQL%FOUND, SQL%NOTFOUND, SQL%ROWCOUNT, SQL%ISOPEN
4. cursor 與refcursor及sys_refcursor的區別 (轉載)




