本文是對Hadoop2.2.0版本的MapReduce進行詳細講解。請大家要註意版本,因為Hadoop的不同版本,源碼可能是不同的。 以下是本文的大綱: ...
本文是對Hadoop2.2.0版本的MapReduce進行詳細講解。請大家要註意版本,因為Hadoop的不同版本,源碼可能是不同的。
以下是本文的大綱:
1.獲取源碼
2.WordCount案例分析
3.客戶端源碼分析
4.小結
5.Mapper詳解
5.1.map輸入
5.2.map輸出
5.3.map小結
6.Reduce詳解
7.總結
若有不正之處,還請多多諒解,並希望批評指正。
請尊重作者勞動成果,轉發請標明blog地址
https://www.cnblogs.com/hongten/p/hongten_hadoop_mapreduce.html
1.獲取源碼
大家可以下載Hbase
Hbase: hbase-0.98.9-hadoop2-bin.tar.gz
在裡面就包含了Hadoop2.2.0版本的jar文件和源碼。
2.WordCount案例分析
在做詳解之前,我們先來看一個例子,就是在一個文件中有一下的內容
hello hongten 1 hello hongten 2 hello hongten 3 hello hongten 4 hello hongten 5 ...... ......
文件中每一行包含一個hello,一個hongten,然後在每一行最後有一個數字,這個數字是遞增的。
我們要統計這個文件裡面的單詞出現的次數(這個可以在網上找到很多相同的例子)
首先,我們要產生這個文件,大家可以使用以下的java代碼生成這個文件
1 import java.io.BufferedWriter; 2 import java.io.File; 3 import java.io.FileWriter; 4 5 /** 6 * @author Hongten 7 * @created 11 Nov 2018 8 */ 9 public class GenerateWord { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 12 13 double num = 12000000; 14 15 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); 16 for(int i=1;i<num;i++){ 17 sb.append("hello").append(" ").append("hongten").append(" ").append(i).append("\n"); 18 } 19 20 File writename = new File("/root/word.txt"); 21 writename.createNewFile(); 22 BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(writename)); 23 out.write(sb.toString()); 24 out.flush(); 25 out.close(); 26 System.out.println("done."); 27 } 28 }
進入Linux系統,編譯GenerateWord.java文件
javac GenerateWord.java
編譯好了以後,會生成GenerateWord.class文件,然後執行
java GenerateWord
等待一段時間....就會生成這個文件了(大概252MB左右)。
接下來,我們來寫統計單詞的map,reduce,以及客戶端的實現。
項目結構

這裡總共有三個java文件
客戶端
首先,我們需要定義Configuration和job,然後就是job的set操作,最後到job.waitForCompletion()方法,才觸發了動作的提交。
這裡可以理解為在客戶端,包含了一個配置分散式運行的相關配置信息,最後提交動作。
1 package com.b510.hongten.hadoop; 2 3 import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; 4 import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; 9 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; 10 11 /** 12 * @author Hongten 13 * @created 11 Nov 2018 14 */ 15 public class WordCount { 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 18 //讀取配置文件 19 Configuration conf = new Configuration(); 20 //創建job 21 Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); 22 23 // Create a new Job 24 job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class); 25 26 // Specify various job-specific parameters 27 job.setJobName("wordcount"); 28 29 job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); 30 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 31 job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 32 33 job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class); 34 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); 35 job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); 36 37 // job.setInputPath(new Path("/usr/input/wordcount")); 38 // job.setOutputPath(new Path("/usr/output/wordcount")); 39 40 FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path("/usr/input/wordcount1")); 41 42 Path output = new Path("/usr/output/wordcount"); 43 if (output.getFileSystem(conf).exists(output)) { 44 output.getFileSystem(conf).delete(output, true); 45 } 46 47 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, output); 48 49 // Submit the job, then poll for progress until the job is complete 50 job.waitForCompletion(true); 51 52 } 53 }
自定義的Mapper
1 package com.b510.hongten.hadoop; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.util.StringTokenizer; 5 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 8 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; 9 10 /** 11 * @author Hongten 12 * @created 11 Nov 2018 13 */ 14 public class MyMapper extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable> { 15 16 private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1); 17 private Text word = new Text(); 18 19 public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 20 StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString()); 21 while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) { 22 word.set(itr.nextToken()); 23 context.write(word, one); 24 } 25 } 26 27 }
自定義的Reduce
1 package com.b510.hongten.hadoop; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 5 import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; 6 import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; 7 import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; 8 9 /** 10 * @author Hongten 11 * @created 11 Nov 2018 12 */ 13 public class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> { 14 15 private IntWritable result = new IntWritable(); 16 17 public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { 18 int sum = 0; 19 for (IntWritable val : values) { 20 sum += val.get(); 21 } 22 result.set(sum); 23 context.write(key, result); 24 } 25 26 }
運行並查看結果
cd /home/hadoop-2.5/bin/ --創建測試文件夾 ./hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /usr/input/wordcount1 --把測試文件放入測試文件夾 ./hdfs dfs -put /root/word.txt /usr/input/wordcount1 --運行測試 ./hadoop jar /root/wordcount.jar com.b510.hongten.hadoop.WordCount --下載hdfs上面的文件 ./hdfs dfs -get /usr/output/wordcount/* ~/ --查看文件最後5行 tail -n5 /root/part-r-00000
運行結果
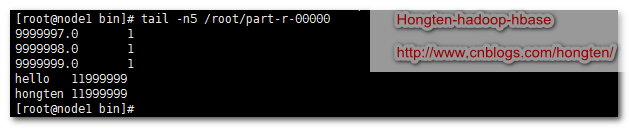
從yarn客戶端可以看到程式運行的時間長度
從11:47:46開始,到11:56:48結束,總共9min2s.(這是在我機器上面的虛擬機裡面跑的結果,如果在真正的集群裡面跑的話,應該要快很多)
數據條數:12000000-1條

3.客戶端源碼分析
當我們在客戶端進行了分散式作業的配置後,最後執行
// Submit the job, then poll for progress until the job is complete job.waitForCompletion(true);
那麼在waiteForCompletion()方法裡面都做了些什麼事情呢?
//我們傳遞的verbose=true public boolean waitForCompletion(boolean verbose ) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { if (state == JobState.DEFINE) { //提交動作 submit(); } //verbose=true if (verbose) { //監控並且列印job的相關信息 //在客戶端執行分散式作業的時候,我們能夠看到很多輸出 //如果verbose=false,我們則看不到作業輸出信息 monitorAndPrintJob(); } else { // get the completion poll interval from the client. int completionPollIntervalMillis = Job.getCompletionPollInterval(cluster.getConf()); while (!isComplete()) { try { Thread.sleep(completionPollIntervalMillis); } catch (InterruptedException ie) { } } } //返回作業的狀態 return isSuccessful(); }
這個方法裡面最重要的就是submit()方法,提交分散式作業。所以,我們需要進入submit()方法。
public void submit() throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { ensureState(JobState.DEFINE); //設置新的API,我使用的2.2.0的HadoopAPI,區別於之前的API setUseNewAPI(); //和集群做連接,集群裡面做出相應,分配作業ID connect(); final JobSubmitter submitter = getJobSubmitter(cluster.getFileSystem(), cluster.getClient()); status = ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<JobStatus>() { public JobStatus run() throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { //提交作業 /* Internal method for submitting jobs to the system. The job submission process involves: 1. Checking the input and output specifications of the job. 2. Computing the InputSplits for the job. 3. Setup the requisite accounting information for the DistributedCache of the job, if necessary. 4. Copying the job's jar and configuration to the map-reduce system directory on the distributed file-system. 5. Submitting the job to the JobTracker and optionally monitoring it's status. */ //在這個方法裡面包含5件事情。 //1.檢查輸入和輸出 //2.為每個job計算輸入切片的數量 //3.4.提交資源文件 //5.提交作業,監控狀態 //這裡要註意的是,在2.x裡面,已經沒有JobTracker了。 //JobTracker is no longer used since M/R 2.x. //This is a dummy JobTracker class, which is used to be compatible with M/R 1.x applications. return submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster); } }); state = JobState.RUNNING; LOG.info("The url to track the job: " + getTrackingURL()); }
所以我們需要進入submitter.submitJObInternal()方法去看看裡面的實現。
//在這個方法裡面包含5件事情。 //1.檢查輸入和輸出 //2.為每個job計算輸入切片的數量 //3.4.提交資源文件 //5.提交作業,監控狀態 //這裡要註意的是,在2.x裡面,已經沒有JobTracker了。 JobStatus submitJobInternal(Job job, Cluster cluster) throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException { //validate the jobs output specs checkSpecs(job); Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, job.getConfiguration()); //configure the command line options correctly on the submitting dfs Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration(); InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); if (ip != null) { submitHostAddress = ip.getHostAddress(); submitHostName = ip.getHostName(); conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOST,submitHostName); conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOSTADDR,submitHostAddress); } JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID(); //設置Job的ID job.setJobID(jobId); Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString()); JobStatus status = null; try { conf.set(MRJobConfig.USER_NAME, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getShortUserName()); conf.set("hadoop.http.filter.initializers", "org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.webproxy.amfilter.AmFilterInitializer"); conf.set(MRJobConfig.MAPREDUCE_JOB_DIR, submitJobDir.toString()); LOG.debug("Configuring job " + jobId + " with " + submitJobDir + " as the submit dir"); // get delegation token for the dir TokenCache.obtainTokensForNamenodes(job.getCredentials(), new Path[] { submitJobDir }, conf); populateTokenCache(conf, job.getCredentials()); // generate a secret to authenticate shuffle transfers if (TokenCache.getShuffleSecretKey(job.getCredentials()) == null) { KeyGenerator keyGen; try { keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(SHUFFLE_KEYGEN_ALGORITHM); keyGen.init(SHUFFLE_KEY_LENGTH); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) { throw new IOException("Error generating shuffle secret key", e); } SecretKey shuffleKey = keyGen.generateKey(); TokenCache.setShuffleSecretKey(shuffleKey.getEncoded(), job.getCredentials()); } copyAndConfigureFiles(job, submitJobDir); Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(submitJobDir); // Create the splits for the job LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + jtFs.makeQualified(submitJobDir)); //寫切片信息,我們主要關係這個方法 :)) int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir); conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps); LOG.info("number of splits:" + maps); // write "queue admins of the queue to which job is being submitted" // to job file. String queue = conf.get(MRJobConfig.QUEUE_NAME, JobConf.DEFAULT_QUEUE_NAME); AccessControlList acl = submitClient.getQueueAdmins(queue); conf.set(toFullPropertyName(queue, QueueACL.ADMINISTER_JOBS.getAclName()), acl.getAclString()); // removing jobtoken referrals before copying the jobconf to HDFS // as the tasks don't need this setting, actually they may break // because of it if present as the referral will point to a // different job. TokenCache.cleanUpTokenReferral(conf); if (conf.getBoolean( MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED, MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED)) { // Add HDFS tracking ids ArrayList<String> trackingIds = new ArrayList<String>(); for (Token<? extends TokenIdentifier> t : job.getCredentials().getAllTokens()) { trackingIds.add(t.decodeIdentifier().getTrackingId()); } conf.setStrings(MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS, trackingIds.toArray(new String[trackingIds.size()])); } // Write job file to submit dir writeConf(conf, submitJobFile); // // Now, actually submit the job (using the submit name) // //到這裡才真正提交job printTokens(jobId, job.getCredentials()); status = submitClient.submitJob( jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials()); if (status != null) { return status; } else { throw new IOException("Could not launch job"); } } finally { if (status == null) { LOG.info("Cleaning up the staging area " + submitJobDir); if (jtFs != null && submitJobDir != null) jtFs.delete(submitJobDir, true); } } }
在這裡我們關心的是
int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
進入writeSplites()方法
private int writeSplits(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException { //可以從job裡面獲取configuration信息 JobConf jConf = (JobConf)job.getConfiguration(); int maps; if (jConf.getUseNewMapper()) { //調用新的切片方法,我們使用的2.x的hadoop,因此 //使用的是新的切片方法 maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir); } else { //舊的切片方法 maps = writeOldSplits(jConf, jobSubmitDir); } return maps; }
我們使用的版本是2.x,所以,我們使用writeNewSplites()方法。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <T extends InputSplit>
int writeNewSplits(JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,
InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
//可以從job裡面獲取configuration信息
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
//通過反射獲取一個輸入格式化
//這裡面返回的是TextInputFormat,即預設值
InputFormat<?, ?> input =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf); // == 1 ==
//輸入格式化進行切片計算
List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job); // == 2 ==
T[] array = (T[]) splits.toArray(new InputSplit[splits.size()]);
// sort the splits into order based on size, so that the biggest
// go first
Arrays.sort(array, new SplitComparator());
JobSplitWriter.createSplitFiles(jobSubmitDir, conf,
jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(conf), array);
return array.length;
}
我們看到‘== 1 ==’,這裡是獲取輸入格式化,進入job.getInputFormatClass()方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
//如果配置信息裡面INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR(mapreduce.job.inputformat.class)沒有配置
//則返回TextInputFormat
//如果有配置,則返回我們配置的信息
//意思是:預設值為TextInputFormat
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}
我們看到,系統預設的輸入格式化為TextInputFormat。
我們看到‘== 2 ==’,這裡從輸入格式化裡面進行切片計算。那麼我們進入getSplites()方法
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException { //minSize = Math.max(1, 1L)=1 long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job)); // == A == //maxSize = Long.MAX_VALUE long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job); // == B == // generate splits List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>(); //獲取輸入文件列表 List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job); //遍歷文件列表 for (FileStatus file: files) { //一個文件一個文件的處理 //然後計算文件的切片 Path path = file.getPath(); //文件大小 long length = file.getLen(); if (length != 0) { BlockLocation[] blkLocations; if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) { blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations(); } else { //通過路徑獲取FileSystem FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration()); //獲取文件所有塊信息 blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length); } //判斷文件是否可以切片 if (isSplitable(job, path)) { //可以切片 //獲取文件塊大小 long blockSize = file.getBlockSize(); //切片大小 splitSize = blockSize //預設情況下,切片大小等於塊的大小 long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize); // == C == long bytesRemaining = length; while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) { //塊的索引 int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining); // == D == //切片詳細信息 splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts())); bytesRemaining -= splitSize; } if (bytesRemaining != 0) { int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining); splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts())); } } else { // not splitable //不可切片 splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts())); } } else { //Create empty hosts array for zero length files splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0])); } } // Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size()); LOG.debug("Total # of splits: " + splits.size()); return splits; }
我們看‘== A ==’, getFormatMinSplitSize()方法返回1,getMinSplitSize()方法返回1L。
protected long getFormatMinSplitSize() { return 1; } public static long getMinSplitSize(JobContext job) { //如果我們在配置文件中有配置SPLIT_MINSIZE(mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize),則取配置文件裡面的 //否則返回預設值1L //這裡我們,沒有配置,所以返回1L return job.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE, 1L); }
我們看‘== B ==’,getMaxSplitSize()方法返回Long.MAX_VALUE(我們沒有進行對SPLIT_MAXSIZE進行配置)
public static long getMaxSplitSize(JobContext context) { //如果我們在配置文件中有配置SPLIT_MAXSIZE(mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize),則取配置文件裡面的 //否則返回預設值Long.MAX_VALUE //這裡我們,沒有配置,所以返回Long.MAX_VALUE return context.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MAXSIZE, Long.MAX_VALUE); }
我們看‘== C ==’,在我們沒有進行配置的情況下,切片大小等於塊大小。
//minSize=1 //maxSize=Long.MAX_VALUE protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize, long maxSize) { //Math.min(maxSize, blockSize) -> Math.min(Long.MAX_VALUE, blockSize) -> blockSize //Math.max(minSize, blockSize) -> Math.max(1, blockSize) -> blockSize return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); }
我們看‘== D ==’,通過偏移量獲取塊的索引信息。
protected int getBlockIndex(BlockLocation[] blkLocations, long offset) { //通過偏移量獲取塊的索引 for (int i = 0 ; i < blkLocations.length; i++) { // is the offset inside this block? if ((blkLocations[i].getOffset() <= offset) && (offset < blkLocations[i].getOffset() + blkLocations[i].getLength())){ return i; } } BlockLocation last = blkLocations[blkLocations.length -1]; long fileLength = last.getOffset() + last.getLength() -1; throw new IllegalArgumentException("Offset " + offset + " is outside of file (0.." + fileLength + ")"); }
4.小結
用通俗的語言來描述上面的事情,可以用下麵的圖來說明:
系統預設的塊大小為128MB,在我們沒有進行其他配置的時候,塊大小等於切片大小。
Type1:塊大小為45MB,小於系統預設大小128MB,
切片信息:path, 0, 45, [3, 8, 10]
切片信息:文件的位置path, 偏移量0, 切片大小45, 塊的位置信息[3, 8, 10]=該文件(塊)存在HDFS文件系統的datanode3,datanode8,datanode10上面。
Type2:塊大小為128MB,即等於系統預設大小128MB,不會分成兩個快,和Type1一樣。
Type3:塊大小為414MB,即大於系統預設128MB,那麼在我們上傳該文件到HDFS的時候,系統就會把該文件分成很多塊,每一塊128MB,每一塊128MB,直到分完為止,最後剩下30MB單獨為一塊。那麼,每一個切片信息由文件位置path, 偏移量,切片大小, 塊的位置信息構成。我們把這一串信息稱為文件的切片清單。
當系統拿到了文件的切片清單了以後,那麼就會把這些清單提交給分散式系統,再由分散式系統去處理各個切片。

5.Mapper詳解
5.1.map輸入
map從HDFS獲取輸入流,然後定位到切片的位置,除了第一個切片,其他切片都是從第二行開始讀取數據進行處理。
在org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask裡面,包含了run()方法
//org.apache.hadoop.mapred.MapTask public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { this.umbilical = umbilical; if (isMapTask()) { // If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map // phase will govern the entire attempt's progress. //我們在客戶端可以設置reduce的個數 // job.setNumReduceTasks(10); //如果沒有Reduce,只有map階段, if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) { //那麼就執行這行 mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f); } else { // If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be // split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%). //只要有Reduce階段, mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f); //就要加入排序 sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f); } } TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical); boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper(); initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi); // check if it is a cleanupJobTask if (jobCleanup) { runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (jobSetup) { runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (taskCleanup) { runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } //是否使用新的API if (useNewApi) { //我們使用的是new mapper runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter); } else { runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter); } done(umbilical, reporter); }
我們進入到runNewMapper()方法,我們可以看到整個map的巨集觀動作
1.輸入初始化
2.調用org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper.run()方法
3.更新狀態
4.關閉輸入
5.關閉輸出
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
//獲取任務上下文
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper
// 通過反射構造mapper
// 得到我們寫的mapper類
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job); // == AA ==



