前言 之前討論了進程,瞭解一個進程能做一件事情,如果想同時處理多件事情,那麼需要多個進程,但是進程間很不方便的一點是,進程間的數據交換似乎沒有那麼方便。Linux提供線程功能,能在一個進程中,處理多任務,而且線程之間的數據是完全共用的。 線程也有PCB,它的PCB和進程的PCB結構完全一樣,只是它里 ...
前言
之前討論了進程,瞭解一個進程能做一件事情,如果想同時處理多件事情,那麼需要多個進程,但是進程間很不方便的一點是,進程間的數據交換似乎沒有那麼方便。Linux提供線程功能,能在一個進程中,處理多任務,而且線程之間的數據是完全共用的。
線程也有PCB,它的PCB和進程的PCB結構完全一樣,只是它裡面保存的虛擬地址空間和創建它的進程的虛擬地址空間完全保持一致。
線程的創建
通過pthread_create函數可以創建一個線程,被創建的線程的常式,就是一個新的執行指令序列了。
#include <pthread.h> void* thread_func(void* p ) { return NULL; } int main() { pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); printf("tid=%d\n", (int)tid); pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); printf("tid=%d\n", (int)tid); pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); printf("tid=%d\n", (int)tid); pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); printf("tid=%d\n", (int)tid); getchar(); }
Compile and link with -lpthread.
補充
intptr_t是一種整型,它的長度依賴機器位長,也就意味著它的長度和指針的長度一樣的。
線程標識
線程使用pthread_t來標識線程,它也是一個非負整數,由系統分配,保證在進程範圍內唯一。pthread_t雖然在Linux下是非負整數,但是在其它平臺下不一定是,所以比較線程號是否想等,應該用pthread_equal。
任何一個函數都可以調用pthread_self來獲取目前代碼運行的線程。
線程終止
| 終止方式 | |
|---|---|
| 常式返回 | 正常退出 |
| 調用pthread_exit | 正常退出 |
| 響應pthread_cancel | 異常退出 |
註意:
-
線上程里調用
exit是退出整個進程。 -
在多線程的進程中,主線程調用
pthread_exit,進程並不會退出,它的其他線程依舊在執行,但是主線程已經退出了。 -
意味著:主線程和其他線程是幾乎是平等的。
-
不平等的是,如果主線程的main函數return了,那麼其他線程也結束了,如果其他線程的入口函數return了,主線程不會跟著結束。
線程的回收
線程退出之後,它的PCB依舊在內核中存在,等著其它線程來獲取它的運行結果,可以通過pthread_join來回收線程。從這個角度看,線程和進程差不多,但是跟進程不同的時,線程沒有父線程的概念,同一個進程內的其它線程都可以來回收它的運行結果。
pthread_join會阻塞調用它的線程,一直到被join的線程結束為止。
pthread_join和wait/waitpid一樣,也是阻塞的調用,它除了有回收PCB的功能,也有等待線程結束的功能。
線程的使用場景
客戶端使用場景
一般來說,線程用於比較複雜的多任務場景,比如:
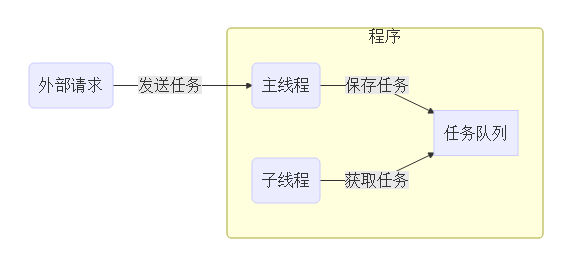
這樣主線程可以基礎處理主線程的事情,不至於被覆雜的任務阻塞。比如:

這樣聊天界面不會卡死在那裡,否則如果網路情況很差,有可能導致界面卡死。
伺服器使用場景
伺服器一般的流程如下:
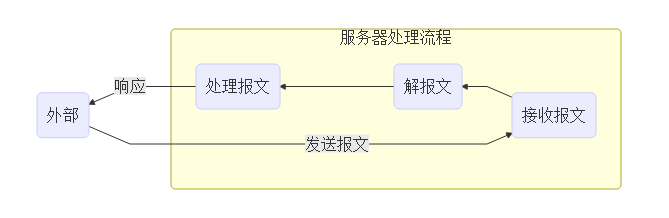
在伺服器上,一個線程來處理整個流程,會導致處理流程非常慢,導致主線程無法及時接收報文。一般會使用子線程來做具體的工作,而主線程只負責接收報文。

有時為了提高處理效率,會使用線程池
7.7 線程的同步
無論上述那種場景,都有一個報文隊列或者消息隊列,一般這個隊列是一個鏈表,主線程需要往鏈表中添加數據,而子線程從鏈表獲取數據。兩個線程同時操作一個全局變數是不安全的,應該避免不安全的訪問。無論這種全局變數是數組、鏈表、還是一個簡單的變數。
線程A:i = i + 1;
線程B:i = i + 1;
7.7.1 不安全的案例
-
多線程操作一個全局變數
-
不安全的生產者消費者模型
7.7.2 鎖(臨界量)
鎖能避免兩個線程同時訪問一個全局變數。
鎖會帶來兩個問題:
-
效率低
-
死鎖
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> int result = 0; // 定義鎖,鎖一般也定義在全局 //pthread_mutex_t mutex; // 粗粒度的鎖 pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; int result1 = 0; pthread_mutex_t mutex1; // 1.一個線程重覆加鎖兩次,會死鎖 void func() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } void foo() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); func(); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } // 2. 一個線程加鎖之後,忘記瞭解鎖 void foo1() { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if(...) // 這種場合容易產生忘記解鎖 return; // .... // 忘記瞭解鎖 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } void foo2() { // 因為別的線程忘記解鎖,所以本線程無法進行加鎖 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 阻塞在這裡 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } void* thread_func(void* ptr) { foo(); int i=0; for(i=0; i<100000; ++i) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1); result1++;//它的值由什麼決定 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1); // 兩個線程同時操作全局變數,結果不可靠 // // 將該操作變成原子操作,或者至少不應該被能影響它操作的人打斷 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); result ++; // result++代碼被鎖保護了,不會被其他線程的result++影響 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } return NULL; } int main() { // 使用鎖之前,要對它進行初始化 // pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1, NULL); pthread_t t1, t2; pthread_create(&t1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&t2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_join(t1, NULL); pthread_join(t2, NULL); printf("result is %d\n", result); }
#include <stdio.h> #include <list> #include <iostream> using namespace std; struct task_t { int task; }; // 全局的任務隊列 list<task_t*> tasks; pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; // pthred_cond_signal和pthread_cond_wait類似不可靠信號,signal不會累計 // 當一個線程發送signal時,如果另外一個線程此時沒有調用wait函數,那麼這個signal就會消失掉 void* work_thread(void* ptr) { while(1) { // 等待條件 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 一旦條件滿足,就應該處理隊列中所有的任務 while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); if(tasks.size() == 0) { pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 特別容易忘記解鎖 break; } task_t* task = *tasks.begin(); tasks.pop_front(); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 處理任務 printf("current task is %d\n", task->task); // new和delete(malloc和free)都是線程安全的 delete task; } } } int main() { pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, work_thread, NULL); while(1) { int i; // 阻塞的,等待任務 cin >> i; // 構造任務結構體 task_t* task = new task_t; task->task = i; // 把任務丟到任務列表中 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); tasks.push_back(task); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); // 喚醒條件變數 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); } }
//運用析構函數 #ifndef __AUTO_LOCK_H__ #define __AUTO_LOCK_H__ #include <pthread.h> class auto_lock { public: auto_lock(pthread_mutex_t& m); ~auto_lock(); private: pthread_mutex_t& mutex; }; #endif #include "auto_lock.h" auto_lock::auto_lock(pthread_mutex_t& m): mutex(m) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); } auto_lock::~auto_lock() { pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } #include <stdio.h> #include "auto_lock.h" pthread_mutex_t mutex; int result = 0; void* thread_func(void*ptr) { for(int i=0 ;i<100000; ++i) { auto_lock var1(mutex); // 重覆加鎖 auto_lock var(mutex); // 在構造里自動加鎖 result++; } } int main() { // 變成遞歸鎖 及迴圈鎖 pthread_mutexattr_t attr;//設計迴圈鎖屬性 pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr); pthread_mutexattr_settype(&attr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE); // 用遞歸屬性去初始化這個鎖 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, &attr); pthread_t tid1, tid2; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); printf("result is %d\n", result); }
相對的解決方法:
-
讀寫鎖
-
#include <pthread.h> pthread_rwlock_t mutex; int result; void* thread_func(void* ptr) { pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&mutex); // 只能對數據讀 result ++; // 寫數據的行為是會導致數據不正確 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&mutex); pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&mutex); // 可以對數據讀寫 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&mutex); } int main() { pthread_rwlock_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); }
-
迴圈鎖
7.7.2.1 基本鎖
類型:pthread_mutex_t
定義的變數一般在全局:pthread_mutex_t g_mutex;
在使用之前要初始化:pthread_mutex_init(&g_mutex, NULL);
訪問敏感對象前加鎖:pthread_mutex_lock(&g_mutex);
訪問結束要解鎖:pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_mutex);
一把所可以負責多個全局變數的安全問題,但是負責的範圍越大,效率越低,代碼相對容易寫。負責全局變數的數量,被稱之為鎖的粒度。
死鎖問題
-
忘瞭解鎖會產生死鎖
-
重覆加鎖會導致死鎖
怎麼解決死鎖問題:
-
忘瞭解鎖:程式員自己要註意
-
重覆加鎖:使用迴圈鎖可以解決問題
7.7.2.2 迴圈鎖
解決重覆加鎖導致死鎖問題,迴圈鎖的特點是,同一個線程進行多次加鎖,不會阻塞。
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); // 第二次加鎖不會阻塞,但是它會給mutex增加一個計數。
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex) // 減少計數
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//減少到0的時候,真正解鎖
怎麼設置迴圈鎖。
pthread_mutexattr_t attr; // 設置成迴圈鎖屬性 pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr); pthread_mutexattr_settype(&attr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE); // 此時mutex是一個迴圈鎖 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, &attr);//頭文件
#ifndef __AUTO_LOCK_H__
#define __AUTO_LOCK_H__
#include <pthread.h>
class auto_lock
{
public:
auto_lock(pthread_mutex_t& m);
~auto_lock();
private:
pthread_mutex_t& mutex;
};
#endif
//頭文件的實現
#include "auto_lock.h"
auto_lock::auto_lock(pthread_mutex_t& m): mutex(m)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
}
auto_lock::~auto_lock()
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
//主函數
#include <stdio.h> #include "auto_lock.h" pthread_mutex_t mutex; int result = 0; void* thread_func(void*ptr) { for(int i=0 ;i<100000; ++i) { auto_lock var1(mutex); // 重覆加鎖 auto_lock var(mutex); // 在構造里自動加鎖 result++; } } int main() { // 變成遞歸鎖 pthread_mutexattr_t attr; pthread_mutexattr_init(&attr); pthread_mutexattr_settype(&attr, PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE); // 用遞歸屬性去初始化這個鎖 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, &attr); pthread_t tid1, tid2; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); printf("result is %d\n", result); }
7.7.2.3 讀共用寫排他鎖(讀寫鎖)
共用鎖/排他鎖
定義鎖:pthread_rwlock_t mutex;
初始化:pthread_rwlock_init(&mutex, NULL);
讀鎖定:pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&mutex);
寫鎖定:pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&mutex);
解鎖:pthread_rwlock_unlock(&mutex);
7.7.2.4 總結
-
無論是什麼鎖,都會導致性能下降,所以能不用就儘量不用
-
鎖能不能用於進程間同步?可以
C++使用構造函數和析構函數自動加鎖解鎖
7.7.3 條件變數
條件變數是另外一種同步機制,它可以使線程在無競爭的等待條件發生。在之前講到的線程場景里,子線程往往要等到隊列有數據才運行,否則它應該休眠,以避免浪費CPU。但是如果用鎖來實現這種機制的話,會非常麻煩。
定義:pthread_cond_t g_cond;
初始化:pthread_cond_init(&g_cond);
等待:pthread_cond_wait(&g_cond, &g_mutex);
喚醒:pthread_cond_signal(&g_cond);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&g_cond);
驚群
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; void* thread_func(void* ptr) { sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); printf("wait ok\n"); } int main() { pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); // 發信號時,線程不是正在調用pthread_cond_wait,而是在執行sleep(1),所以signal發送之後,就消失了,不會保留 // 按照剛纔的說法,這個signal根本無效 // 所以當一個線程發送多次的signal時,那麼最多只有一次是有作用的 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); pthread_join(tid, NULL); }
7.7.3.1 條件變數的等待和喚醒
如果沒有線程在等待條件,此時喚醒函數pthread_cond_signal不會喚醒任何的線程,也不會記錄。
如果有多個線程在執行pthread_cond_wait,而此時有一個線程調用pthread_cond_signal,那麼只會喚醒其中一個線程。
如果想喚醒所有線程,那麼調用pthread_cond_broadcast,該函數可以喚醒等待該條件的所有線程。
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> // 假如有三個線程同時調用pthread_cond_wait,一個線程調用pthread_cond_signal // pthread_mutex_t mutex; pthread_cond_t cond; void* thread_func(void* ptr) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); printf("wait ok\n"); } int main() { pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_cond_init(&cond, NULL); pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, thread_func, NULL); sleep(1); // 喚醒一個線程 // pthread_cond_signal(&cond); // 喚醒所有正在等待的線程 pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); pthread_join(tid3, NULL); }
7.7.4 信號量
信號量類似條件變數,但是信號量可以保存信號數量。
-
定義: sem_t sem;
-
初始化:sem_init(&sem, 0, 0);
初始化的第二個參數,如果是0表示同一進程內的多線程之間的信號量,如果是非0,那麼該信號量可以使用在進程之間。第三個參數表示信號量的初始值。 -
等待:sem_wait(&sem);
sem_wait函數會導致該線程休眠,喚醒的條件是sem的值大於0。並且sem_wait調用結束後,會自動將sem值減1。 -
喚醒:sem_post(&sem);
sem_post只是簡單的將sem值+1#include <stdio.h> #include <semaphore.h> #include <pthread.h> sem_t sem; void* thread_func(void* ptr) { sleep(1); sem_wait(&sem); printf("wait ok\n"); } int main() { sem_init(&sem, 0, 0); pthread_t tid1, tid2, tid3; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid3, NULL, thread_func, NULL); // 發送信號 sem_post(&sem); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); pthread_join(tid3, NULL); }
7.8 重入
如果函數操作了全局變數,這個函數就不是可重入的函數了。
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <string.h> int result = 0; void foo() { // 因為這個函數操作了全局變數 result ++; } void* thread_func(void* ptr) { #if 0 int i; for(i=0; i<10000; ++i) { // 該函數是不可重入的函數 // 用鎖來保護它 foo(); } #endif char p[] = "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0"; char* saveptr; char* sub = strtok_r(p, " ", &saveptr); while(sub) { usleep(1000); // 1毫秒 printf("%s, tid=%d\n", sub, (int)pthread_self()); sub = strtok_r(NULL, " ", &saveptr); } } int main() { pthread_t tid1, tid2; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, NULL); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); printf("result=%d\n", result); }
7.9 分離的線程
分離的線程不用pthread_join,也無法通過pthread_join來獲取結果。因為它運行結束之後,它的PCB同時被釋放了。
#include <errno.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <inttypes.h> // intptr_t 整數類型:char short int long (long long) // 整數:8 16 32 64 // 有些機器的int是32位,有的機器是64位 // void*指針類型都是按照機器的字長決定 // // intptr_t是一個整數,並且它總是和指針的位元組數是一樣的 void* thread_func(void* ptr) { // 用的是地址本身,而不是地址指向的值 printf("%d\n", (int)(intptr_t)ptr); sleep(1); } int foo() { char p[] = "hello world"; int a = 100; pthread_attr_t attr; pthread_attr_init(&attr); pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED); pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, &attr, thread_func, (void*)(intptr_t)a); // 該線程自生自滅 // pthread_detach(tid); int ret = pthread_join(tid, NULL); printf("join error, ret=%d, errno=%d, EINVAL=%d\n", ret, errno, EINVAL); } int main() { foo(); sleep(2); }
7.10 線程私有數據
線程可以定義私有數據,私有數據只供該線程使用。
線程私有數據可以在該線程調用函數中訪問,其他線程調用的函數中,不可訪問。
#include <string.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> pthread_key_t key; // 可能被線程A調用 // 也可能線程B調用 void foo() { char* p = (char*)pthread_getspecific(key); printf("%s\n", p); } void my_malloc() { // 去這個線程的記憶體池去申請記憶體 void* mempool = pthread_getspecific(key); // __my_malloc(mempool, ...); } void* thread_func(void* ptr) { // setspecific,需要線上程中調用,當然也可以在主線程中調用 // 為這個線程設置私有數據 pthread_setspecific(key, ptr); foo(); my_malloc(); return NULL; } void free_func(void* ptr) { printf("free call\n"); free(ptr); } int main() { pthread_key_create(&key, free_func); pthread_t tid1, tid2; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func, strdup("thread1")); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func, strdup("thread2")); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); }
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <unistd.h> // 線程本地變數,每個線程都有一份拷貝 thread_local int result = 0; void foo() { // 全局變數 thread_local static int a = 0; a++; printf("%d\n", a); } void* thread_func1(void* ptr) { foo(); foo(); result = 100; } void* thread_func2(void* ptr) { foo(); foo(); sleep(1); // printf("%d\n", result); // 100 printf("%d\n", result); // thread_local時,這個值是0 } int main() { pthread_t tid1, tid2; pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thread_func1, NULL); pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thread_func2, NULL); pthread_join(tid1, NULL); pthread_join(tid2, NULL); }
7.11 線程取消
取消線程也結束線程,但是應該避免這種設計。
退出點函數:man pthreads搜索cancel關鍵字,找到這些退出點函數。
pthread_cancel線上程外部(其他線程)來退出另外一個線程A,當線程A調用了cancelpoint函數時,會退出。
如果希望調用cancelpoint函數不退出,應該設置當前的線程狀態為:不理會線程退出(cancelability disabled)
pthread_setcancelstate(...)
#include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> void* thread_func(void* ptr) { // 因為這個線程沒有cancel point while(1) { // 關閉cancel檢測 pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_DISABLE, NULL); sleep(10); // 打開cancel檢測 pthread_setcancelstate(PTHREAD_CANCEL_ENABLE, NULL); // 檢查cancel point pthread_testcancel(); } return NULL; } int main() { pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, thread_func, NULL); // 讓線程退出 pthread_cancel(tid); // 等待線程退出 pthread_join(tid, NULL); }


