接上篇博文《C#快速導出到excel》:由於此種方法不能導出成.xlsx格式,為解決此問題,本次分享使用NPOI。 參考:https://www.cnblogs.com/lazyneal/p/6148912.html 1、添加程式包。 在項目名右鍵。 選擇管理NuGet程式包,瀏覽處搜索NPOI並安 ...
接上篇博文《C#快速導出到excel》:由於此種方法不能導出成.xlsx格式,為解決此問題,本次分享使用NPOI。
參考:https://www.cnblogs.com/lazyneal/p/6148912.html
1、添加程式包。
在項目名右鍵。
選擇管理NuGet程式包,瀏覽處搜索NPOI並安裝。
2、代碼引用。
using System.IO; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.Diagnostics; using NPOI.HSSF.UserModel; using NPOI.SS.UserModel; using NPOI.XSSF.UserModel;
3、導出Excel方法:
public void ExportDataToExcel(DataTable TableName, string FileName) { SaveFileDialog saveFileDialog = new SaveFileDialog(); //設置文件標題 saveFileDialog.Title = "導出Excel文件"; //設置文件類型 saveFileDialog.Filter = "Excel 工作簿(*.xlsx)|*.xlsx|Excel 97-2003 工作簿(*.xls)|*.xls"; //設置預設文件類型顯示順序 saveFileDialog.FilterIndex = 1; //是否自動在文件名中添加擴展名 saveFileDialog.AddExtension = true; //是否記憶上次打開的目錄 saveFileDialog.RestoreDirectory = true; //設置預設文件名 saveFileDialog.FileName = FileName; //按下確定選擇的按鈕 if (saveFileDialog.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK) { //獲得文件路徑 string localFilePath = saveFileDialog.FileName.ToString(); //數據初始化 int TotalCount; //總行數 int RowRead = 0; //已讀行數 int Percent = 0; //百分比 TotalCount = TableName.Rows.Count; lblStatus.Text = "共有" + TotalCount + "條數據"; lblStatus.Visible = true; barStatus.Visible = true; //NPOI IWorkbook workbook; string FileExt = Path.GetExtension(localFilePath).ToLower(); if (FileExt == ".xlsx") { workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(); } else if (FileExt == ".xls") { workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(); } else { workbook = null; } if (workbook == null) { return; } ISheet sheet = string.IsNullOrEmpty(FileName) ? workbook.CreateSheet("Sheet1") : workbook.CreateSheet(FileName); //秒鐘 Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch(); timer.Start(); try { //讀取標題 IRow rowHeader = sheet.CreateRow(0); for (int i = 0; i < TableName.Columns.Count; i++) { ICell cell = rowHeader.CreateCell(i); cell.SetCellValue(TableName.Columns[i].ColumnName); } //讀取數據 for (int i = 0; i < TableName.Rows.Count; i++) { IRow rowData = sheet.CreateRow(i + 1); for (int j = 0; j < TableName.Columns.Count; j++) { ICell cell = rowData.CreateCell(j); cell.SetCellValue(TableName.Rows[i][j].ToString()); } //狀態欄顯示 RowRead++; Percent = (int)(100 * RowRead / TotalCount); barStatus.Maximum = TotalCount; barStatus.Value = RowRead; lblStatus.Text = "共有" + TotalCount + "條數據,已讀取" + Percent.ToString() + "%的數據。"; Application.DoEvents(); } //狀態欄更改 lblStatus.Text = "正在生成Excel..."; Application.DoEvents(); //轉為位元組數組 MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(); workbook.Write(stream); var buf = stream.ToArray(); //保存為Excel文件 using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(localFilePath, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { fs.Write(buf, 0, buf.Length); fs.Flush(); fs.Close(); } //狀態欄更改 lblStatus.Text = "生成Excel成功,共耗時" + timer.ElapsedMilliseconds + "毫秒。"; Application.DoEvents(); //關閉秒鐘 timer.Reset(); timer.Stop(); //成功提示 if (MessageBox.Show("導出成功,是否立即打開?", "提示", MessageBoxButtons.YesNo, MessageBoxIcon.Information) == DialogResult.Yes) { System.Diagnostics.Process.Start(localFilePath); } //賦初始值 lblStatus.Visible = false; barStatus.Visible = false; } catch (Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "提示", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information); } finally { //關閉秒鐘 timer.Reset(); timer.Stop(); //賦初始值 lblStatus.Visible = false; barStatus.Visible = false; } } }
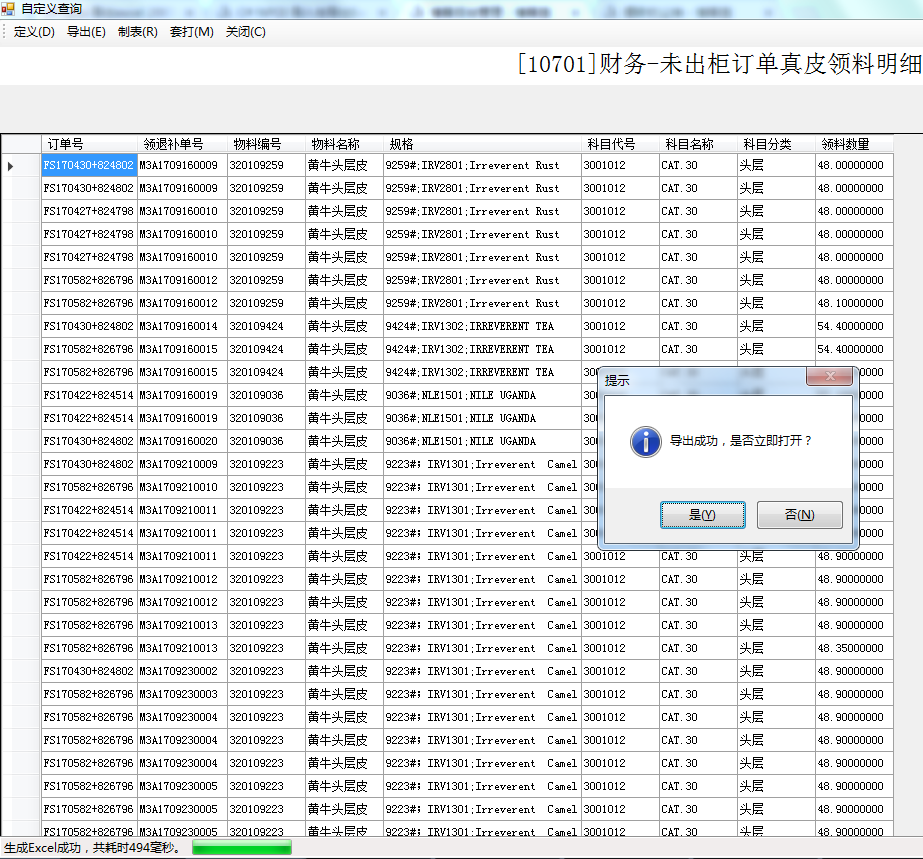
4、結果演示: