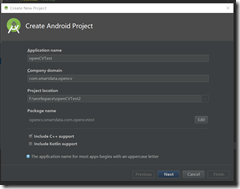
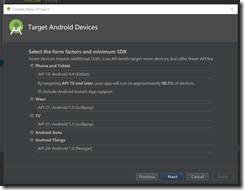
Note:這篇文章是基於Android Studio 3.01版本的,NDK是R16。step1:創建一個包含C++的項目其他預設就可以了。C++ Standard指定編譯庫的環境,其中Toolchain Default使用的是預設的CMake環境;C++ 11也就是C++環境。兩種環境都可以編庫,... ...
Note:這篇文章是基於Android Studio 3.01版本的,NDK是R16。
step1:創建一個包含C++的項目
其他預設就可以了。
C++ Standard
指定編譯庫的環境,其中Toolchain Default使用的是預設的CMake環境;C++ 11也就是C++環境。兩種環境都可以編庫,至於區別,後續會跟進,當前博文使用的是CMake環境。
Exceptions Support
如果選中覆選框,則表示當前項目支持C++異常處理,如果支持,在項目Module級別的build.gradle文件中會增加一個標識 -fexceptions到cppFlags屬性中,並且在so庫構建時,gradle會把該屬性值傳遞給CMake進行構建。
Runtime Type Information Support
同理,選中覆選框,項目支持RTTI,屬性cppFlags增加標識-frtti
切換到project 模式,生成的目錄的結構如下:
3、認識CMakeLists.txt構建腳本文件
CMakeLists.txt文件用於配置JNI項目屬性,主要用於聲明CMake使用版本、so庫名稱、C/CPP文件路徑等信息,下麵是該文件內容:
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the # documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html # Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library. cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1) # Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC # or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code. # You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you. # Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK. add_library( # Sets the name of the library. native-lib # Sets the library as a shared library. SHARED # Provides a relative path to your source file(s). src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp ) # Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a # variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by # default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library # you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before # completing its build. find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable. log-lib # Specifies the name of the NDK library that # you want CMake to locate. log ) # Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You # can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this # build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries. target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library. native-lib # Links the target library to the log library # included in the NDK. ${log-lib} )
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
CMake最小版本使用的是3.4.1。-
add_library()
配置so庫信息(為當前當前腳本文件添加庫)- native-lib
這個是聲明引用so庫的名稱,在項目中,如果需要使用這個so文件,引用的名稱就是這個。值得註意的是,實際上生成的so文件名稱是libnative-lib。當Run項目或者build項目是,在Module級別的build文件下的intermediates\transforms\mergeJniLibs\debug\folders\2000\1f\main下會生成相應的so庫文件。
- native-lib
SHARED
這個參數表示共用so庫文件,也就是在Run項目或者build項目時會在目錄intermediates\transforms\mergeJniLibs\debug\folders\2000\1f\main下生成so庫文。此外,so庫文件都會在打包到.apk裡面,可以通過選擇菜單欄的Build->Analyze Apk...*查看apk中是否存在so庫文件,一般它會存放在lib目錄下。src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp
構建so庫的源文件。
STATIC:靜態庫,是目標文件的歸檔文件,在鏈接其它目標的時候使用。
SHARED:動態庫,會被動態鏈接,在運行時被載入。
MODULE:模塊庫,是不會被鏈接到其它目標中的插件,但是可能會在運行時使用dlopen-系列的函數動態鏈接。
更詳細的解釋請參考這篇文章:C++靜態庫與動態庫
- 頭文件
也可以配置頭文件路徑,方法是(註意這裡指定的是目錄而非文件):
include_directories([AFTER|BEFORE] [SYSTEM] dir1 [dir2 ...])
下麵的配置實際上與自定義的JNI項目(自定義的so庫)沒有太大關係。
find_library()
這個方法與我們要創建的so庫無關而是使用NDK的Apis或者庫,預設情況下Android平臺集成了很多NDK庫文件,所以這些文件是沒有必要打包到apk裡面去的。直接聲明想要使用的庫名稱即可(猜測:貌似是在Sytem/libs目錄下)。在這裡不需要指定庫的路徑,因為這個路徑已經是CMake路徑搜索的一部分。如示例中使用的是log相關的so庫。log-lib
這個指定的是在NDK庫中每個類型的庫會存放一個特定的位置,而log庫存放在log-lib中log
指定使用log庫target_link_libraries()
如果你本地的庫(native-lib)想要調用log庫的方法,那麼就需要配置這個屬性,意思是把NDK庫關聯到本地庫。native-lib
要被關聯的庫名稱${log-lib}
要關聯的庫名稱,要用大括弧包裹,前面還要有$符號去引用。
實際上,我們可以自己創建CMakeLists.txt文件,而且路徑不受限制,只要在build.gradle中配置externalNativeBuild.cmake.path來指定該文件路徑即可。
add_subdirectory 可以執行子路徑的CMakeLists.txt
添加自定義的C++庫mathlib
創建源文件
- 我的項目名稱為OpenCVTest,所以右鍵這個項目點擊
New->Module,然後選Android Library,輸入庫的名稱MathLib,然後Finish,系統就會生成對應的模塊,並構建好初始的目錄樹。系統將庫命名為MathLib,但是目錄樹中還是小寫的mathlib。這個時候系統會自動在頂級settings.gradle添加對於這個新模塊的include語句。並且在模塊目錄下構建好了初始的build.gradle。 - 現在我們開始創建自己的C++庫,首先右鍵
mathlib目錄下的src/main,然後選擇New->Directory,輸入cpp並確定。這個目錄就是我們要創建的庫的源文件的位置。 - 右鍵
add,點擊New->C/C++ Source File,輸入add.cpp,並選中Create an associated header。 - 在
.cpp文件中定義好一個簡單的加法函數,併在.h文件中添加好對應聲明。
add.cpp
#include "add.h" int add(int a,int b) { return a + b; }
add.h
#ifndef OPENCVTEST_ADD_H #define OPENCVTEST_ADD_H int add(int a,int b); #endif //OPENCVTEST_ADD_H
將源文件關聯到構建系統中
我們用CMake來構建C++庫,然後CMake又要和gradle結合,在Android Studio裡面協作管理C++和Java的代碼。
我們在模塊mathlib的根目錄下創建一個名為CMakeLists.txt的文件,寫入
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1) add_library(add SHARED src/main/cpp/add.cpp) set(distribution_DIR ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/../distribution) set_target_properties(add PROPERTIES LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${distribution_DIR}/libs/${ANDROID_ABI}) target_include_directories(add PUBLIC ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/main/cpp) add_custom_command(TARGET add POST_BUILD COMMAND "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" -E copy "${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/src/main/cpp/add.h" "${distribution_DIR}/include/mathlib/add.h" # **** the following 2 lines are for potential future debug purpose **** # COMMAND "${CMAKE_COMMAND}" -E # remove_directory "${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}" COMMENT "Copying gmath to output directory")
set可以自定義變數。這裡定義生成so文件的目錄set_target_properties命令的意思是設置目標的一些屬性來改變它們構建的方式。這個命令中設置了 add的ARCHIVE_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY屬性。也就是改變了輸出路徑。
add_custom_command命令是自定義命令。命令中把頭文件也複製到了distribution_DIR中。
target_include_directories,它對創建的庫設置include路徑,針對目標來設置,可以避免與其他庫的衝突,並且此時對自定義的庫設置好了此路徑後,後續導入這個庫就不需要再次設置了。但對於預構建的庫,就需要設置,稍後會有詳細講解。
接下來我們在模塊mathlib的build.gradle中的defaultConfig{}中添加如下語句:
externalNativeBuild { cmake { arguments '-DANDROID_PLATFORM=android-19', '-DANDROID_TOOLCHAIN=clang', '-DANDROID_STL=gnustl_static' targets 'add' } }
這裡arguments是編譯參數,而targets則是相比於add_subdirectory更高許可權的方法。一般來說可以把它刪去,即預設構建所有目標。
然後在android{}最後添加如下語句,將CMakeLists.txt關聯起來。
externalNativeBuild { cmake { path 'CMakeLists.txt' } }
C++庫已經創建好了,接下來就要在主模塊中使用它了。
為了使用自定義C++庫,我們需要一個中間人,它從Android本身的Java程式中獲取請求,然後使用我們的C++庫中的函數計算得到結果,並將數據傳回Android本身的Java程式中。
創建一個中間文件native-math.cpp
#include <jni.h> #include <string> #include "mathlib/add.h" extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_bill_opencvtest_MainActivity_stringFromJNI( JNIEnv *env, jobject /* this */) { std::string hello = "Hello from C++ From Android openCVTest"; return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str()); } extern "C" JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL Java_com_example_bill_opencvtest_MainActivity_addFromCpp(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jint a, jint b) { // TODO return add(a,b); }
在app/CMakeLists.txt 加上這個自定義庫的引用
set(distribution_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../distribution)
include_directories(${distribution_DIR}/include)
add_library(lib_add SHARED IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(lib_add PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/libs/${ANDROID_ABI}/libadd.so)
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-math
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/native-math.cpp )
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
set_target_properties(native-math PROPERTIES
LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY
${distribution_DIR}/libs/${ANDROID_ABI})
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
native-math
android
log
lib_add
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib} )在模塊app的局部build.gradle中,像之前一樣添加好對應的語句:
defaultConfig{}中:
externalNativeBuild { cmake { arguments '-DANDROID_PLATFORM=android-19', '-DANDROID_TOOLCHAIN=clang', '-DANDROID_STL=gnustl_static' } } ndk { //abiFilters 'armeabi-v7a','x86_64' }
其中ndk指定abi平臺
ABI(Application binary interface)應用程式二進位介面。不同的CPU 與指令集的每種組合都有定義的 ABI (應用程式二進位介面),一段程式只有遵循這個介面規範才能在該 CPU 上運行,所以同樣的程式代碼為了相容多個不同的CPU,需要為不同的 ABI 構建不同的庫文件。當然對於CPU來說,不同的架構並不意味著一定互不相容。
- armeabi設備只相容armeabi;
- armeabi-v7a設備相容armeabi-v7a、armeabi;
- arm64-v8a設備相容arm64-v8a、armeabi-v7a、armeabi;
- X86設備相容X86、armeabi;
- X86_64設備相容X86_64、X86、armeabi;
- mips64設備相容mips64、mips;
- mips只相容mips;
接著在src/main/java/*/MainActivity.java中的MainActivity類下麵,載入庫,以及設置好對應的方法聲明:
static { System.loadLibrary("native-math"); } /** * A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library, * which is packaged with this application. */ public native String stringFromJNI(); public native int addFromCpp(int a, int b);
然後就可以在onCreate方法中使用這個C++庫定義的函數,在Java中對應的函數了super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // Example of a call to a native method TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text); tv.setText(stringFromJNI() + "____" + addFromCpp(2,88));
最後別忘了在項目中添加模塊的依賴關係才可以正常運行這個Android App。右鍵項目OpenCVTest,選擇Open Module Settings。選擇app->Dependencies,添加Module dependency,選擇mathlib,確定即可
添加OpenCV庫的支持
導入OpenCV進項目
- 從OpenCV的官網將OpenCV4Android 3.4下載下來,解壓到某個目錄。
- 點擊Android Studio的
File->New->Import Module,然後選擇路徑為OpenCV-android-sdk/sdk/java,確定。併在導入之後,修改build.gradle中的SDK版本。- 在
Open Module Settings中添加模塊的依賴關係,使app依賴openCVLibrary340。現在已經可以在
.java文件中看得到OpenCV的自動補全了。配置OpenCV的C++預構建庫
把包含文件夾
OpenCV-android-sdk/sdk/native/jni/include和預構建庫文件夾OpenCV-android-sdk/sdk/native/libs也複製到項目的distribution中。由於之前已經在添加C++庫時修改了
app的build.gradle,所以這個步驟現在不需要再執行了。由於OpenCV是預構建庫,所以沒有編譯的過程,因此模塊
openCVLibrary320中不需要添加CMakeLists.txt等。我們直接在app模塊中根目錄下的CMakeLists.txt導入OpenCV的庫即可。set(libs "${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/src/main/jniLibs") include_directories(${distribution_DIR}/include) # set add lib add_library(libopencv_java3 SHARED IMPORTED ) set_target_properties(libopencv_java3 PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION "${libs}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libopencv_java3.so") add_library( # Sets the name of the library. native-opencv # Sets the library as a shared library. SHARED # Provides a relative path to your source file(s). src/main/cpp/native-opencv.cpp ) set_target_properties(native-opencv PROPERTIES LIBRARY_OUTPUT_DIRECTORY ${distribution_DIR}/libs/${ANDROID_ABI}) target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library. native-opencv android log libopencv_java3 # Links the target library to the log library # included in the NDK. ${log-lib} )需要註意的是
.so使用SHARED,.a使用STATIC。註意:預構建庫:so文件和.a文件必須copy在src/main/jniLibs這個目錄,才可以自動被打包。其他路徑都不可以,連source這個命令也不起作用
現在可以使用openCV庫了,新建一個文件native-opencv.cpp
// // Created by bill on 2018/1/13. // #include <jni.h> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <vector> using namespace cv; using namespace std; extern "C" JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_example_bill_opencvtest_MainActivity_nativeProcessFrame(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jlong addrGray, jlong addrRGBA) { // TODO Mat& gray = *(Mat *) addrGray; Mat& rgba = *(Mat *) addrRGBA; vector<KeyPoint> v; Ptr<ORB> orb = ORB::create(); orb->detect(gray, v, cv::Mat()); for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); ++i) { const KeyPoint& kp = v[i]; circle(rgba, Point(kp.pt.x, kp.pt.y), 10, Scalar(255,0,0,255)); } }現在就可以在
src/main/java/*/MainActivity.java中按照同樣的方法,載入庫,寫上方法聲明。最後,如下所示。static { System.loadLibrary("native-opencv"); System.loadLibrary("native-math"); } /** * A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library, * which is packaged with this application. */ public native String stringFromJNI(); public native int addFromCpp(int a, int b); private native void nativeProcessFrame(long addrGray, long addrRGBA);完整的MainActivity
package com.example.bill.opencvtest; import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.WindowManager; import android.widget.TextView; import org.opencv.android.CameraBridgeViewBase; import org.opencv.android.OpenCVLoader; import org.opencv.core.CvType; import org.opencv.core.Mat; public class MainActivity extends Activity implements CameraBridgeViewBase.CvCameraViewListener2{ static { System.loadLibrary("native-opencv"); System.loadLibrary("native-math"); } /** * A native method that is implemented by the 'native-lib' native library, * which is packaged with this application. */ public native String stringFromJNI(); public native int addFromCpp(int a, int b); private native void nativeProcessFrame(long addrGray, long addrRGBA); private static final String TAG = "MainActivity"; private Mat rgba; private Mat gray; private CameraBridgeViewBase mOpenCvCameraView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // Example of a call to a native method TextView tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.sample_text); tv.setText(stringFromJNI() + "____" + addFromCpp(2,88)); getWindow().addFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_KEEP_SCREEN_ON); mOpenCvCameraView = (CameraBridgeViewBase) findViewById(R.id.activity_camera_view); mOpenCvCameraView.setVisibility(CameraBridgeViewBase.VISIBLE); mOpenCvCameraView.setCvCameraViewListener(this); } @Override public void onPause() { super.onPause(); if (mOpenCvCameraView != null){ mOpenCvCameraView.disableView(); } } @Override public void onResume() { super.onResume(); if (!OpenCVLoader.initDebug()) { Log.d(TAG, "Internal OpenCV library not found. Using OpenCV Manager for initialization"); } else { Log.d(TAG, "OpenCV library found inside package. Using it!"); mOpenCvCameraView.enableView(); } } public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); if (mOpenCvCameraView != null){ mOpenCvCameraView.disableView(); } } public void onCameraViewStarted(int width, int height){ rgba = new Mat(height, width, CvType.CV_8UC4); gray = new Mat(height, width, CvType.CV_8UC1); } public void onCameraViewStopped() { rgba.release(); gray.release(); } public Mat onCameraFrame(CameraBridgeViewBase.CvCameraViewFrame inputFrame){ rgba = inputFrame.rgba(); gray = inputFrame.gray(); nativeProcessFrame(gray.getNativeObjAddr(), rgba.getNativeObjAddr()); return rgba; } }activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:opencv="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context="com.example.bill.opencvtest.MainActivity"> <TextView android:id="@+id/sample_text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Hello World!" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> <org.opencv.android.JavaCameraView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:id="@+id/activity_camera_view" opencv:show_fps="true" opencv:camera_id="any"/> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
- 為了愉快的使用OpenCV Library,可以直接在AndroidManifest.xml裡面加入如下許可權
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="com.example.bill.opencvtest"> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA"/> <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera"/> <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.autofocus"/> <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.front"/> <uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.front.autofocus"/> <application android:allowBackup="true" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:label="@string/app_name" android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" android:supportsRtl="true" android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:screenOrientation="landscape" android:configChanges="keyboardHidden|orientation"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> </application> </manifest>