spring mvc簡介與運行原理 Spring的模型-視圖-控制器(MVC)框架是圍繞一個DispatcherServlet來設計的,這個Servlet會把請求分發給各個處理器,並支持可配置的處理器映射、視圖渲染、本地化、時區與主題渲染等,甚至還能支持文件上傳。 原理.png (1) Http請求 ...
spring mvc簡介與運行原理
Spring的模型-視圖-控制器(MVC)框架是圍繞一個DispatcherServlet來設計的,這個Servlet會把請求分發給各個處理器,並支持可配置的處理器映射、視圖渲染、本地化、時區與主題渲染等,甚至還能支持文件上傳。
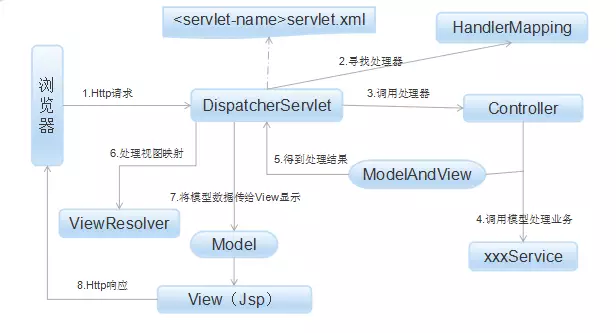
原理.png
-
-
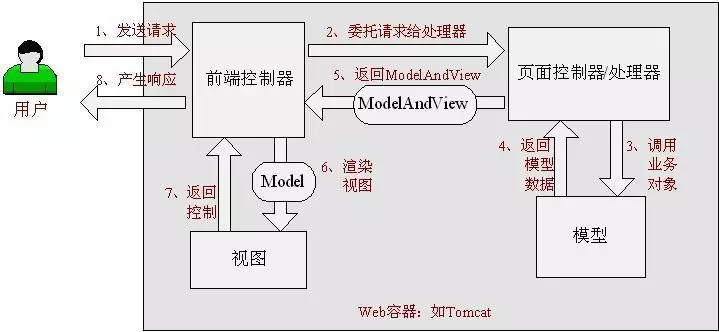
(1) Http請求:客戶端請求提交到DispatcherServlet。
-
(2) 尋找處理器:由DispatcherServlet控制器查詢一個或多個HandlerMapping,找到處理請求的Controller。
-
(3) 調用處理器:DispatcherServlet將請求提交到Controller。
-
(4)(5)調用業務處理和返回結果:Controller調用業務邏輯處理後,返回ModelAndView。
-
(6)(7)處理視圖映射並返回模型: DispatcherServlet查詢一個或多個ViewResoler視圖解析器,找到ModelAndView指定的視圖。
-
(8) Http響應:視圖負責將結果顯示到客戶端。
-
主要註解
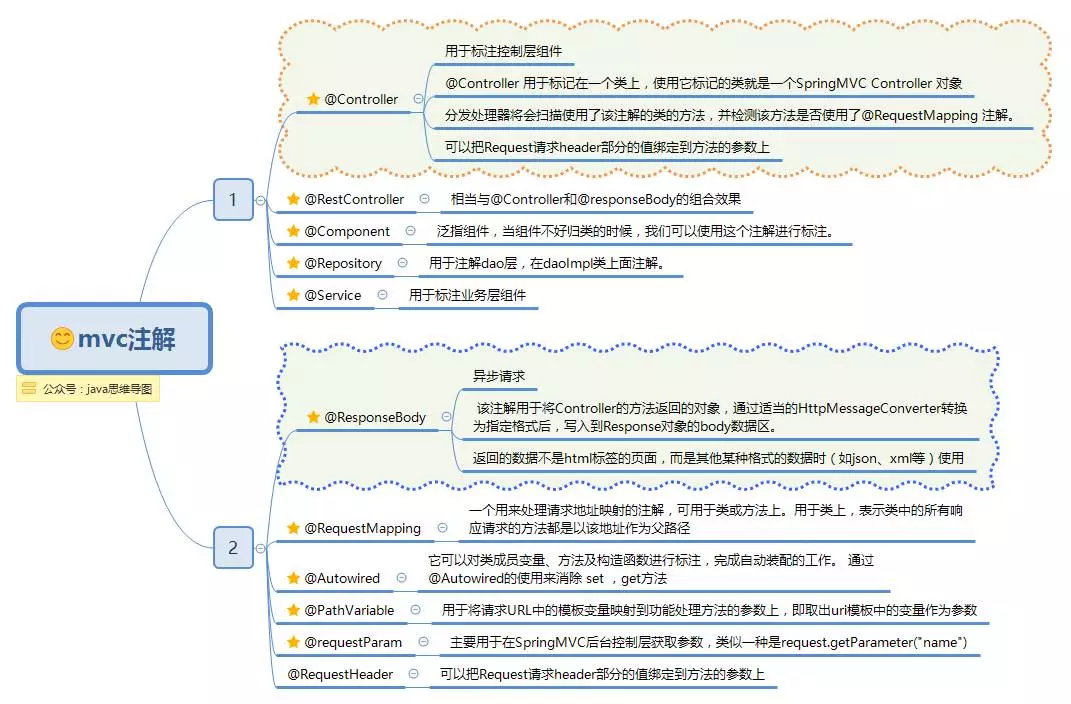
spring mvc註解.png
ContextLoaderListener
在講ContextLoaderListener之前,首先來瞭解一下web.xml的作用。
-
一個web中可以沒有web.xml文件,也就是說,web.xml文件並不是web工程必須的。web.xml文件是用來初始化配置信息:比如Welcome頁面、servlet、servlet-mapping、filter、listener、啟動載入級別等。當你的web工程沒用到這些時,你可以不用web.xml文件來配置你的Application。
-
當要啟動某個web項目時,伺服器軟體或容器如(tomcat)會第一步載入項目中的web.xml文件,通過其中的各種配置來啟動項目,只有其中配置的各項均無誤時,項目才能正確啟動。web.xml有多項標簽,在其載入的過程中順序依次為:context-param >> listener >> fileter >> servlet。(同類多個節點以出現順序依次載入)
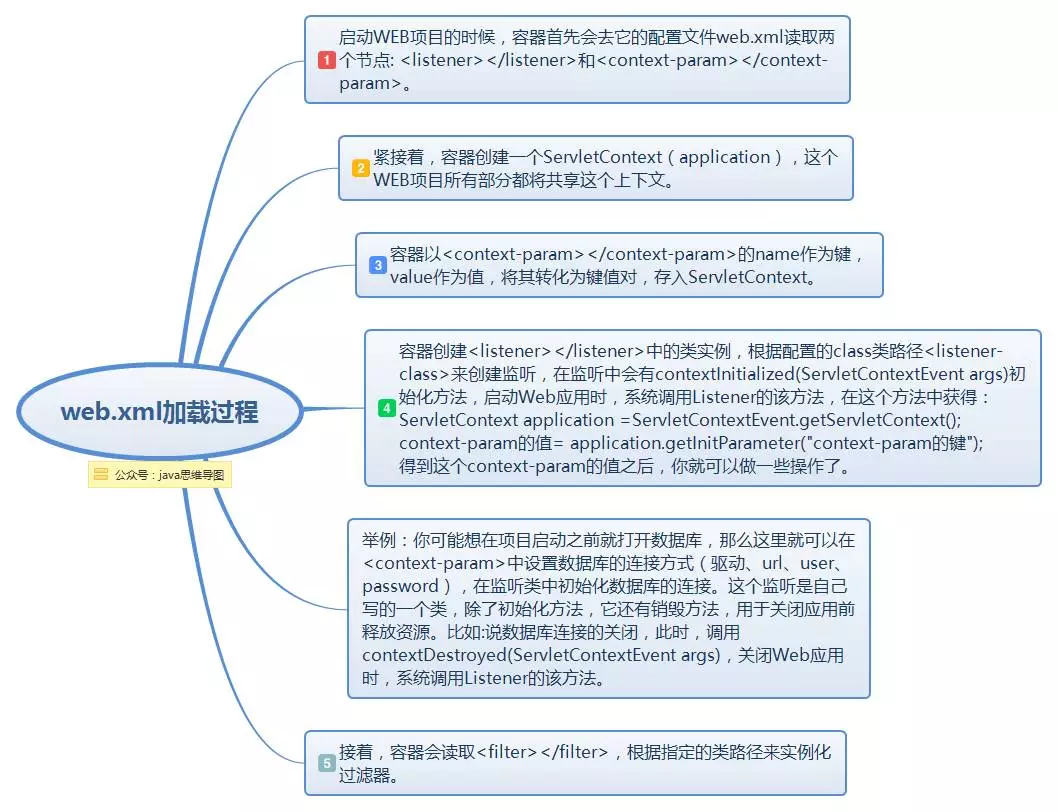
而spring mvc啟動過程大致分為兩個過程:
-
ContextLoaderListener初始化,實例化IoC容器,並將此容器實例註冊到ServletContext中。
-
DispatcherServlet初始化。
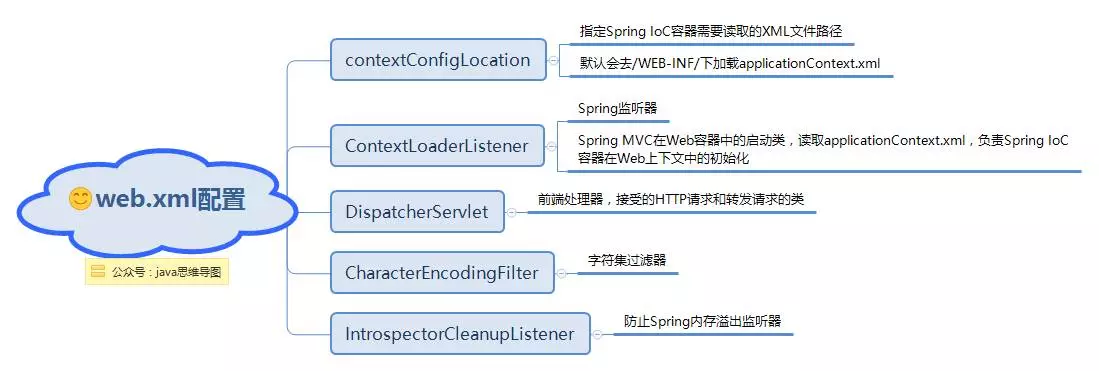
web.xml配置.png
其中ContextLoaderListener監聽器它實現了ServletContextListener這個介面,在web.xml配置這個監聽器,啟動容器時,就會預設執行它實現的方法。在ContextLoaderListener中關聯了ContextLoader這個類,所以整個載入配置過程由ContextLoader來完成。
-
ContextLoaderListener在web.xml中的配置
<!-- 配置contextConfigLocation初始化參數 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- 配置ContextLoaderListerner --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
ServletContextListener 介面有兩個方法:contextInitialized,contextDestroyed
DispatcherServlet
Spring MVC框架,與其他很多web的MVC框架一樣:請求驅動;所有設計都圍繞著一個中央Servlet來展開,它負責把所有請求分發到控制器;同時提供其他web應用開發所需要的功能。不過Spring的中央處理器,DispatcherServlet,能做的比這更多。
下圖展示了Spring Web MVC的DispatcherServlet處理請求的工作流。熟悉設計模式的朋友會發現,DispatcherServlet應用的其實就是一個“前端控制器”的設計模式(其他很多優秀的web框架也都使用了這個設計模式)。
- 流程圖
-
在web.xml中的配置
<!-- servlet定義 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
其中
-
load-on-startup:表示啟動容器時初始化該Servlet;
-
url-pattern:表示哪些請求交給Spring Web MVC處理, “/” 是用來定義預設servlet映射的。也可以如“*.html”表示攔截所有以html為擴展名的請求。
在Spring MVC中,每個DispatcherServlet都持有一個自己的上下文對象WebApplicationContext,它又繼承了根(root)WebApplicationContext對象中已經定義的所有bean。這些繼承的bean可以在具體的Servlet實例中被重載,在每個Servlet實例中你也可以定義其scope下的新bean。
WebApplicationContext繼承自ApplicationContext,它提供了一些web應用經常需要用到的特性。它與普通的ApplicationContext不同的地方在於,它支持主題的解析,並且知道它關聯到的是哪個servlet(它持有一個該ServletContext的引用)

DispatcherServlet繼承結構
spring mvc同時提供了很多特殊的註解,用於處理請求和渲染視圖等。DispatcherServlet初始化的過程中會預設使用這些特殊bean進行配置。如果你想指定使用哪個特定的bean,你可以在web應用上下文WebApplicationContext中簡單地配置它們。
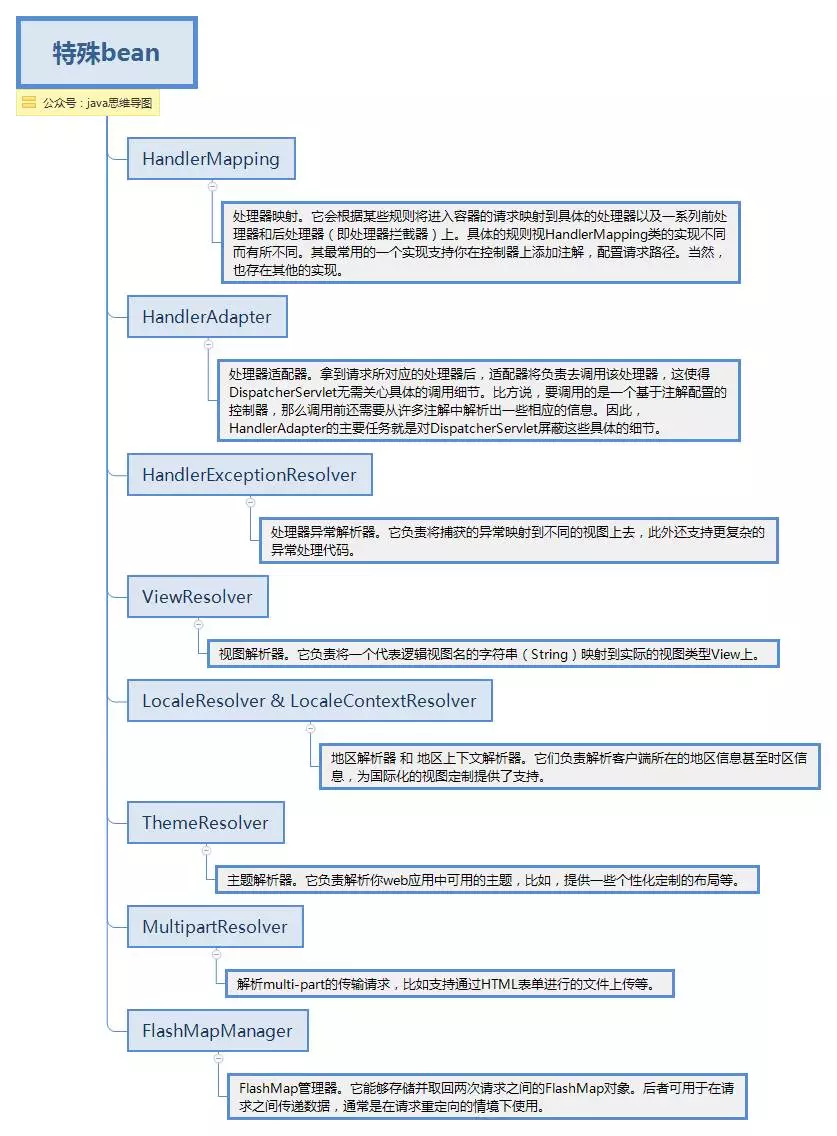
特殊bean.png
其中,常用的ViewResolver的配置。以jsp作為視圖為例
<!-- 對模型視圖名稱的解析,即在模型視圖名稱添加前尾碼 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean>
配置上傳文件限制MultipartResolver
<!-- 上傳限制 --> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <!-- 上傳文件大小限製為31M,31*1024*1024 --> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="32505856"/> </bean>
applicationContext.xml中的標簽
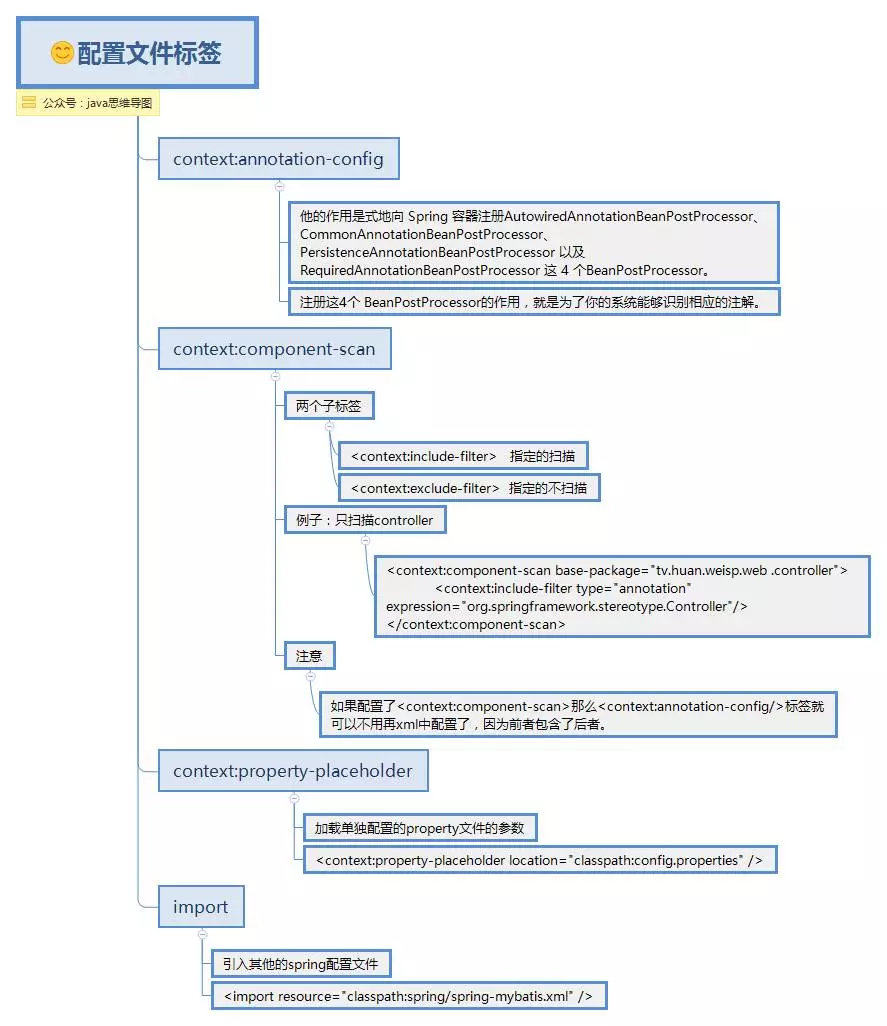
applicationContext.xml配置文件標簽.png
文件上傳
前面說到DispatcherServlet中有個特殊的Bean叫MultipartResolver,可用於限制文件的上傳大小等。當解析器MultipartResolver完成處理時,請求便會像其他請求一樣被正常流程處理。
- 表單
<form method="post" action="/form" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="text" name="name"/> <input type="file" name="file"/> <input type="submit"/> </form>
- 控制器
@RequestMapping(path = "/form", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String handleFormUpload(@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
if (!file.isEmpty()) {
byte[] bytes = file.getBytes();
// store the bytes somewhere
return "redirect:uploadSuccess";
}
return "redirect:uploadFailure";
}
異常處理
先來說下常見的異常處理有幾種方式,如下圖:
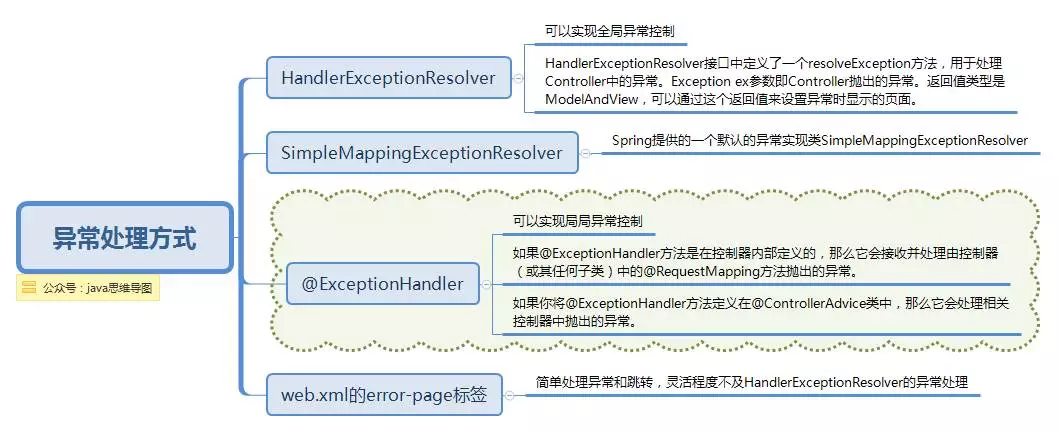
異常處理方式.png
Spring的處理器異常解析器HandlerExceptionResolver介面的實現負責處理各類控制器執行過程中出現的異常。也是上面提到的,是DispatcherServlet中的特殊bean,可以自定義配置處理。
某種程度上講,HandlerExceptionResolver與你在web應用描述符web.xml文件中能定義的異常映射(exception mapping)很相像,不過它比後者提供了更靈活的方式。比如它能提供異常被拋出時正在執行的是哪個處理器這樣的信息。
-
HandlerExceptionResolver 提供resolveException介面
public interface HandlerExceptionResolver { ModelAndView resolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex); }
-
在BaseController中使用 @ExceptionHandler註解處理異常
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) public Object exceptionHandler(Exception ex, HttpServletResponse response, HttpServletRequest request) throws IOException { String url = ""; String msg = ex.getMessage(); Object resultModel = null;
try {
if (ex.getClass() == HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class) { url = "admin/common/500"; System.out.println("--------毛有找到對應方法---------"); } else if (ex.getClass() == ParameterException.class) {//自定義的異常 } else if (ex.getClass() == UnauthorizedException.class) { url = "admin/common/unauth"; System.out.println("--------毛有許可權---------"); } String header = req.getHeader("X-Requested-With"); boolean isAjax = "XMLHttpRequest".equalsIgnoreCase(header); String method = req.getMethod(); boolean isPost = "POST".equalsIgnoreCase(method);
if (isAjax || isPost) {
return Message.error(msg); } else { ModelAndView view = new ModelAndView(url); view.addObject("error", msg); view.addObject("class", ex.getClass()); view.addObject("method", request.getRequestURI());
return view; } } catch (Exception exception) { logger.error(exception.getMessage(), exception);
return resultModel; } finally { logger.error(msg, ex); ex.printStackTrace(); } }
-
在web.xml中處理異常
<!-- 預設的錯誤處理頁面 --> <error-page> <error-code>403</error-code> <location>/403.html</location> </error-page> <error-page> <error-code>404</error-code> <location>/404.html</location> </error-page> <!-- 僅僅在調試的時候註視掉,在正式部署的時候不能註釋 --><!-- 這樣配置也是可以的,表示發生500錯誤的時候,轉到500.jsp頁面處理。 --> <error-page> <error-code>500</error-code> <location>/500.html</location> </error-page> <!-- 這樣的配置表示如果jsp頁面或者servlet發生java.lang.Exception類型(當然包含子類)的異常就會轉到500.jsp頁面處理。 --> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.Exception</exception-type> <location>/500.jsp</location> </error-page> <error-page> <exception-type>java.lang.Throwable</exception-type> <location>/500.jsp</location> </error-page> <!-- 當error-code和exception-type都配置時,exception-type配置的頁面優先順序高及出現500錯誤,發生異常Exception時會跳轉到500.jsp-->
-
來一個問題:HandlerExceptionResolver和web.xml中配置的error-page會有衝突嗎?
解答:如果resolveException返回了ModelAndView,會優先根據返回值中的頁面來顯示。不過,resolveException可以返回null,此時則展示web.xml中的error-page的500狀態碼配置的頁面。
當web.xml中有相應的error-page配置,則可以在實現resolveException方法時返回null。
API文檔中對返回值的解釋:
return a corresponding ModelAndView to forward to, or null for default processing.
--------轉自微信公眾號


