一、下載Spring的jar包 通過http://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/地址下載最新的Spring的zip包,當然,如果你是在使用maven工程的話,可以不用下載Zip包,可以直接在maven工程的pom.xml文件中添加 ...
一、下載Spring的jar包
通過http://repo.spring.io/release/org/springframework/spring/地址下載最新的Spring的zip包,當然,如果你是在使用maven工程的話,可以不用下載Zip包,可以直接在maven工程的pom.xml文件中添加Spring的依賴即可。
二、創建工程導入jar包
第一篇的內容記錄一些入門知識點,所以只需要導入幾個必要的基礎包則可,這裡項目只導入Spring的以下幾個包:
spring-core-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-beans-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-context-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-4.3.9.RELEASE.jar
除此之外,還需要導入兩個日誌jar包:
log4j-1.2.15.jar
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar
三、創建測試工程
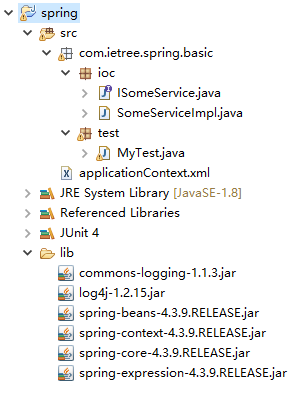
整個工程目錄如下圖所示:
3.1 編寫ISomeService介面類
package com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc; /** * 介面類 * * @author Root */ public interface ISomeService { void doSomeThing(); }
3.2 編寫SomeServiceImpl類,實現ISomeService
package com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc; /** * 實現類 * * @author Root */ public class SomeServiceImpl implements ISomeService { public SomeServiceImpl() { System.out.println("執行無參構造器,創建SomeServiceImpl對象"); } @Override public void doSomeThing() { System.out.println("執行doSomeThing()方法..."); } }
3.3 編寫applicationContext.xml配置文件
其中xml中的schema配置可以直接從Spring官方文檔中複製(spring-framework-4.3.9.RELEASE\docs\spring-framework-reference\html\xsd-configuration.html)
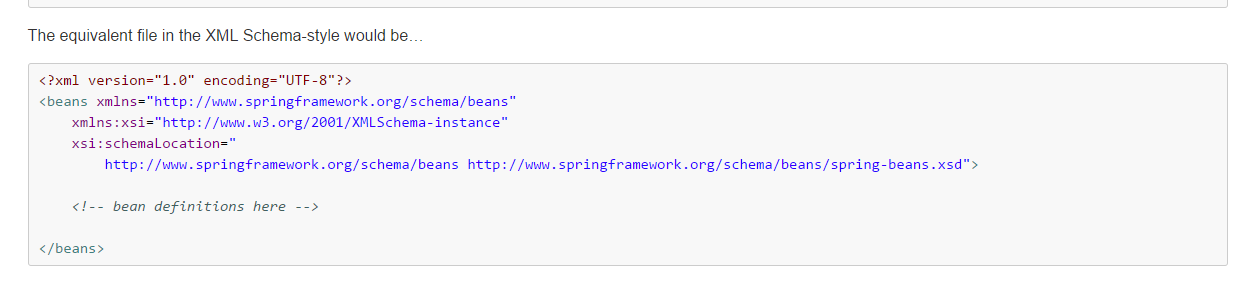
所以將schema複製之後需要配置對應的bean,這裡的id可以隨便命名,只需要對應需要創建的類即可,之後需要根據配置的bean的id值來獲取對象,不要再通過最早的那種通過new Object()的方式獲取了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 註冊Service 這裡相當於容器做了SomeServiceImpl myService = new SomeServiceImpl(); --> <bean id="myService" class="com.ietree.spring.basic.ioc.SomeServiceImpl"/> </beans>
以上步驟配置完成之後,Spring的環境就算簡單搭建完成了,現在來測試一下。
四、獲取對象的幾種方式
1、通過new Object();方式獲取對象
@Test public void test01() { ISomeService service = new SomeServiceImpl(); service.doSomeThing(); }
2、通過ClassPathXmlApplicationContext對象載入Spring的配置文件,採用getBean的方式獲取對象
@Test public void test02() { // 創建容器對象,載入Spring配置文件 // ClassPathXmlApplicationContext會從類路徑下查找配置文件 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
3、通過FileSystemXmlApplicationContext對象載入Spring的配置文件,採用getBean的方式獲取對象
@Test public void test03() { // FileSystemXmlApplicationContext會從項目的根下查找配置文件,或者從當前系統的D盤根目錄下查找配置文件 ApplicationContext ac = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) ac.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }
4、通過BeanFactory對象載入Spring的配置文件,採用getBean的方式獲取對象
// ApplicationContext與BeanFactory容器的區別: // 1)ApplicationContext容器在進行初始化時,會將其中的所有Bean(對象)進行創建。 // 缺點:占用系統資源(記憶體、CPU等) // 優點:響應速度快 // 2)BeanFactory容器中的對象,在容器初始化時並不會被創建,而是在真正獲取該對象時才被創建。 // 缺點:響應速度慢 // 優點:不多占用系統資源(記憶體、CPU等) @Test public void test04() { // 創建容器對象,載入Spring配置文件 BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml")); ISomeService service = (ISomeService) bf.getBean("myService"); service.doSomeThing(); }



