已知:流感訓練數據集,預定義兩個類別; 求:用ID3演算法建立流感的屬性描述決策樹 流感訓練數據集 No. 頭痛 肌肉痛 體溫 患流感 1 是(1) 是(1) 正常(0) 否(0) 2 是(1) 是(1) 高(1) 是(1) 3 是(1) 是(1) 很高(2) 是(1) 4 否(0) 是(1) 正常( ...
已知:流感訓練數據集,預定義兩個類別;
求:用ID3演算法建立流感的屬性描述決策樹
流感訓練數據集
|
No. |
頭痛 |
肌肉痛 |
體溫 |
患流感 |
|
1 |
是(1) |
是(1) |
正常(0) |
否(0) |
|
2 |
是(1) |
是(1) |
高(1) |
是(1) |
|
3 |
是(1) |
是(1) |
很高(2) |
是(1) |
|
4 |
否(0) |
是(1) |
正常(0) |
否(0) |
|
5 |
否(0) |
否(0) |
高(1) |
否(0) |
|
6 |
否(0) |
是(1) |
很高(2) |
是(1) |
|
7 |
是(1) |
否(0) |
高(1) |
是(1) |
原理分析:
在決策樹的每一個非葉子結點劃分之前,先計算每一個屬性所帶來的信息增益,選擇最大信息增益的屬性來劃分,因為信息增益越大,區分樣本的能力就越強,越具有代表性其中。
信息熵計算:
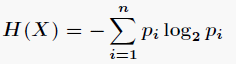
信息增益:

計算的結果(草稿上的字醜別噴):

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
*************************************************************************************************************
************************實現*********************************************

package ID3Tree; import java.util.Comparator;; @SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") public class Comparisons implements Comparator { public int compare(Object a, Object b) throws ClassCastException{ String str1 = (String)a; String str2 = (String)b; return str1.compareTo(str2); } }
package ID3Tree; public class Entropy { //信息熵 public static double getEntropy(int x, int total) { if (x == 0) { return 0; } double x_pi = getShang(x,total); return -(x_pi*Logs(x_pi)); } public static double Logs(double y) { return Math.log(y) / Math.log(2); } public static double getShang(int x, int total) { return x * Double.parseDouble("1.0") / total; } }
package ID3Tree; public class TreeNode { //父節點 TreeNode parent; //指向父節點的屬性 String parentAttribute; String nodeName; String[] attributes; TreeNode[] childNodes; }
package ID3Tree; import java.util.*; public class UtilID3 { TreeNode root; private boolean[] flag; //訓練集 private Object[] trainArrays; //節點索引 private int nodeIndex; public static void main(String[] args) { //初始化訓練集數組 Object[] arrays = new Object[]{ new String[]{"是","是","正常","否"}, new String[]{"是","是","高","是"}, new String[]{"是","是","很高","是"}, new String[]{"否","是","正常","否"}, new String[]{"否","否","高","否"}, new String[]{"否","是","很高","是"}, new String[]{"是","否","高","是"}}; UtilID3 ID3Tree = new UtilID3(); ID3Tree.create(arrays, 3); } //創建 public void create(Object[] arrays, int index) { this.trainArrays = arrays; initial(arrays, index); createDTree(arrays); printDTree(root); } //初始化 public void initial(Object[] dataArray, int index) { this.nodeIndex = index; //數據初始化 this.flag = new boolean[((String[])dataArray[0]).length]; for (int i = 0; i<this.flag.length; i++) { if (i == index) { this.flag[i] = true; } else { this.flag[i] = false; } } } //創建決策樹 public void createDTree(Object[] arrays) { Object[] ob = getMaxGain(arrays); if (this.root == null) { this.root = new TreeNode(); root.parent = null; root.parentAttribute = null; root.attributes = getAttributes(((Integer)ob[1]).intValue()); root.nodeName = getNodeName(((Integer)ob[1]).intValue()); root.childNodes = new TreeNode[root.attributes.length]; insert(arrays, root); } } //插入決策樹 public void insert(Object[] arrays, TreeNode parentNode) { String[] attributes = parentNode.attributes; for (int i = 0; i < attributes.length; i++) { Object[] Arrays = pickUpAndCreateArray(arrays, attributes[i],getNodeIndex(parentNode.nodeName)); Object[] info = getMaxGain(Arrays); double gain = ((Double)info[0]).doubleValue(); if (gain != 0) { int index = ((Integer)info[1]).intValue(); TreeNode currentNode = new TreeNode(); currentNode.parent = parentNode; currentNode.parentAttribute = attributes[i]; currentNode.attributes = getAttributes(index); currentNode.nodeName = getNodeName(index); currentNode.childNodes = new TreeNode[currentNode.attributes.length]; parentNode.childNodes[i] = currentNode; insert(Arrays, currentNode); } else { TreeNode leafNode = new TreeNode(); leafNode.parent = parentNode; leafNode.parentAttribute = attributes[i]; leafNode.attributes = new String[0]; leafNode.nodeName = getLeafNodeName(Arrays); leafNode.childNodes = new TreeNode[0]; parentNode.childNodes[i] = leafNode; } } } //輸出 public void printDTree(TreeNode node) { System.out.println(node.nodeName); TreeNode[] childs = node.childNodes; for (int i = 0; i < childs.length; i++) { if (childs[i] != null) { System.out.println("如果:"+childs[i].parentAttribute); printDTree(childs[i]); } } } //剪取數組 public Object[] pickUpAndCreateArray(Object[] arrays, String attribute, int index) { List<String[]> list = new ArrayList<String[]>(); for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { String[] strs = (String[])arrays[i]; if (strs[index].equals(attribute)) { list.add(strs); } } return list.toArray(); } //取得節點名 public String getNodeName(int index) { String[] strs = new String[]{"頭痛","肌肉痛","體溫","患流感"}; for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { if (i == index) { return strs[i]; } } return null; } //取得葉子節點名 public String getLeafNodeName(Object[] arrays) { if (arrays != null && arrays.length > 0) { String[] strs = (String[])arrays[0]; return strs[nodeIndex]; } return null; } //取得節點索引 public int getNodeIndex(String name) { String[] strs = new String[]{"頭痛","肌肉痛","體溫","患流感"}; for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { if (name.equals(strs[i])) { return i; } } return -1; } //得到最大信息增益 public Object[] getMaxGain(Object[] arrays) { Object[] result = new Object[2]; double gain = 0; int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i<this.flag.length; i++) { if (!this.flag[i]) { double value = gain(arrays, i); if (gain < value) { gain = value; index = i; } } } result[0] = gain; result[1] = index; if (index != -1) { this.flag[index] = true; } return result; } //取得屬性數組 public String[] getAttributes(int index) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") TreeSet<String> set = new TreeSet<String>(new Comparisons()); for (int i = 0; i<this.trainArrays.length; i++) { String[] strs = (String[])this.trainArrays[i]; set.add(strs[index]); } String[] result = new String[set.size()]; return set.toArray(result); } //計算信息增益 public double gain(Object[] arrays, int index) { String[] playBalls = getAttributes(this.nodeIndex); int[] counts = new int[playBalls.length]; for (int i = 0; i<counts.length; i++) { counts[i] = 0; } for (int i = 0; i<arrays.length; i++) { String[] strs = (String[])arrays[i]; for (int j = 0; j<playBalls.length; j++) { if (strs[this.nodeIndex].equals(playBalls[j])) { counts[j]++; } } } double entropyS = 0; for (int i = 0;i <counts.length; i++) { entropyS = entropyS + Entropy.getEntropy(counts[i], arrays.length); } String[] attributes = getAttributes(index); double total = 0; for (int i = 0; i<attributes.length; i++) { total = total + entropy(arrays, index, attributes[i], arrays.length); } return entropyS - total; } public double entropy(Object[] arrays, int index, String attribute, int totals) { String[] playBalls = getAttributes(this.nodeIndex); int[] counts = new int[playBalls.length]; for (int i = 0; i < counts.length; i++) { counts[i] = 0; } for (int i = 0; i < arrays.length; i++) { String[] strs = (String[])arrays[i]; if (strs[index].equals(attribute)) { for (int k = 0; k<playBalls.length; k++) { if (strs[this.nodeIndex].equals(playBalls[k])) { counts[k]++; } } } } int total = 0; double entropy = 0; for (int i = 0; i < counts.length; i++) { total = total +counts[i]; } for (int i = 0; i < counts.length; i++) { entropy = entropy + Entropy.getEntropy(counts[i], total); } return Entropy.getShang(total, totals)*entropy; } }




