Exercise 1:Linear Regression 實現一個線性回歸 關於如何實現一個線性回歸,請參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/6079012.html Exercise 2:Logistic Regression 實現一個邏輯回歸 問題描述:用邏輯回歸 ...
Exercise 1:Linear Regression---實現一個線性回歸
關於如何實現一個線性回歸,請參考:http://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/6079012.html
Exercise 2:Logistic Regression---實現一個邏輯回歸
問題描述:用邏輯回歸根據學生的考試成績來判斷該學生是否可以入學。
這裡的訓練數據(training instance)是學生的兩次考試成績,以及TA是否能夠入學的決定(y=0表示成績不合格,不予錄取;y=1表示錄取)
因此,需要根據trainging set 訓練出一個classification model。然後,拿著這個classification model 來評估新學生能否入學。
訓練數據的成績樣例如下:第一列表示第一次考試成績,第二列表示第二次考試成績,第三列表示入學結果(0--不能入學,1--可以入學)
34.62365962451697, 78.0246928153624, 0
30.28671076822607, 43.89499752400101, 0
35.84740876993872, 72.90219802708364, 0
60.18259938620976, 86.30855209546826, 1
....
....
....
訓練數據圖形表示 如下:橫坐標是第一次考試的成績,縱坐標是第二次考試的成績,右上角的 + 表示允許入學,圓圈表示不允許入學。(分數決定命運,太悲慘了!)
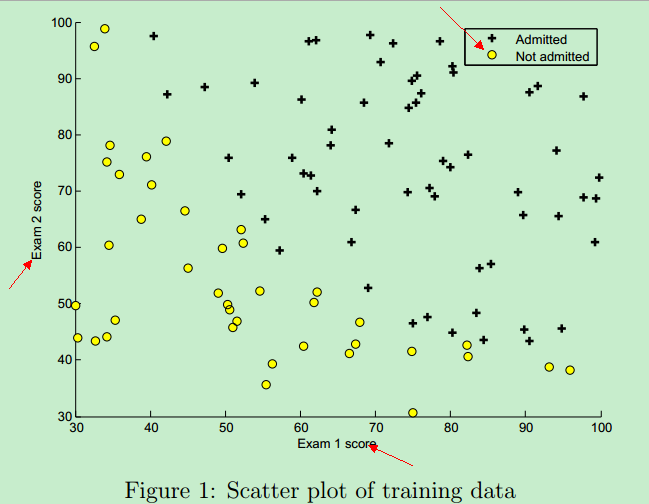
該訓練數據的圖形 可以通過Matlab plotData函數畫出來,它調用Matlab中的plot函數和find函數,Matlab代碼實現如下:
function plotData(X, y) %PLOTDATA Plots the data points X and y into a new figure % PLOTDATA(x,y) plots the data points with + for the positive examples % and o for the negative examples. X is assumed to be a Mx2 matrix. % Create New Figure figure; hold on; % ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ====================== % Instructions: Plot the positive and negative examples on a % 2D plot, using the option 'k+' for the positive % examples and 'ko' for the negative examples. % pos = find(y==1); neg = find(y==0); plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+', 'LineWidth', 2, 'MarkerSize', 7); plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', 'MarkerSize', 7); % ========================================================================= hold off; end
Matlab載入數據:
%% Load Data
% The first two columns contains the exam scores and the third column
% contains the label.
data = load('ex2data1.txt');
X = data(:, [1, 2]); y = data(:, 3);% 矩陣 X 取數據的所有行的第一列和第二列,向量 y 取數據的第三列
由上面代碼可知:Matlab將文本文件中的訓練數據載入到 矩陣X 和 向量 y 中
載入完數據之後,執行以下代碼(調用自定義的plotData函數),將圖形畫出來:
plotData(X, y);
% Put some labels
hold on;
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Exam 1 score') %標記圖形的 X 軸
ylabel('Exam 2 score') %標記圖形的 Y 軸
% Specified in plot order
legend('Admitted', 'Not admitted') %圖形的右上角標簽
hold off;
圖形畫出來之後,對訓練數據就有了一個大體的可視化的認識了。接下來就要實現 模型了,這裡需要訓練一個邏輯回歸模型。
①sigmoid function
對於 logistic regression而言,它針對的是 classification problem。這裡只討論二分類問題,比如上面的“根據成績入學”,結果只有兩種:y==0時,成績未合格,不予入學;y==1時,可入學。即,y的輸出要麼是0,要麼是1
如果採用 linear regression,它的假設函數是這樣的:

假設函數的取值即可以遠遠大於1,也可以遠遠小於0,並且容易受到一些特殊樣本的影響。比如在上圖中,就只能約定:當假設函數大於等於0.5時;預測y==1,小於0.5時,預測y==0。
而如果引入了sigmoid function,就可以把假設函數的值域“約束”在[0, 1]之間。總之,引入sigmoid function,就能夠更好的擬合分類問題中的數據,即從這個角度看:regression model 比 linear model 更合適 classification problem.
引入sigmoid後,假設函數如下:

sigmoid function 用Matlab 實現如下:
function g = sigmoid(z)
%SIGMOID Compute sigmoid functoon
% J = SIGMOID(z) computes the sigmoid of z.
% You need to return the following variables correctly
g = zeros(size(z));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the sigmoid of each value of z (z can be a matrix,
% vector or scalar).
g = 1./(ones(size(z)) + exp(-z)); % ‘點除’ 表示 1 除以矩陣(向量)中的每一個元素
% =============================================================
end
②模型的代價函數(cost function)
什麼是代價函數呢?
把訓練好的模型對新數據進行預測,那預測結果有好有壞。因此,就用cost function 來衡量預測的"準確性"。cost function越小,表示測的越準。這裡的代價函數的本質是”最小二乘法“---ordinary least squares
代價函數的最原始的定義是下麵的這個公式:可見,它是關於 theta 的函數。(X,y 是已知的,由training set 中的數據確定了)

那如何求解 cost function的參數 theta,從而確定J(theta)呢?有兩種方法:一種是梯度下降演算法(Gradient descent),另一種是正規方程(Normal Equation),本文只討論Gradient descent。
而梯度下降演算法,本質上是求導數(偏導數),或者說是:方嚮導數。方嚮導數所代表的方向--梯度方向,下降得最快。
而我們知道,對於某些圖形所代表的函數,它可能有很多個導數為0的點,這類函數稱為非凸函數(non-convex function);而某些函數,它只有一個全局唯一的導數為0的點,稱為 convex function,比如下圖:

convex function能夠很好地讓Gradient descent尋找全局最小值。而上圖左邊的non-convex就不太適用Gradient descent了。
就是因為上面這個原因,logistic regression 的 cost function被改寫成了下麵這個公式:

可以看出,引入log 函數(對數函數),讓non-convex function 變成了 convex function
再精簡一下cost function,其實它可以表示成:

J(theta)可用向量表示成:

其Matlab語言表示公式如下:
J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m);
③梯度下降演算法
上面已經講到梯度下降演算法本質上是求偏導數,目標就是尋找theta,使得 cost function J(theta)最小。公式如下:

上面對theta(j)求偏導數,得到的值就是梯度j,記為:grad(j)
通過線性代數中的矩陣乘法以及向量的乘法規則,可以將梯度grad表示成向量的形式:

至於如何證明的,可參考:Exercise 1:Linear Regression---實現一個線性回歸
其Matlab語言表示公式如下:
grad = ( X' * ( sigmoid(X*theta)-y ) )/m; % X 為 training set 中的 feature variables, y 為training instance(訓練樣本的結果)結果
需要註意的是:對於logistic regression,假設函數h(x)=g(z),即它引入了sigmoid function.

最終,Matlab中costfunction.m如下:
function [J, grad] = costFunction(theta, X, y)
%COSTFUNCTION Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression
% J = COSTFUNCTION(theta, X, y) computes the cost of using theta as the
% parameter for logistic regression and the gradient of the cost
% w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
%
%J = (log(theta'*X')*y + (1-y)*log(1-theta'*X'))/(-m);
%attention matlab's usage
J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m);
% theta = theta - (alpha/m)*X'*(X*theta-y);
grad = ( X' * ( sigmoid(X*theta)-y ) )/m;
% =============================================================
end
通過調用costfunction.m文件中定義的coustFunction函數,從而運行梯度下降演算法找到使代價函數J(theta)最小化的 邏輯回歸模型參數theta。調用costFunction函數的代碼如下:
%% ============= Part 3: Optimizing using fminunc =============
% In this exercise, you will use a built-in function (fminunc) to find the
% optimal parameters theta.
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial_theta, options);
從上面代碼的最後一行可以看出,我們是通過 fminunc 調用 costFunction函數,來求得 theta的,而不是自己使用 Gradient descent 在for 迴圈求導來計算 theta。for迴圈中求導計算theta,可參考:Exercise 1:Linear Regression---實現一個線性回歸
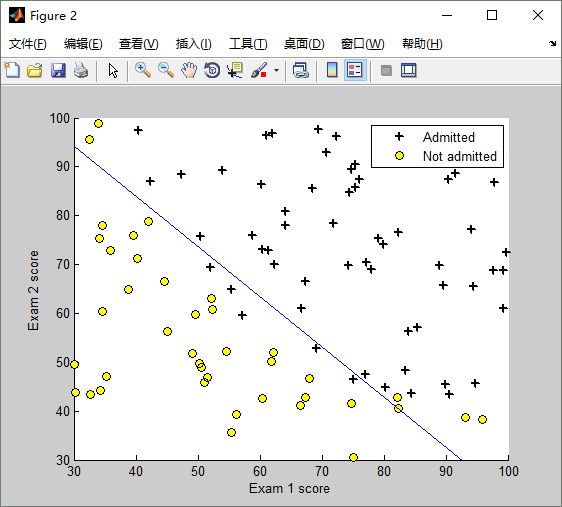
既然已經通過Gradient descent演算法求得了theta,將theta代入到假設函數中,就得到了 logistic regression model,用圖形表示如下:
④模型的評估(Evaluating logistic regression)
那如何估計,求得的邏輯回歸模型是好還是壞呢?預測效果怎麼樣?因此,就需要拿一組數據測試一下,測試代碼如下:
%% ============== Part 4: Predict and Accuracies ==============
% After learning the parameters, you'll like to use it to predict the outcomes
% on unseen data. In this part, you will use the logistic regression model
% to predict the probability that a student with score 45 on exam 1 and
% score 85 on exam 2 will be admitted.
%
% Furthermore, you will compute the training and test set accuracies of
% our model.
%
% Your task is to complete the code in predict.m
% Predict probability for a student with score 45 on exam 1
% and score 85 on exam 2
prob = sigmoid([1 45 85] * theta); %這是一組測試數據,第一次考試成績為45,第二次成績為85
fprintf(['For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission ' ...
'probability of %f\n\n'], prob);
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);% 調用predict函數測試模型
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
fprintf('\nProgram paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
模型的測試結果如下:
For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission probability of 0.774323
Train Accuracy: 89.000000
那predict函數是如何實現的呢?predict.m 如下:
function p = predict(theta, X)
%PREDICT Predict whether the label is 0 or 1 using learned logistic
%regression parameters theta
% p = PREDICT(theta, X) computes the predictions for X using a
% threshold at 0.5 (i.e., if sigmoid(theta'*x) >= 0.5, predict 1)
m = size(X, 1); % Number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
p = zeros(m, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
p = X*theta >= 0;
% =========================================================================
end
非常簡單,只有一行代碼:p = X * theta >= 0,原理如下:
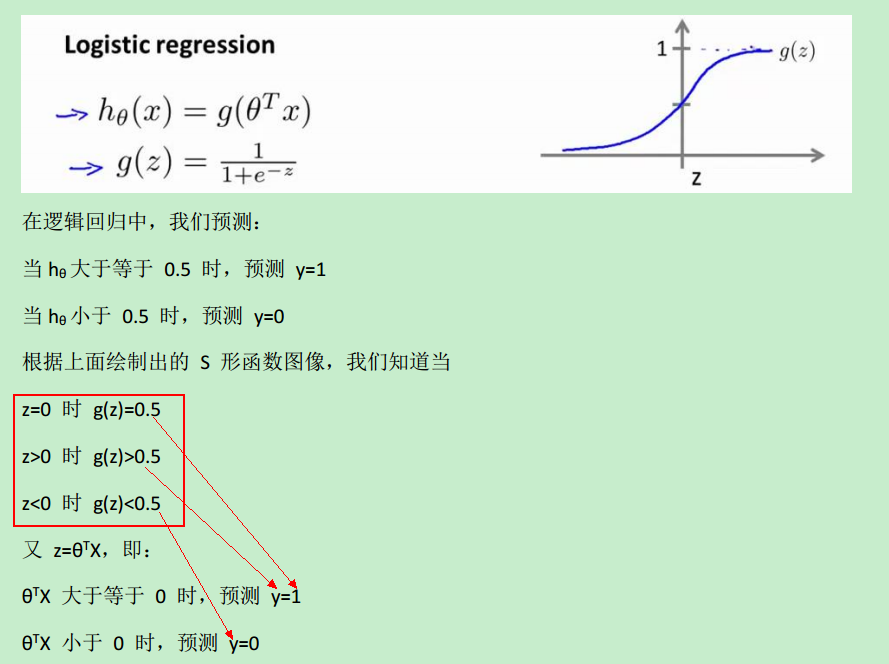
當h(x)>=0.5時,預測y==1,而h(x)>=0.5 等價於 z>=0
⑤邏輯回歸的正則化(Regularized logistic regression)
為什麼需要正則化?正則化就是為瞭解決過擬合問題(overfitting problem)。那什麼又是過擬合問題呢?
一般而言,當模型的特征(feature variables)非常多,而訓練的樣本數目(training set)又比較少的時候,訓練得到的假設函數(hypothesis function)能夠非常好地匹配training set中的數據,此時的代價函數幾乎為0。下圖中最右邊的那個模型 就是一個過擬合的模型。
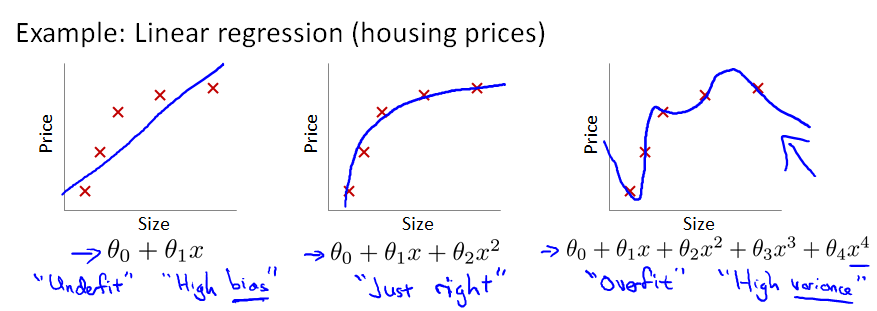
所謂過擬合,從圖形上看就是:假設函數曲線完美地通過中樣本中的每一個點。也許有人會說:這不正是最完美的模型嗎?它完美地匹配了traing set中的每一個樣本呀!
過擬合模型不好的原因是:儘管它能完美匹配traing set中的每一個樣本,但它不能很好地對未知的 (新樣本實例)input instance 進行預測呀!通俗地講,就是過擬合模型的預測能力差。
因此,正則化(regularization)就出馬了。
前面提到,正是因為 feature variable非常多,導致 hypothesis function 的冪次很高,hypothesis function變得很複雜(彎彎曲曲的),從而通過穿過每一個樣本點(完美匹配每個樣本)。如果添加一個"正則化項",減少 高冪次的特征變數的影響,那 hypothesis function不就變得平滑了嗎?
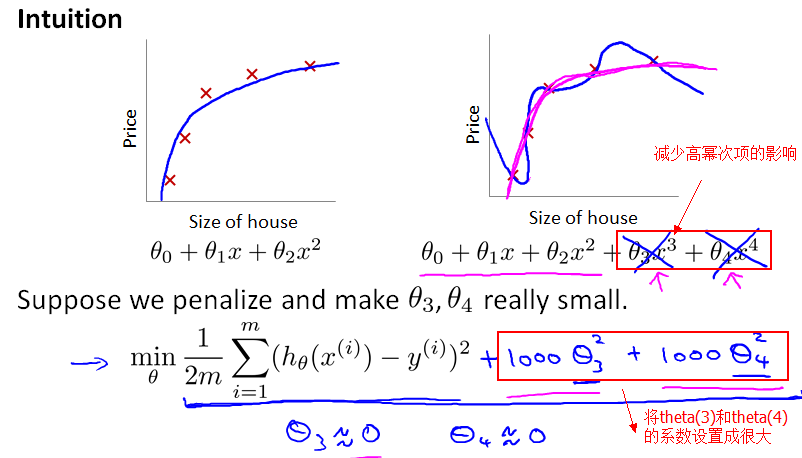
正如前面提到,梯度下降演算法的目標是最小化cost function,而現在把 theta(3) 和 theta(4)的繫數設置為1000,設得很大,求偏導數時,相應地得到的theta(3) 和 theta(4) 就都約等於0了。
更一般地,我們對每一個theta(j),j>=1,進行正則化,就得到了一個如下的代價函數:其中的 lambda(λ)就稱為正則化參數(regularization parameter)

從上面的J(theta)可以看出:如果lambda(λ)=0,則表示沒有使用正則化;如果lambda(λ)過大,使得模型的各個參數都變得很小,導致h(x)=theta(0),從而造成欠擬合;如果lambda(λ)很小,則未充分起到正則化的效果。因此,lambda(λ)的值要合適。
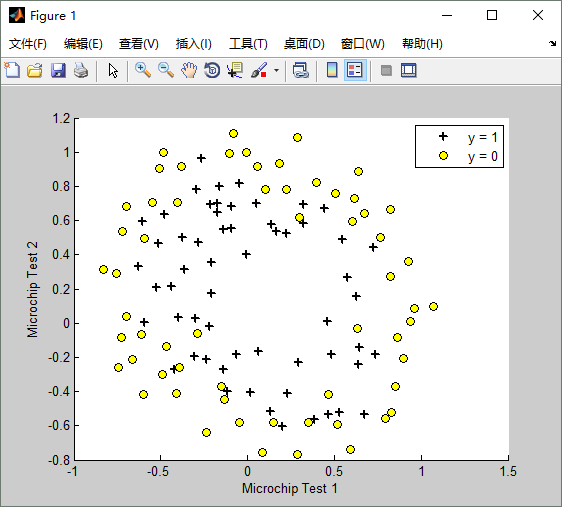
最後,我們來看一個實際的過擬合的示例,原始的訓練數據如下圖:
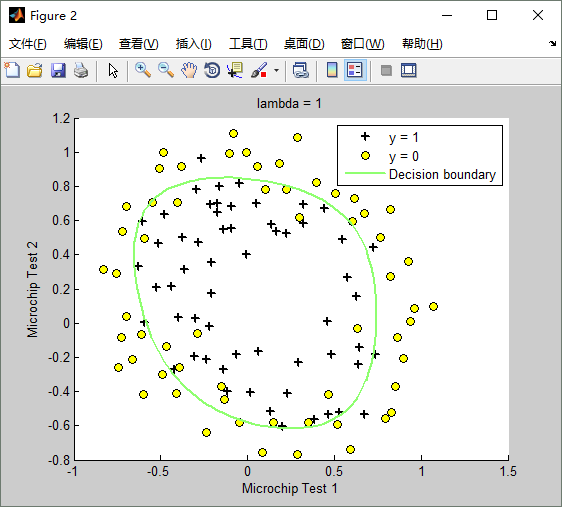
lambda(λ)==1時,訓練出來的模型(hypothesis function)如下:Train Accuracy: 83.050847
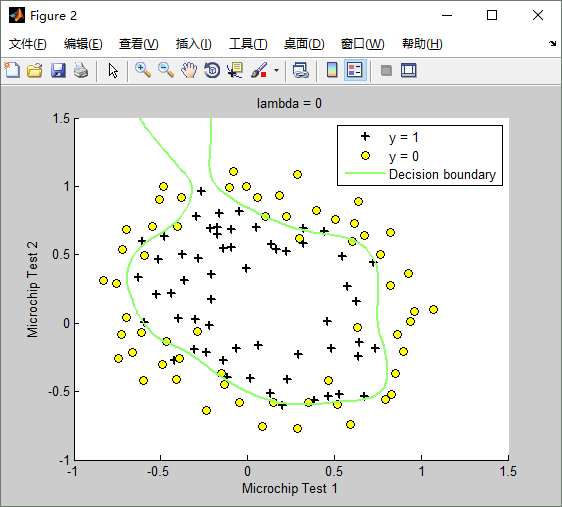
lambda(λ)==0時,不使用正則化,訓練出來的模型(hypothesis function)如下:Train Accuracy: 87.288136
lambda(λ)==100時,訓練出來的模型(hypothesis function)如下:Train Accuracy: 61.016949
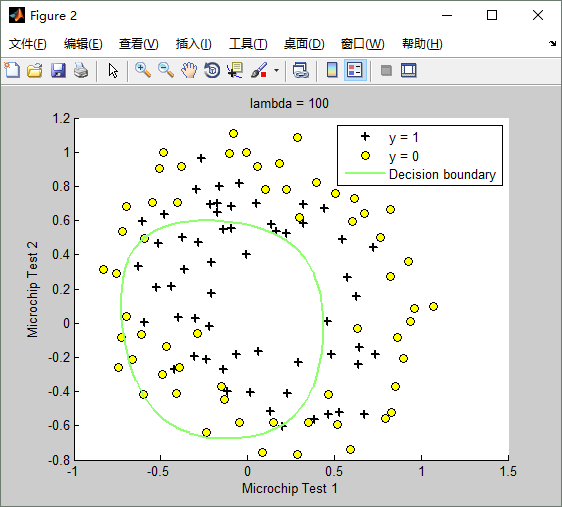
Matlab正則化代價函數的實現文件costFunctionReg.m如下:
function [J, grad] = costFunctionReg(theta, X, y, lambda)
%COSTFUNCTIONREG Compute cost and gradient for logistic regression with regularization
% J = COSTFUNCTIONREG(theta, X, y, lambda) computes the cost of using
% theta as the parameter for regularized logistic regression and the
% gradient of the cost w.r.t. to the parameters.
% Initialize some useful values
m = length(y); % number of training examples
% You need to return the following variables correctly
J = 0;
grad = zeros(size(theta));
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m);
%J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m) + (lambda / (2*m)) * (theta'*theta);
J = ( log( sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * y + log( 1-sigmoid(theta'*X') ) * (1 - y) )/(-m) + (lambda / (2*m)) * ( ( theta( 2:length(theta) ) )' * theta(2:length(theta)) );
%grad = ( X' * ( sigmoid(X*theta)-y ) )/m;
grad = ( X' * ( sigmoid(X*theta)-y ) )/m + ( lambda / m ) * ( [0; ones( length(theta) - 1 , 1 )].*theta );
% =============================================================
end
調用costFunctionReg.m的代碼如下:
%% ============= Part 2: Regularization and Accuracies =============
% Optional Exercise:
% In this part, you will get to try different values of lambda and
% see how regularization affects the decision coundart
%
% Try the following values of lambda (0, 1, 10, 100).
%
% How does the decision boundary change when you vary lambda? How does
% the training set accuracy vary?
%
% Initialize fitting parameters
initial_theta = zeros(size(X, 2), 1);
% Set regularization parameter lambda to 1 (you should vary this)
lambda = 1;
% Set Options
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Optimize
[theta, J, exit_flag] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunctionReg(t, X, y, lambda)), initial_theta, options);
% Plot Boundary
plotDecisionBoundary(theta, X, y);
hold on;
title(sprintf('lambda = %g', lambda))
% Labels and Legend
xlabel('Microchip Test 1')
ylabel('Microchip Test 2')
legend('y = 1', 'y = 0', 'Decision boundary')
hold off;
% Compute accuracy on our training set
p = predict(theta, X);
fprintf('Train Accuracy: %f\n', mean(double(p == y)) * 100);
⑥總結:
本文是對Stanford Machine Learning課程中的logistic regression的總結。結合課後編程習題,對logistic regression 各個知識點和編程作業中的代碼、實現原理作了詳細的解釋。
有興趣並且有時間學一名新技術是一件幸福的事情。
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/hapjin/p/6078530.html



