Python3 數字(Number) 定義:a=1 特性: 1.只能存放一個值 2.一經定義,不可更改 3.直接訪問 分類:整型,長整型,布爾,浮點,複數 python2.*與python3.*關於整型的區別 Python 數字數據類型用於存儲數值。 數據類型是不允許改變的,這就意味著如果改變數字數 ...
Python3 數字(Number)
定義:a=1
特性:
1.只能存放一個值
2.一經定義,不可更改
3.直接訪問
分類:整型,長整型,布爾,浮點,複數
python2.*與python3.*關於整型的區別
python2.* 在32位機器上,整數的位數為32位,取值範圍為-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系統上,整數的位數為64位,取值範圍為-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807 python3.*整形長度無限制
Python 數字數據類型用於存儲數值。
數據類型是不允許改變的,這就意味著如果改變數字數據類型得值,將重新分配記憶體空間。
整型工廠函數int()
class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self):
""" 返回表示該數字的時占用的最少位數 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回該複數的共軛複數 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass
def __abs__(self):
""" 返回絕對值 """
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __and__(self, y):
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y):
""" 比較兩個數大小 """
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y):
""" 強制生成一個元組 """
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y):
""" 相除,得到商和餘數組成的元組 """
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __float__(self):
""" 轉換為浮點類型 """
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 內部調用 __new__方法或創建對象時傳入參數使用 """
pass
def __hash__(self):
"""如果對象object為哈希表類型,返回對象object的哈希值。哈希值為整數。在字典查找中,哈希值用於快速比較字典的鍵。兩個數值如果相等,則哈希值也相等。"""
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __hex__(self):
""" 返回當前數的 十六進位 表示 """
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass
def __index__(self):
""" 用於切片,數字無意義 """
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 構造方法,執行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 時,自動調用,暫時忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self):
""" 轉換為整數 """
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __invert__(self):
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass
def __long__(self):
""" 轉換為長整數 """
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lshift__(self, y):
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __oct__(self):
""" 返回改值的 八進位 表示 """
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass
def __or__(self, y):
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" 冪,次方 """
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rand__(self, y):
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self):
"""轉化為解釋器可讀取的形式 """
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __str__(self):
"""轉換為人閱讀的形式,如果沒有適於人閱讀的解釋形式的話,則返回解釋器課閱讀的形式"""
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __ror__(self, y):
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass
def __rshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y):
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" 返回數值被截取為整形的值,在整形中無意義 """
pass
def __xor__(self, y):
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虛數,無意義 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 數字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 實屬,無意義 """
"""the real part of a complex number"""
int
python2.7
class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> integer
int(x, base=10) -> integer
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point
numbers, this truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,
bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the
given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded
by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.
Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self): # real signature unknown; restored from __doc__
""" 返回表示該數字的時占用的最少位數 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回該複數的共軛複數 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass
@classmethod # known case
def from_bytes(cls, bytes, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__
"""
int.from_bytes(bytes, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> int
Return the integer represented by the given array of bytes.
The bytes argument must be a bytes-like object (e.g. bytes or bytearray).
The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the
integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the
beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most
significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native
byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value.
The signed keyword-only argument indicates whether two's complement is
used to represent the integer.
"""
pass
def to_bytes(self, length, byteorder, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown; NOTE: unreliably restored from __doc__
"""
int.to_bytes(length, byteorder, *, signed=False) -> bytes
Return an array of bytes representing an integer.
The integer is represented using length bytes. An OverflowError is
raised if the integer is not representable with the given number of
bytes.
The byteorder argument determines the byte order used to represent the
integer. If byteorder is 'big', the most significant byte is at the
beginning of the byte array. If byteorder is 'little', the most
significant byte is at the end of the byte array. To request the native
byte order of the host system, use `sys.byteorder' as the byte order value.
The signed keyword-only argument determines whether two's complement is
used to represent the integer. If signed is False and a negative integer
is given, an OverflowError is raised.
"""
pass
def __abs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" abs(self) """
pass
def __add__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self+value. """
pass
def __and__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self&value. """
pass
def __bool__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" self != 0 """
pass
def __ceil__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
整數返回自己
如果是小數
math.ceil(3.1)返回4
"""
""" Ceiling of an Integral returns itself. """
pass
def __divmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 相除,得到商和餘數組成的元組 """
""" Return divmod(self, value). """
pass
def __eq__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self==value. """
pass
def __float__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" float(self) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self//value. """
pass
def __floor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Flooring an Integral returns itself. """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return getattr(self, name). """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __ge__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>=value. """
pass
def __gt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>value. """
pass
def __hash__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return hash(self). """
pass
def __index__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 用於切片,數字無意義 """
""" Return self converted to an integer, if self is suitable for use as an index into a list. """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 構造方法,執行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 時,自動調用,暫時忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> integer
int(x, base=10) -> integer
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is a number, return x.__int__(). For floating point
numbers, this truncates towards zero.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string,
bytes, or bytearray instance representing an integer literal in the
given base. The literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded
by whitespace. The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36.
Base 0 means to interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" int(self) """
pass
def __invert__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" ~self """
pass
def __le__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<=value. """
pass
def __lshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<<value. """
pass
def __lt__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self<value. """
pass
def __mod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self%value. """
pass
def __mul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self*value. """
pass
def __neg__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" -self """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(*args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature. """
pass
def __ne__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self!=value. """
pass
def __or__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self|value. """
pass
def __pos__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" +self """
pass
def __pow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return pow(self, value, mod). """
pass
def __radd__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value+self. """
pass
def __rand__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value&self. """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return divmod(value, self). """
pass
def __repr__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return repr(self). """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value//self. """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value<<self. """
pass
def __rmod__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value%self. """
pass
def __rmul__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value*self. """
pass
def __ror__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value|self. """
pass
def __round__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
"""
Rounding an Integral returns itself.
Rounding with an ndigits argument also returns an integer.
"""
pass
def __rpow__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return pow(value, self, mod). """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value>>self. """
pass
def __rshift__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self>>value. """
pass
def __rsub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value-self. """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value/self. """
pass
def __rxor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return value^self. """
pass
def __sizeof__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Returns size in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __str__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return str(self). """
pass
def __sub__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self-value. """
pass
def __truediv__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self/value. """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Truncating an Integral returns itself. """
pass
def __xor__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" Return self^value. """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
"""the real part of a complex number"""
python3.5
長整型long:
python2.*: 跟C語言不同,Python的長整型沒有指定位寬,也就是說Python沒有限制長整型數值的大小, 但是實際上由於機器記憶體有限,所以我們使用的長整型數值不可能無限大。 在使用過程中,我們如何區分長整型和整型數值呢? 通常的做法是在數字尾部加上一個大寫字母L或小寫字母l以表示該整數是長整型的,例如: a = 9223372036854775808L 註意,自從Python2起,如果發生溢出,Python會自動將整型數據轉換為長整型, 所以如今在長整型數據後面不加字母L也不會導致嚴重後果了。
python3.* 長整型,整型統一歸為整型
python2.7 >>> a=9223372036854775807 >>> a >>> a+=1 >>> a 9223372036854775808L python3.5 >>> a=9223372036854775807 >>> a >>> a+=1 >>> a 查看
以下實例在變數賦值時 Number 對象將被創建:
var1 = 1 var2 = 10
int(整型)
在32位機器上,整數的位數為32位,取值範圍為-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647 在64位系統上,整數的位數為64位,取值範圍為-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807class int(object):
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
"""
def bit_length(self):
""" 返回表示該數字的時占用的最少位數 """
"""
int.bit_length() -> int
Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
>>> bin(37)
'0b100101'
>>> (37).bit_length()
"""
return 0
def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 返回該複數的共軛複數 """
""" Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
pass
def __abs__(self):
""" 返回絕對值 """
""" x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __and__(self, y):
""" x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
pass
def __cmp__(self, y):
""" 比較兩個數大小 """
""" x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
pass
def __coerce__(self, y):
""" 強制生成一個元組 """
""" x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
pass
def __divmod__(self, y):
""" 相除,得到商和餘數組成的元組 """
""" x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
pass
def __div__(self, y):
""" x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __float__(self):
""" 轉換為浮點類型 """
""" x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
pass
def __floordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
pass
def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
""" 內部調用 __new__方法或創建對象時傳入參數使用 """
pass
def __hash__(self):
"""如果對象object為哈希表類型,返回對象object的哈希值。哈希值為整數。在字典查找中,哈希值用於快速比較字典的鍵。兩個數值如果相等,則哈希值也相等。"""
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __hex__(self):
""" 返回當前數的 十六進位 表示 """
""" x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
pass
def __index__(self):
""" 用於切片,數字無意義 """
""" x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
pass
def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
""" 構造方法,執行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 時,自動調用,暫時忽略 """
"""
int(x=0) -> int or long
int(x, base=10) -> int or long
Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
>>> int('0b100', base=0)
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __int__(self):
""" 轉換為整數 """
""" x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
pass
def __invert__(self):
""" x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
pass
def __long__(self):
""" 轉換為長整數 """
""" x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
pass
def __lshift__(self, y):
""" x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, y):
""" x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
pass
def __neg__(self):
""" x.__neg__() <==> -x """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __nonzero__(self):
""" x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
pass
def __oct__(self):
""" 返回改值的 八進位 表示 """
""" x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
pass
def __or__(self, y):
""" x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
pass
def __pos__(self):
""" x.__pos__() <==> +x """
pass
def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
""" 冪,次方 """
""" x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __radd__(self, y):
""" x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
pass
def __rand__(self, y):
""" x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
pass
def __rdivmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
pass
def __rdiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __repr__(self):
"""轉化為解釋器可讀取的形式 """
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __str__(self):
"""轉換為人閱讀的形式,如果沒有適於人閱讀的解釋形式的話,則返回解釋器課閱讀的形式"""
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
""" x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
pass
def __rlshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, y):
""" x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
pass
def __ror__(self, y):
""" x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
pass
def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
""" y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
pass
def __rrshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
pass
def __rshift__(self, y):
""" x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
pass
def __rsub__(self, y):
""" x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
pass
def __rtruediv__(self, y):
""" x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
pass
def __rxor__(self, y):
""" x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
pass
def __sub__(self, y):
""" x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
pass
def __truediv__(self, y):
""" x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
pass
def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
""" 返回數值被截取為整形的值,在整形中無意義 """
pass
def __xor__(self, y):
""" x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
pass
denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分母 = 1 """
"""the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 虛數,無意義 """
"""the imaginary part of a complex number"""
numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 分子 = 數字大小 """
"""the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
""" 實屬,無意義 """
"""the real part of a complex number"""
int
您也可以使用del語句刪除一些數字對象的引用。
del語句的語法是:
del var1[,var2[,var3[....,varN]]]]
您可以通過使用del語句刪除單個或多個對象的引用,例如:
del var del var_a, var_b
Python 支持三種不同的數值類型:
- 整型(Int) - 通常被稱為是整型或整數,是正或負整數,不帶小數點。Python3 整型是沒有限制大小的,可以當作 Long 類型使用,所以 Python3 沒有 Python2 的 Long 類型。
- 浮點型(float) - 浮點型由整數部分與小數部分組成,浮點型也可以使用科學計數法表示(2.5e2 = 2.5 x 102 = 250)
- 複數( (complex)) - 複數由實數部分和虛數部分構成,可以用a + bj,或者complex(a,b)表示, 複數的實部a和虛部b都是浮點型。
我們可以使用十六進位和八進位來代表整數:
>>> number = 0xA0F # 十六進位 >>> number 2575 >>> number=0o37 # 八進位 >>> number 31
| int | float | complex |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.0 | 3.14j |
| 100 | 15.20 | 45.j |
| -786 | -21.9 | 9.322e-36j |
| 080 | 32.3+e18 | .876j |
| -0490 | -90. | -.6545+0J |
| -0x260 | -32.54e100 | 3e+26J |
| 0x69 | 70.2-E12 | 4.53e-7j |
- Python支持複數,複數由實數部分和虛數部分構成,可以用a + bj,或者complex(a,b)表示, 複數的實部a和虛部b都是浮點型。
Python 數字類型轉換
有時候,我們需要對數據內置的類型進行轉換,數據類型的轉換,你只需要將數據類型作為函數名即可。
-
int(x) 將x轉換為一個整數。
-
float(x) 將x轉換到一個浮點數。
-
complex(x) 將x轉換到一個複數,實數部分為 x,虛數部分為 0。
-
complex(x, y) 將 x 和 y 轉換到一個複數,實數部分為 x,虛數部分為 y。x 和 y 是數字表達式。
以下實例將浮點數變數 a 轉換為整數:
>>> a = 1.0 >>> int(a) 1
Python 數字運算
Python 解釋器可以作為一個簡單的計算器,您可以在解釋器里輸入一個表達式,它將輸出表達式的值。
表達式的語法很直白: +, -, * 和 / 和其它語言(如Pascal或C)里一樣。例如:
>>> 2 + 2 4 >>> 50 - 5*6 20 >>> (50 - 5*6) / 4 5.0 >>> 8 / 5 # 總是返回一個浮點數 1.6
註意:在不同的機器上浮點運算的結果可能會不一樣。
在整數除法中,除法(/)總是返回一個浮點數,如果只想得到整數的結果,丟棄可能的分數部分,可以使用運算符 // :
>>> 17 / 3 # 整數除法返回浮點型 5.666666666666667 >>> >>> 17 // 3 # 整數除法返迴向下取整後的結果 5 >>> 17 % 3 # %操作符返回除法的餘數 2 >>> 5 * 3 + 2 17
等號(=)用於給變數賦值。賦值之後,除了下一個提示符,解釋器不會顯示任何結果。
>>> width = 20 >>> height = 5*9 >>> width * height 900
Python 可以使用 ** 操作來進行冪運算:
>>> 5 ** 2 # 5 的平方 25 >>> 2 ** 7 # 2的7次方 128
變數在使用前必須先"定義"(即賦予變數一個值),否則會出現錯誤:
>>> n # 嘗試訪問一個未定義的變數 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'n' is not defined
不同類型的數混合運算時會將整數轉換為浮點數:
>>> 3 * 3.75 / 1.5 7.5 >>> 7.0 / 2 3.5
在交互模式中,最後被輸出的表達式結果被賦值給變數 _ 。例如:
>>> tax = 12.5 / 100 >>> price = 100.50 >>> price * tax 12.5625 >>> price + _ 113.0625 >>> round(_, 2) 113.06
此處, _ 變數應被用戶視為只讀變數。
數學函數
| 函數 | 返回值 ( 描述 ) |
|---|---|
| abs(x) | 返回數字的絕對值,如abs(-10) 返回 10 |
| ceil(x) | 返回數字的上入整數,如math.ceil(4.1) 返回 5 |
|
cmp(x, y) |
如果 x < y 返回 -1, 如果 x == y 返回 0, 如果 x > y 返回 1。 Python 3 已廢棄 。使用 使用 (x>y)-(x<y) 替換。 |
| exp(x) | 返回e的x次冪(ex),如math.exp(1) 返回2.718281828459045 |
| fabs(x) | 返回數字的絕對值,如math.fabs(-10) 返回10.0 |
| floor(x) | 返回數字的下舍整數,如math.floor(4.9)返回 4 |
| log(x) | 如math.log(math.e)返回1.0,math.log(100,10)返回2.0 |
| log10(x) | 返回以10為基數的x的對數,如math.log10(100)返回 2.0 |
| max(x1, x2,...) | 返回給定參數的最大值,參數可以為序列。 |
| min(x1, x2,...) | 返回給定參數的最小值,參數可以為序列。 |
| modf(x) | 返回x的整數部分與小數部分,兩部分的數值符號與x相同,整數部分以浮點型表示。 |
| pow(x, y) | x**y 運算後的值。 |
| round(x [,n]) | 返回浮點數x的四捨五入值,如給出n值,則代表舍入到小數點後的位數。 |
| sqrt(x) | 返回數字x的平方根,數字可以為負數,返回類型為實數,如math.sqrt(4)返回 2+0j |
隨機數函數
隨機數可以用於數學,游戲,安全等領域中,還經常被嵌入到演算法中,用以提高演算法效率,並提高程式的安全性。
Python包含以下常用隨機數函數:
| 函數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| choice(seq) | 從序列的元素中隨機挑選一個元素,比如random.choice(range(10)),從0到9中隨機挑選一個整數。 |
| randrange ([start,] stop [,step]) | 從指定範圍內,按指定基數遞增的集合中獲取一個隨機數,基數預設值為1 |
| random() | 隨機生成下一個實數,它在[0,1)範圍內。 |
| seed([x]) | 改變隨機數生成器的種子seed。如果你不瞭解其原理,你不必特別去設定seed,Python會幫你選擇seed。 |
| shuffle(lst) | 將序列的所有元素隨機排序 |
| uniform(x, y) | 隨機生成下一個實數,它在[x,y]範圍內。 |
三角函數
Python包括以下三角函數:
| 函數 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|
| acos(x) | 返回x的反餘弦弧度值。 | |
| asin(x) | 返回x的反正弦弧度值。 | |
| atan(x) | 返回x的反正切弧度值。 | |
| atan2(y, x) | 返回給定的 X 及 Y 坐標值的反正切值。 | |
| cos(x) | 返回x的弧度的餘弦值。 | |
| hypot(x, y) | 返回歐幾里德範數 sqrt(x*x + y*y)。 | |
| sin(x) | 返回的x弧度的正弦值。 | |
| tan(x) | 返回x弧度的正切值。 | |
| degrees(x) | 將弧度轉換為角度,如degrees(math.pi/2) , 返回90.0 | |
| radians(x) | 將角度轉換為弧度 |
數學常量
| 常量 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| pi | 數學常量 pi(圓周率,一般以π來表示) |
| e | 數學常量 e,e即自然常數(自然常數)。 |
布爾值 真或假 1 或 0
浮點數float:
Python的浮點數就是數學中的小數,類似C語言中的double。 在運算中,整數與浮點數運算的結果是浮點數 浮點數也就是小數,之所以稱為浮點數,是因為按照科學記數法表示時, 一個浮點數的小數點位置是可變的,比如,1.23*109和12.3*108是相等的。
浮點數可以用數學寫法,如1.23,3.14,-9.01,等等。但是對於很大或很小的浮點數, 就必須用科學計數法表示,把10用e替代,1.23*109就是1.23e9,或者12.3e8,0.000012 可以寫成1.2e-5,等等。 整數和浮點數在電腦內部存儲的方式是不同的,
整數運算永遠是精確的而浮點數運算則可能會有 四捨五入的誤差。
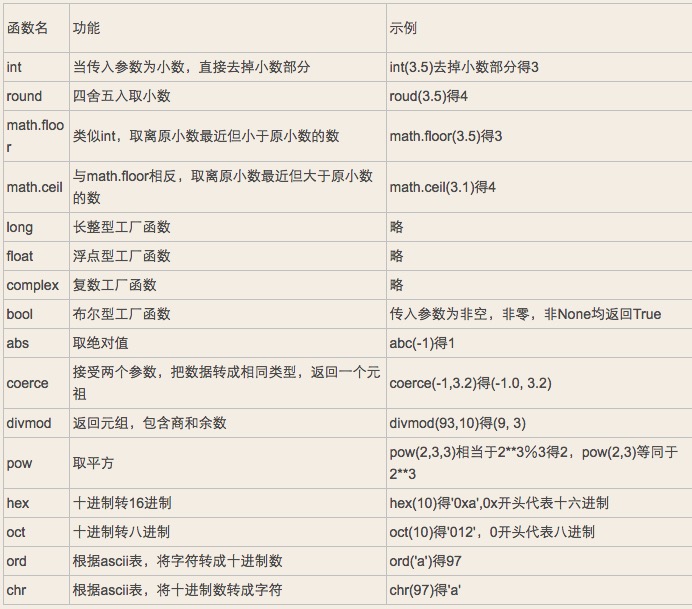
數字相關內建函數
Python3 字元串
字元串是 Python 中最常用的數據類型。我們可以使用引號('或")來創建字元串。
定義:它是一個有序的字元的集合,用於存儲和表示基本的文本信息,‘’或“”或‘’‘ ’‘’中間包含的內容稱之為字元串 特性:
1.只能存放一個值 2.不可變 3.按照從左到右的順序定義字元集合,下標從0開始順序訪問,有序
補充:
1.字元串的單引號和雙引號都無法取消特殊字元的含義,如果想讓引號內所有字元均取消特殊意義,在引號前面加r,如name=r'l\thf'
2.unicode字元串與r連用必需在r前面,如name=ur'l\thf'
字元串常用功能:
- 移除空白
- 分割
- 長度
- 索引
- 切片
class str(basestring):
"""
str(object='') -> string
Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
"""
def capitalize(self):
""" 首字母變大寫 """
"""
S.capitalize() -> string
Return a copy of the string S with only its first character
capitalized.
"""
return ""
def center(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 內容居中,width:總長度;fillchar:空白處填充內容,預設無 """
"""
S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> string
Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return ""
def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列個數 """
"""
S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted
as in slice notation.
"""
return 0
def decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 解碼 """
"""
S.decode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object
Decodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
a UnicodeDecodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore' and 'replace'
as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that is
able to handle UnicodeDecodeErrors.
"""
return object()
def encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
""" 編碼,針對unicode """
"""
S.encode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object
Encodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
codecs.register_error that is able to handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
"""
return object()
def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否以 xxx 結束 """
"""
S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False
def expandtabs(self, tabsize=None):
""" 將tab轉換成空格,預設一個tab轉換成8個空格 """
"""
S.expandtabs([tabsize]) -> string
Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
"""
return ""
def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 尋找子序列位置,如果沒找到,返回 -1 """
"""
S.find(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0
def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
""" 字元串格式化,動態參數,將函數式編程時細說 """
"""
S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> string
Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
"""
pass
def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
""" 子序列位置,如果沒找到,報錯 """
S.index(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0
def isalnum(self):
""" 是否是字母和數字 """
"""
S.isalnum() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isalpha(self):
""" 是否是字母 """
"""
S.isalpha() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isdigit(self):
""" 是否是數字 """
"""
S.isdigit() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are digits
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def islower(self):
""" 是否小寫 """
"""
S.islower() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def isspace(self):
"""
S.isspace() -> bool
Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def istitle(self):
"""
S.istitle() -> bool
Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
character in S, i.e. uppercase characters may only follow uncased
characters and lowercase characters only cased ones. Return False
otherwise.
"""
return False
def isupper(self):
"""
S.isupper() -> bool
Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
"""
return False
def join(self, iterable):
""" 連接 """
"""
S.join(iterable) -> string
Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
iterable. The separator between elements is S.
"""
return ""
def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None):
""" 內容左對齊,右側填充 """
"""
S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> string
Return S left-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
"""
return ""
def lower(self):
""" 變小寫 """
"""
S.lower() -> string
Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
"""
return ""
def lstrip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除左側空白 """
"""
S.lstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode
Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return ""
def partition(self, sep):
""" 分割,前,中,後三部分 """
"""
S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
found, return S and two empty strings.
"""
pass
def replace(self, old, new, count=None):
""" 替換 """
"""
S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> string
Return a copy of string S with all occurrences of substring
old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
"""
return ""
def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""
S.rfind(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
Return -1 on failure.
"""
return 0
def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
"""
S.rindex(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
"""
return 0
def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None):
"""
S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> string
Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
"""
return ""
def rpartition(self, sep):
"""
S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
"""
pass
def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
"""
S.rsplit([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and working
to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are
done. If sep is not specified or is None, any whitespace string
is a separator.
"""
return []
def rstrip(self, chars=None):
"""
S.rstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode
Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return ""
def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
""" 分割, maxsplit最多分割幾次 """
"""
S.split([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are removed
from the result.
"""
return []
def splitlines(self, keepends=False):
""" 根據換行分割 """
"""
S.splitlines(keepends=False) -> list of strings
Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
is given and true.
"""
return []
def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None):
""" 是否起始 """
"""
S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
"""
return False
def strip(self, chars=None):
""" 移除兩段空白 """
"""
S.strip([chars]) -> string or unicode
Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
whitespace removed.
If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
"""
return ""
def swapcase(self):
""" 大寫變小寫,小寫變大寫 """
"""
S.swapcase() -> string
Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters
converted to lowercase and vice versa.
"""
return ""
def title(self):
"""
S.title() -> string
Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with uppercase
characters, all remaining cased characters have lowercase.
"""
return ""
def translate(self, table, deletechars=None):
"""
轉換,需要先做一個對應表,最後一個表示刪除字元集合
intab = "aeiou"
outtab = "12345"
trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
print str.translate(trantab, 'xm')
"""
"""
S.translate(table [,deletechars]) -> string
Return a copy of the string S, where all characters occurring
in the optional argument deletechars are removed, and the
remaining characters have been mapped through the given
translation table, which must be a string of length 256 or None.
If the table argument is None, no translation is applied and
the operation simply removes the characters in deletechars.
"""
return ""
def upper(self):
"""
S.upper() -> string
Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase.
"""
return ""
def zfill(self, width):
"""方法返回指定長度的字元串,原字元串右對齊,前面填充0。"""
"""
S.zfill(width) -> string
Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
"""
return ""
def _formatter_field_name_split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def _formatter_parser(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __add__(self, y):
""" x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
pass
def __contains__(self, y):
""" x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
pass
def __eq__(self, y):
""" x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
pass
def __format__(self, format_spec):
"""
S.__format__(format_spec) -> string
Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
"""
return ""
def __getattribute__(self, name):
""" x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
pass
def __getitem__(self, y):
""" x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
pass
def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
pass
def __getslice__(self, i, j):
"""
x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
Use of negative indices is not supported.
"""
pass
def __ge__(self, y):
""" x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
pass
def __gt__(self, y):
""" x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
pass
def __hash__(self):
""" x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
pass
def __init__(self, string=''): # known special case of str.__init__
"""
str(object='') -> string
Return a nice string representation of the object.
If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
# (copied from class doc)
"""
pass
def __len__(self):
""" x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
pass
def __le__(self, y):
""" x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
pass
def __lt__(self, y):
""" x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
pass
def __mod__(self, y):
""" x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
pass
def __mul__(self, n):
""" x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
pass
@staticmethod # known case of __new__
def __new__(S, *more):
""" T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
pass
def __ne__(self, y):
""" x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
pass
def __repr__(self):
""" x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
pass
def __rmod__(self, y):
""" x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
pass
def __rmul__(self, n):
""" x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
pass
def __sizeof__(self):
""" S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
pass
def __str__(self):
""" x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
pass
str
num = "1" #unicode
num.isdigit() # True
num.isdecimal() # True
num.isnumeric() # True
num = "1" # 全形
num.isdigit() # True
num.isdecimal() # True
num.isnumeric() # True
num = b"1" # byte
num.isdigit() # True
num.isdecimal() # AttributeError 'bytes' object has no attribute 'isdecimal'
num.isnumeric() # AttributeError 'bytes' object has no attribute 'isnumeric'
num = "IV" # 羅馬數字
num.isdigit() # True
num.isdecimal() # False
num.isnumeric() # True
num = "四" # 漢字
num.isdigit() # False
num.isdecimal() # False
num.isnumeric() # True
===================
isdigit()
True: Unicode數字,byte數字(單位元組),全形數字(雙位元組),羅馬數字
False: 漢字數字
Error: 無
isdecimal()
True: Unicode數字,,全形數字(雙位元組)
False: 羅馬數字,漢字數字
Error: byte數字(單位元組)
isnumeric()
True: Unicode數字,全形數字(雙位元組),羅馬數字,漢字數字
False: 無
Error: byte數字(單位元組)
================
import unicodedata
unicodedata.digit("2") # 2
unicodedata.decimal("2") # 2
unicodedata.numeric("2") # 2.0
unicodedata.digit("2") # 2
unicodedata.decimal("2") # 2
unicodedata.numeric("2") # 2.0
unicodedata.digit(b"3") # TypeError: must be str, not bytes
unicodedata.decimal(b"3") # TypeError: must be str, not bytes
unicodedata.numeric(b"3") # TypeError: must be str, not bytes
unicodedata.digit("Ⅷ") # ValueError: not a digit
unicodedata.decimal("Ⅷ") # ValueError: not a decimal
unicodedata.numeric("Ⅷ") # 8.0
unicodedata.digit("四") # ValueError: not a digit
unicodedata.decimal("四") # ValueError: not a decimal
unicodedata.numeric("四") # 4.0
#"〇","零","一","壱","二","弐","三","參","四","五","六","七","八","九","十","廿","卅","卌","百","千","萬","萬","億"
python中str函數isdigit、isdecimal、isnumeric的區別
創建字元串很簡單,只要為變數分配一個值即可。例如:
var1 = 'Hello World!' var2 = "Runoob"
Python 訪問字元串中的值
Python 不支持單字元類型,單字元也在Python也是作為一個字元串使用。
Python 訪問子字元串,可以使用方括弧來截取字元串,如下實例:
#!/usr/bin/python3
var1 = 'Hello World!'
var2 = "Runoob"
print ("var1[0]: ", var1[0])
print ("var2[1:5]: ", var2[1:5])
以上實例執行結果:
var1[0]: H var2[1:5]: unoo
Python字元串更新
你可以對已存在的字元串進行修改,並賦值給另一個變數,如下實例:
#!/usr/bin/python3
var1 = 'Hello World!'
print ("已更新字元串 : ", var1[:6] + 'Runoob!')
以上實例執行結果
已更新字元串 : Hello Runoob!
Python轉義字元
在需要在字元中使用特殊字元時,python用反斜杠(\)



