Android 樣式 android中的樣式和CSS樣式作用相似,都是用於為界面元素定義顯示風格,它是一個包含一個或者多個view控制項屬性的集合。如:需要定義字體的顏色和大小。 在CSS中是這樣定義的: 可以像這樣使用上面的css樣式:<div class="wu">wuyudong‘blog</d ...
Android 樣式
android中的樣式和CSS樣式作用相似,都是用於為界面元素定義顯示風格,它是一個包含一個或者多個view控制項屬性的集合。如:需要定義字體的顏色和大小。
在CSS中是這樣定義的:
<style> .wu{COLOR:#0000CC;font-size:18px;} </style>
可以像這樣使用上面的css樣式:<div class="wu">wuyudong‘blog</div>
在Android中可以這樣定義樣式:
在res/values/styles.xml文件中添加以下內容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <style name=“wu”> <!-- 為樣式定義一個全局唯一的名字--> <item name=“android:textSize”>18px</item> <!-- name屬性的值為使用了該樣式的View控制項的屬性 --> <item name="android:textColor">#0000CC</item> </style> </resources>
在layout文件中可以像下麵這樣使用上面的android樣式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" ....> <TextView style="@style/wu" ..... /> </LinearLayout>
下麵來實踐一下
在style.xml中添加下麵的代碼:
<resources xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <!-- Base application theme, dependent on API level. This theme is replaced by AppBaseTheme from res/values-vXX/styles.xml on newer devices. --> <style name="AppBaseTheme" parent="android:Theme.Light"> <!-- Theme customizations available in newer API levels can go in res/values-vXX/styles.xml, while customizations related to backward-compatibility can go here. --> </style> <!-- Application theme. --> <style name="AppTheme" parent="AppBaseTheme"> <!-- All customizations that are NOT specific to a particular API-level can go here. --> </style> <style name="text_content_style" parent="AppBaseTheme"> <item name="android:layout_width">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:layout_height">wrap_content</item> <item name="android:textColor">#66ff00</item> <item name="android:textSize">20sp</item> </style> </resources>
佈局代碼如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <TextView style="@style/text_content_style" android:text="我是一個文本" /> <TextView style="@style/text_content_style" android:text="我是一個文本" /> <TextView style="@style/text_content_style" android:text="我是一個文本" /> <TextView style="@style/text_content_style" android:text="我是一個文本" /> <TextView style="@style/text_content_style" android:text="我是一個文本" /> </LinearLayout>
運行項目後
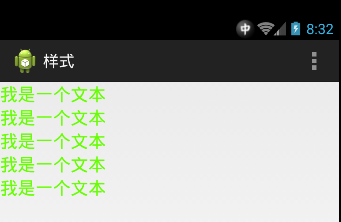
Android 主題
android中主題也是用於為應用定義顯示風格,它的定義和樣式的定義相同,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <style name=“wuTheme"> <item name=“android:windowNoTitle”>true</item> <!–- 沒標題 --> <item name=“android:windowFullscreen”>?android:windowNoTitle</item> <!–- 全屏顯示 --> </style> </resources>
上面“?android:windowNoTitle”中的問號用於引用在當前主題中定義過的資源的值。下麵代碼顯示在AndroidManifest.xml中如何為應用設置上面定義的主題:
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name" android:theme="@style/wuTheme"> ...... </application>
除了可以在AndroidManifest.xml中設置主題,同樣也可以在代碼中設置主題,如下:
setTheme(R.style.itcastTheme);
儘管在定義上,樣式和主題基本相同,但是它們使用的地方不同。樣式用在單獨的View,如:EditText、TextView等;主題通過AndroidManifest.xml中的<application>和<activity>用在整個應用或者某個 Activity,主題對整個應用或某個Activity進行全局性影響。如果一個應用使用了主題,同時應用下的view也使用了樣式,那麼當主題和樣式屬性發生衝突時,樣式的優先順序高於主題。
另外android系統也定義了一些主題,例如:<activity android:theme=“@android:style/Theme.Dialog”>,該主題可以讓Activity看起來像一個對話框,還有透明主題:@android:style/Theme.Translucent 。如果需要查閱這些主題,可以在文檔的referenceandroid-->R.style 中查看。



