集合框架體系Collection和Map常用API【彙總】 Collection公共的方法 Collection是單列結合的頂層介面,它的方法是所有單列集合都可以繼承使用的。 //把給定元素添加到集合中 public boolean add(E e) //把給定元素從集合中刪除 public boo ...
集合框架體系Collection和Map常用API【彙總】
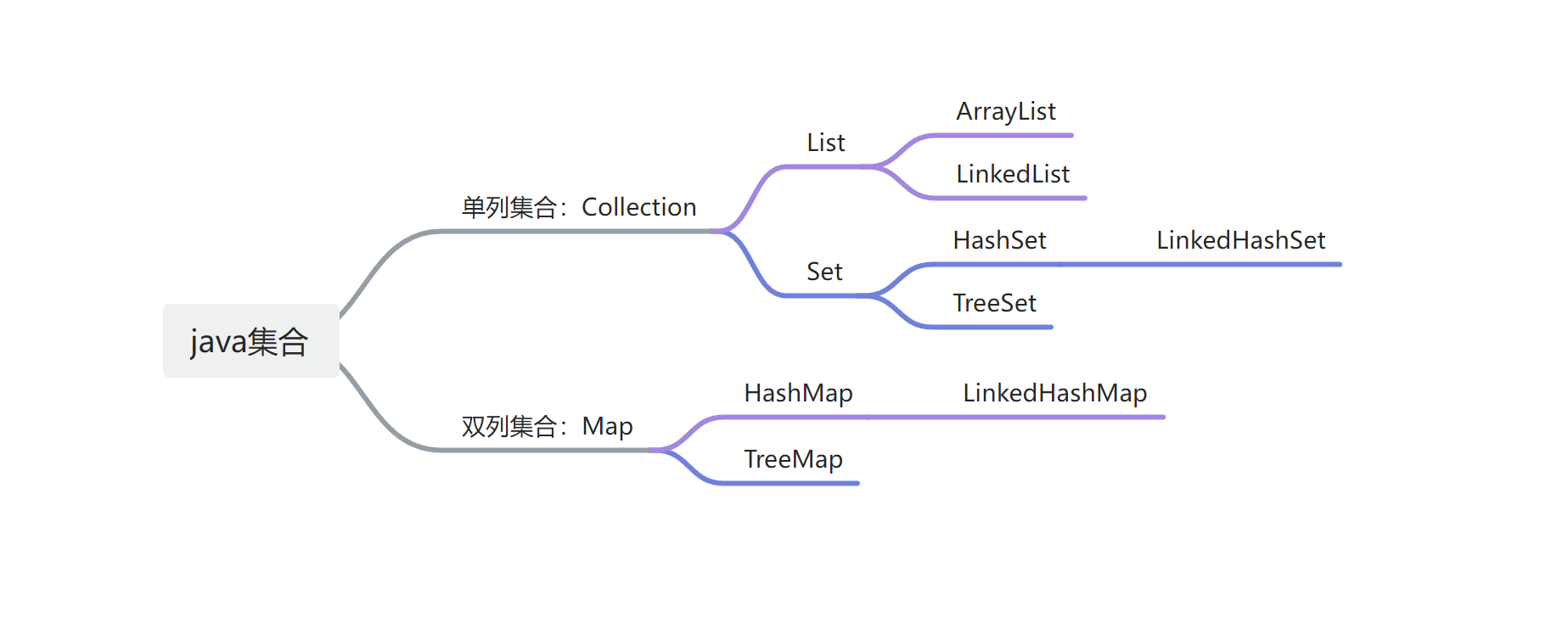
Collection公共的方法
- Collection是單列結合的頂層介面,它的方法是所有單列集合都可以繼承使用的。
//把給定元素添加到集合中
public boolean add(E e)
//把給定元素從集合中刪除
public boolean remove(E e)
//清空集合中的所有元素
public void clear()
//判斷集合中是否包含給定對象
public boolean contains(Object obj)
//判斷集合是否為空
public boolean isEmpty()
//返回集合中的長度
public int size()
註意:
-
coll.remove(E e):Collection定義的是所有子類共有的方法,Set沒有索引,所以remove方法的參數是元素。
-
coll.contains(Object object):Collection中contains方法底層是用object.equals()來判斷元素是否相等的,所以比較的是地址值。當自定義對象類型的集合使用此方法時,需要重寫equals方法。
List特有的方法
- List繼承了Collection介面的方法
- List集合因為有索引,所以定義了很多索引操作方法
//增:根據索引插入指定元素
public void add(int index,E e)
//刪:刪除指定索引處的元素,並返回被刪除元素
public E remove(int index)
//改:修改指定索引處的元素,並返回被修改的元素
public E set(int index,E e)
//返回指定索引處的元素
public E get(int index)
註意:
- list.remove(int index)是List介面重載Collection中remove的方法,功能為刪除指定索引處的元素。當list中的元素為Integer類型時,要註意以下細節:
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.remove(1);// int index 刪除索引為1的元素
list.remove(Integer.valueOf(1));// Object object 刪除元素為1的元素
System.out.println(list);
}
Set特有的方法
-
Set繼承了Collection介面的方法
-
Set的常用方法與Collection基本一致
Map公共的方法
//添加鍵值對元素,並返回添加之前的值(若已存在鍵,則覆蓋鍵值對元素)
public V put(K key,V value)
//根據鍵刪除鍵值對元素,並返回被刪除的值
public V remove(Object key)
//清空所有鍵值對元素
public void clear()
//判斷集合是否包含指定的鍵
public boolean containsKey(Object key)
//判斷集合是否包含指定的值
public boolean containsValue(Object value)
//判斷集合是否為空
public boolean isEmpty()
//返回集合的長度
public int size()
Collections工具類
-
java.util.Collections:是集合的工具類
-
常用方法(省略泛型):
//批量添加元素
public static boolean addAll(Collection coll, T... elements)
//隨機打亂元素
public static void shuffle(List list)
//根據指定規則排序(可傳比較器)
public static void sort(List list)
//二分查找指定元素
public static int binarySearch(List list, T key)
//拷貝集合中的元素
public static void copy(List dest, List src)
//以指定元素填充集合
public static int fill(List list, T object)
//返回集合中的最大/最小值
public static T max/min(Collection coll)
//交換集合中指定位置的元素
public static void swap(List list, int i, int j)
//反轉集合
public static void reverse(List list)
Collection與Map的遍歷方式
- Collection
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> coll = new ArrayList<>();
coll.add("aaa");
coll.add("bbb");
coll.add("ccc");
// 迭代器
Iterator<String> it = coll.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = it.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
// 增強for
for (String s : coll) {
System.out.println(s);
}
// Lambda表達式
coll.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
//以下為List特有的遍歷方式
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
// 普通for迴圈
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
// 列表迭代器遍歷
ListIterator<String> itList = list.listIterator();
while (itList.hasNext()) {
String s = itList.next();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
- Map
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("k1", "v1");
map.put("k2", "v2");
map.put("k3", "v3");
//鍵找值
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for (String key : set) {
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
//鍵值對
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
System.out.println("key:" + entry.getKey());
System.out.println("value:" + entry.getValue());
}
//lambda表達式
map.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("key:" + key);
System.out.println("value:" + value);
});
}
隨著學習與應用的深入,後期可能會有更新
本文作者:CodingOrange
本文鏈接:https://www.cnblogs.com/CodingOrange/p/17075280.html
轉載請註明出處!


