SpringBoot HelloWorld 1.創建Meven工程 2.引入依賴 pom.xml <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifact ...
SpringBoot
HelloWorld
1.創建Meven工程
2.引入依賴
pom.xml
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3 .創建主程式
/**
* 主程式類
* @SpringBootApplication:一個springboot應用
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
4.寫業務
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String handle01(){
return "Hello SpringBoot2!";
}
}
5.運行main,瀏覽器打開localhost:8080/hello
6.簡化配置
application.properties
server.port=8888
7.簡化部署
打包方式jar
把項目打成jar包,直接在目標伺服器執行即可
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
自動配置原理
1.依賴管理
- 父項目做依賴管理
依賴管理
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
他的父項目
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
- 開發導入starter場景啟動器
1、見到很多 spring-boot-starter-* : *就某種場景
2、只要引入starter,這個場景的所有常規需要的依賴我們都自動引入
3、SpringBoot所有支持的場景
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
4、見到的 *-spring-boot-starter: 第三方為我們提供的簡化開發的場景啟動器。
5、所有場景啟動器最底層的依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
- 無需關註版本號,自動版本仲裁
1、引入依賴預設都可以不寫版本
2、引入非版本仲裁的jar,要寫版本號。
- 可以修改版本號
1、查看spring-boot-dependencies裡面規定當前依賴的版本用的key。
2、在當前項目裡面重寫配置
<properties>
<mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
</properties>
2.自動配置
- 自動配好Tomcat
- 引入Tomcat依賴
- 配置Tomcat
- 自動配好SpringMVC
- 引入SpringMVC全套組件
- 自動配好SpringMVC常用組件(功能)
- 自動配好Web常見功能,如字元編碼問題
- SpringBoot幫我們配置好了web開發常見場景
- 預設的包結構
- 主程式所在包及其子包中的組件預設會被掃描
- 無需配置包掃描
- 改變掃描路徑@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages="com.xust")或@ComponentScan 指定掃描路徑
- 各種配置擁有預設值
- 預設配置最終都是映射到某個類上,如:MultipartProperties
- 配置文件的值最終會綁定每個類上,這個類會在容器中創建對象
- 按需載入所有預設配置項
配置文件
1.文件類型
yaml
適合做以數據為中心的配置文件
基本語法
- key: value,value前有空格
- 大小寫敏感
- 使用縮進表示層級關係
- 縮進不允許用tab,只能用空格
- 縮進的空格數不重要,只要同層級元素左對齊就行
-
表示註釋
- 字元串不需要加引號,‘ ’和“ ”表示轉義/不轉義,'\n'不換行,"\n"換行
數據類型
- 字面量:單個的、不可再分的值。date、boolean、string、number、null
k: v
- 對象:鍵值對的集合。map、hash、set、object
行內寫法:k: {k1:v1,k2:v2,k3:v3}
#或
k:
k1: v1
k2: v2
k3: v3
- 數組:一組按次序排列的值。array、list、queue
行內寫法: k: [v1,v2,v3]
#或者
k:
- v1
- v2
- v3
舉例
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Component
@ToString
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Boolean boss;
private Date birth;
private Integer age;
private Pet pet;
private String[] interests;
private List<String> animal;
private Map<String, Object> score;
private Set<Double> salarys;
private Map<String, List<Pet>> allPets;
public Person() {
}
}
@Data
@ToString
public class Pet {
private String name;
private Double weight;
}
application.yaml
person:
userName: zhangsan
boss: false
birth: 2019/12/12 20:12:33
age: 18
pet:
name: tomcat
weight: 23.4
interests: [籃球,游泳]
animal:
- jerry
- mario
score:
english:
first: 30
second: 40
third: 50
math: [131,140,148]
chinese: {first: 128,second: 136}
salarys: [3999,4999.98,5999.99]
allPets:
sick:
- {name: tom}
- {name: jerry,weight: 47}
health: [{name: mario,weight: 47}]
2.自定義綁定的配置提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Web開發
簡單功能分析
靜態資源
(1)靜態資源目錄
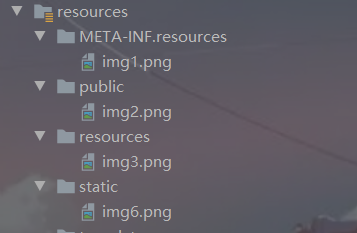
將靜態資源放在/static,/public,/resources,/META-INF/resources
訪問:當前項目根路徑/+靜態資源名
優先順序:resources>static>public
原理:靜態映射/**
請求進來,先去找Controller看能不能處理。不能處理的所有請求又去交給靜態資源處理器。如果靜態資源也找不到則響應404頁面
(2)靜態資源訪問首碼
預設無首碼
application.yaml中配置訪問首碼為res,改變預設靜態資源路徑
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
web:
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/hehe/]
歡迎頁支持
- 靜態資源路徑下index.html
- 可以修改靜態資源預設訪問路徑,但是不能配置訪問首碼,否則會導致index.html文件不能被預設訪問
- controller處理index.html
favicon圖標
將圖標圖片名稱改為favicon.ico置於靜態資源目錄下即可
配置訪問首碼會使該功能失效
模板引擎
SpringBoot不支持jsp,需要引入第三方模板引擎進行頁面渲染
模板引擎-Thymeleaf
Thymeleaf的使用
1.引入starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.自動配置好了Thymeleaf
預設前尾碼
將html頁面置於resources/templates目錄下即可自動渲染
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; //xxx.html
3.頁面開發
引入名稱空間xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${msg}">哈哈</h1>
<h2>
<a href="www.test.com" th:href="${link}">去百度1</a><br>
<a href="www.test.com" th:href="@{link}">去百度2</a>
</h2>
</body>
</html>
@Controller
public class ViewTestController {
@GetMapping("/xust")
public String xust(Model model){
//model中的數據會被放在請求域中,相當於request.setAttribute("a",aa)
model.addAttribute("msg","你好,xust");
model.addAttribute("link","http://www.baidu.com");
return "success.html";
}
}
構建後臺管理系統
攔截器
文件上傳
數據訪問
數據源的自動配置-HikariDataSource
導入jdbc場景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
資料庫驅動(預設8.0.22)
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
修改配置項
application.yaml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account
username: root
password: xpx24167830
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
Test
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class Boot03WebAdminApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Long aLong = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from t_emp", Long.class);
log.info("記錄總數:{}",aLong);
}
}
Druid數據源
自定義方式
依賴
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
整合MyBatis
pom.xml
<!--第三方-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
application.yaml
server:
port: 8888
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: xpx24167830
#?serverTimezone=UTC解決時區的報錯
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.xust.pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
UserMapper.java
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> queryUserList();
}
UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.xust.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="queryUserList" resultType="User">
select * from t_emp
</select>
</mapper>
UserController.java
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping("/queryUserList")
private List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> userList = userMapper.queryUserList();
for (User user:userList){
System.out.println(user);
}
return userList;
}
}


