結果映射指的是將數據表中的欄位與實體類中的屬性關聯起來,這樣 MyBatis 就可以根據查詢到的數據來填充實體對象的屬性,幫助我們完成賦值操作。其實 MyBatis 的官方文檔對映射規則的講解還是非常清楚的,但考慮到自己馬上就會成為一名 SQL Boy,以後免不了經常跟 SQL 打交道(公司使用的也... ...
前言
結果映射指的是將數據表中的欄位與實體類中的屬性關聯起來,這樣 MyBatis 就可以根據查詢到的數據來填充實體對象的屬性,幫助我們完成賦值操作。其實 MyBatis 的官方文檔對映射規則的講解還是非常清楚的,但考慮到自己馬上就會成為一名 SQL Boy,以後免不了經常跟 SQL 打交道(公司使用的也是 MyBatis),所以希望用更加通俗的語言對官方文檔所介紹的常用映射規則做一個總結,既為剛入門的同學提供一個參考,也方便自己以後查閱。本文會結合一些常見的應用場景,並通過簡單的示例來介紹不同的映射方法。如有理解錯誤,還請大家批評指正!
簡單欄位映射
MyBatis 中的 resultType 和 resultMap 均支持結果映射,對於一些簡單的映射操作,我們可以直接使用 resultType 來完成。但如果實體類中的屬性為複雜類型,或者屬性名和欄位名無法對應,那麼我們就需要使用 resultMap 來創建自定義的映射關係。下麵用一個示例來演示 resultType 和 resultMap 的使用方法。
首先創建實體類 User:
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String userName;
private int age;
private String address;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然後創建 user 表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 16 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接著向 user 表中插入數據:

配置 MyBatis,啟用別名和駝峰式命名映射:
#application.yaml
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/* # 指定 mapper.xml 文件的路徑,該文件用於編寫 SQL 語句
type-aliases-package: com.example.entity # 設置別名,它的作用是告訴 MyBatis 需要設置別名的實體類的所在的包。預設情況下,MyBatis 會使用實體類的非限定類名來作為它的別名,如將 com.example.entity.User 的別名設置為 User 或 user(別名不區分大小寫)
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true # 開啟駝峰命名自動映射,如將數據表中的欄位 user_name 映射到實體對象的屬性 userName
創建 mapper 文件,其內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
上述代碼中,我們使用 resultMap 來指定 SQL 語句的出參類型。預設情況下,如果數據表的欄位名與實體類的屬性名完全相同(如 id 對應 id),或者二者符合駝峰式命名映射的規則(如 user_name 對應 userName),那麼 MyBatis 可以直接完成賦值操作。但 gmt_create 和 gmt_modified 不會映射為 createTime 和 updateTime,因此我們需要使用 resultMap 來創建新的映射關係。如果將 user 表的欄位 gmt_create 和 gmt_modified 分別改為 create_time 和 update_time,那麼就可以使用 resulType="User" 或 resulType="user" 來替換 resultMap="UserMap"。
調用 findUserById(參數 id 等於 1)查詢用戶信息,可得到如下結果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同學"
}
利用 constructor 指定構造方法
MyBatis 查詢出數據後,會調用實體類的無參構造方法創建實體對象,然後為該對象的屬性賦值。有時候我們會在實體類中重載多個構造方法,例如在不同的構造方法中執行不同的初始化操作,這種情況下我們希望 MyBatis 能夠調用指定的構造方法來初始化對象。此外,如果實體類中僅有帶參的構造方法,那麼也需要通知 MyBatis 調用指定的構造方法。對於這兩個問題,我們可以使用 MyBatis 提供的 constructor 元素來解決。
MyBatis 官方文檔在介紹
constructor時有提到,constructor允許我們在始化對象時就為對象的屬性賦值,這樣可以不用暴露出公有方法。
首先在 User 類中添加帶參的構造方法:
public User(String userName, int age) {
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
}
然後將 mapper 文件修改為:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<constructor>
<arg column="user_name" javaType="String" />
<arg column="age" javaType="_int"/>
</constructor>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
註意,<arg> 標簽的定義順序必須與構造方法中的參數順序相同,因為 MyBatis 是根據 <constructor> 標簽中的參數類型列表來匹配實體類的構造方法的,例如在本例中,匹配的構造方法為 User.<init>(java.lang.String, int)。如果將 xml 文件中的兩個 <arg> 標簽互換位置,那麼 User 對象將不會被實例化成功,因為 User 類中並沒有參數類型列表為 (int, java.lang.String) 的構造方法。如果我們不指定 javaType 屬性的值,那麼 MyBatis 預設將其置為 Object,此時構造方法中對應的參數類型也必須為 Object。
MyBatis 中的 _int 類型對應 Java 中的 int 類型,int 類型對應 Integer 類型。
經過上述配置,MyBatis 在實例化對象的時候就會調用我們指定的構造方法。另外,MyBatis 也支持跟據參數名稱來匹配構造方法:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<constructor>
<arg column="age" name="age" javaType="_int"/>
<arg column="user_name" name="userName" javaType="String"/>
</constructor>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
</resultMap>
<arg> 標簽中的 name 屬性用於設置構造方法的參數名稱,如果我們設置了 name 的值,那麼 MyBatis 會根據該屬性匹配對應的構造方法,且 <arg> 標簽的位置可以隨意放置。上述代碼中,我們將兩個 <arg> 標簽互換位置,然後調用 findUserById,仍然可以查詢出用戶的信息。
利用 association 關聯一個複雜類型
博客系統中,每個用戶都擔任著某種角色,如普通用戶、管理員、版主等。為了更好地描述用戶信息,我們需要為 User 類添加一個 Role 類型的成員變數,記錄當前用戶所屬的角色。但 Role 類型與 String、int 等類型不同,Role 對象本身也存儲了一些特定的屬性,如 id、roleName 等,預設情況下 MyBatis 無法為這些屬性賦值。為了能夠正確初始化 Role 變數,我們需要使用 association 元素將查詢到的結果與 Role 對象的屬性關聯起來。
首先修改 User 類/創建 Role 類:
@Data
public class User {
// 省略部分屬性
private Role role;
}
@Data
public class Role {
private int id;
private String roleName;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然後創建 role 表(存儲角色信息)和 user_roles 表(存儲用戶和角色的關聯信息):
# 創建 `role` 表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;
CREATE TABLE `role` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`role_name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT = 3 CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
# 創建 `user_roles` 表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_roles`;
CREATE TABLE `user_roles` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`role_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接著向 role 表和 user_roles 表中插入數據:

MyBatis 為我們提供了三種處理子對象(如 Role 對象)的方式,分別為 嵌套結果映射、嵌套查詢 和 關聯多個結果集。
1. 嵌套結果映射
嵌套結果映射 指的是在 resultMap 中嵌套一個映射關係,mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
u.id,
u.user_name,
u.age,
u.address,
u.gmt_create,
u.gmt_modified,
r.id as 'role_id',
r.role_name
from user as u
left join user_roles as ur on ur.user_id = u.id
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where u.id = #{id}
</select>
上述代碼中,我們將查詢到的 role_id 和 role_name 分別映射到 Role 對象(User 對象的屬性)的 id 和 roleName。
調用 findUserById 查詢用戶信息,可得到如下結果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"role":{
"id":1,
"roleName":"管理員"
},
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同學"
}
我們也可以將 association 中的映射關係獨立出來,改寫為如下形式,方便復用:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" column="role_id" javaType="Role" resultMap="RoleMap"/>
</resultMap>
<resultMap id="RoleMap" type="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</resultMap>
2. 嵌套查詢
嵌套查詢 指的是在 resultMap 中嵌套一個查詢語句,mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role" column="{user_id=id}" select="selectUserRole"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserRole" parameterType="Map" resultType="Role">
select
r.id,
r.role_name
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where ur.user_id = #{user_id}
</select>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
resultMap 中嵌套了一個子查詢 selectUserRole,MyBatis 首先從 user 表中查詢出 id、user_name 等信息,然後將 user_id 作為參數傳遞給 selectUserRole,selectUserRole 負責從 role 表和 user_roles 表中查詢出當前用戶的角色信息。column="{user_id=id}" 指的是將查詢到的 id 賦值給變數 user_id,然後將 user_id 作為子查詢的入參(如果直接將 id 作為入參,那麼 User 對象的 id 屬性將不會被賦值),如果需要傳入多個參數,那麼可以使用一個複合屬性,如 column="{param1=value1, param2=value2}"。註意,嵌套子查詢時,子查詢中的 parameterType 必須設置為 Map 或省略不寫。
3. 關聯多個結果集
關聯多個結果集 指的是一次性執行多個查詢語句,並得到多個結果集,然後利用某個結果集的數據來填充對象的屬性。
首先在 MySQL 資料庫中創建存儲過程 findUserAndRole:
-- 將結束標誌符更改為 $$
delimiter $$
create procedure findUserAndRole(in user_id int)
begin
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = user_id;
select
r.id as role_id,
r.role_name as role_name,
ur.user_id as user_id
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r
on ur.role_id = r.id;
end $$
-- 將結束標誌符改回 ;
delimiter ;
然後修改 mapper 文件的內容:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<association property="role" javaType="Role" resultSet="role" column="id" foreignColumn="user_id">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultSets="user,role" resultMap="UserMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findUserAndRole(#{user_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
解釋一下上述操作的含義,我們在存儲過程 findUserAndRole 中定義了兩條 SQL 語句,第一條的執行邏輯是利用 user_id 從 user 表中查詢出當前用戶的 id,user_name 等信息;第二條的執行邏輯是利用關聯查詢從 role 表和 user_roles 表中查詢出 user_id、role_id 以及 role_name 等信息。我們將兩次查詢得到的結果集分別表示為 user 和 role,即 resultSets="user,role",然後通過 association 將結果集 role 中的 role_id 和 role_name 分別映射到 Role 對象的 id 和 roleName 屬性。column="id" foreignColumn="user_id" 用於關聯兩個結果集中的數據,因為結果集 role 中包含了所有用戶的角色信息(雖然本例中我們只設置了一個用戶,但實際上結果集 role 中包含著所有用戶的信息),因此在進行屬性填充之前,我們需要指明利用哪一個角色信息進行屬性填充,column="id" foreignColumn="user_id" 的作用就是從結果集 role 中篩選出 user_id 為 id 的角色信息。
resultSets 中不同的結果集之間用逗號分隔,中間千萬不能加空格!
利用 collection 關聯多個複雜類型
上文中我們分析了一個用戶擔任一種角色的情況,然而在實際開發中,每個用戶都有可能同時擔任多種角色,例如 "John同學" 既可以是管理員,又可以是版主。此時使用 association 無法正確查詢出用戶的角色信息,因為 association 處理的是一對一的映射關係。當需要關聯多個對象時,我們需要使用 collection 元素。
首先修改實體類:
@Data
public class User {
// 省略部分屬性
private List<Role> roles;
}
然後在 user_roles 表中插入一條記錄:
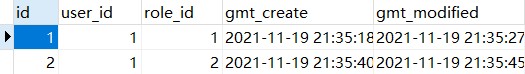
collection 的使用方法和 association 非常相似,在上文中介紹的三種方法中,我們只需要做一些簡單的修改,就可以查詢出用戶的所有角色信息。
1. 嵌套結果映射
mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
u.id,
u.user_name,
u.age,
u.address,
u.gmt_create,
u.gmt_modified,
r.id as 'role_id',
r.role_name
from user as u
left join user_roles as ur on ur.user_id = u.id
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where u.id = #{id}
</select>
與上文中使用 association 嵌套結果映射的區別在於,我們將 javaType 替換為了 ofType,以此來指定 Java 集合中的泛型類型。
調用 findUserById 查詢用戶信息,可得到如下結果:
{
"address":"BUPT",
"age":24,
"createTime":1637164800000,
"id":1,
"roles":[
{
"id":1,
"roleName":"管理員"
},
{
"id":2,
"roleName":"版主"
}
],
"updateTime":1637164800000,
"userName":"John同學"
}
2. 嵌套查詢
mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role" column="user_id=id" select="selectUserRole"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectUserRole" parameterType="Map" resultType="Role">
select
r.id,
r.role_name
from user_roles as ur
left join role as r on ur.role_id = r.id
where ur.user_id = #{user_id}
</select>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultMap="UserMap">
select
id,
user_name,
age,
address,
gmt_create,
gmt_modified
from user
where id = #{id}
</select>
同樣地,我們將 javaType 改為 ofType。
3. 關聯多個結果集
mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="UserMap" type="User">
<id column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="user_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName"/>
<result column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="age"/>
<result column="address" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="address"/>
<result column="gmt_create" jdbcType="DATE" property="createTime"/>
<result column="gmt_modified" jdbcType="DATE" property="updateTime"/>
<collection property="roles" ofType="Role" resultSet="roles" column="id" foreignColumn="user_id">
<id column="role_id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="role_name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="roleName"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="Integer" resultSets="user,roles" resultMap="UserMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findUserAndRole(#{user_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
同理,存儲過程中的執行邏輯保持不變,只需將 javaType 改為 ofType。
改用
collection後,還要註意將 property 由 role 改為 roles。當然,這個名稱可自由定義。
查詢具有樹形結構的數據
樹形結構數據在實際開發中非常常見,比較典型的就是菜單表,每個父菜單都可能包含一個或多個子菜單,而每個子菜單也可能包含孫子菜單。有時候我們希望查詢出某個菜單下的所有子菜單,並分級展示,這種情況應該如何處理呢?其實上文中介紹的三種方法均支持多級結果映射,我們只需要在 mapper 文件中做一些簡單的處理。
首先創建 Menu 類:
@Data
public class Menu {
private long id;
private String name;
private long parentId;
private List<Menu> childMenus;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
}
然後創建 menu 表:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `menu`;
CREATE TABLE `menu` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`parent_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_create` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
`gmt_modified` datetime(0) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE = InnoDB CHARACTER SET = utf8mb4 COLLATE = utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci ROW_FORMAT = Dynamic;
接著向 menu 表中插入數據:
為了更直觀地展示各層級菜單之間的關係,我們將數據整理在下麵的表格中:
| id | name | parent_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 文章 | 0 |
| 11 | 所有文章 | 1 |
| 12 | 寫文章 | 1 |
| 121 | 載入草稿 | 12 |
| 2 | 用戶 | 0 |
| 21 | 個人資料 | 2 |
| 3 | 附件 | 0 |
可以看到,菜單表總共有三個層級(不包含第 0 級),第一級的 "所有文章" 下有子菜單 "寫文章",第二級的 "寫文章" 下有子菜單 "載入草稿"。每個層級的菜單都可能有零個、一個或多個子菜單,為了將所有的菜單查詢出來,我們既要修改 SQL 語句,又要修改 resultMap 中的映射關係,下麵介紹三種查詢方式。
1. 嵌套結果映射
mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="menuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu">
<id column="id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name2" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu">
<id column="id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name3" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="parentId"/>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultMap="menuMap">
select
m1.id as id,
m1.name as name,
m1.parent_id as parent_id,
m2.id as id2,
m2.name as name2,
m2.parent_id as parent_id2,
m3.id as id3,
m3.name as name3,
m3.parent_id as parent_id3
from
menu as m1
left join menu as m2 on m1.id = m2.parent_id
left join menu as m3 on m2.id = m3.parent_id
where m1.parent_id = #{menu_id}
</select>
因為菜單表中最多有三個層級,所以我們在 SQL 語句中使用了三表聯查,分別從表 m1、m2、m3(均為 menu 表)中查詢出各個級別(從上到下)的菜單,然後在 collection 中新增一個嵌套,表 m2 和表 m3 中查出的數據均用於填充前一級別的 childMenus 屬性。
調用 findMenus(參數 menu_id 等於 0)查詢菜單信息,可得到如下結果:
[
{
"childMenus":[
{
"childMenus":[
{
"id":121,
"name":"載入草稿",
"parentId":12
}
],
"id":12,
"name":"寫文章",
"parentId":1
},
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":11,
"name":"所有文章",
"parentId":1
}
],
"id":1,
"name":"文章",
"parentId":0
},
{
"childMenus":[
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":21,
"name":"個人資料",
"parentId":2
}
],
"id":2,
"name":"用戶",
"parentId":0
},
{
"childMenus":[
],
"id":3,
"name":"附件",
"parentId":0
}
]
註意,嵌套結果映射 的方式不具備通用性,因為菜單表的結構可能不止三層。如果有多個層級的菜單,那麼我們就需要繼續修改 SQL 語句並新增嵌套。
2. 嵌套查詢
mapper 文件的內容如下:
<resultMap id="menuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="name" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id" property="parentId"/>
<collection column="{menu_id=id}" property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" select="findMenus"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultMap="menuMap">
select
id,
name,
parent_id
from
menu
where parent_id = #{menu_id}
</select>
上述代碼中,我們將嵌套的子查詢設置為 findMenus 本身,MyBatis 首先調用 findMenus 查詢出 parent_id 為 menu_id 的菜單,然後將查詢出的菜單的 id 賦值給 menu_id,繼續調用 findMenus 查詢出下一層級的菜單。此種方式可以遞歸的查詢出所有菜單,無論菜單表有多少個層級。
3. 關聯多個結果集
首先創建存儲過程 findMenu:
delimiter $$
create procedure findMenu(in menu_id int)
begin
select
id as id1,
name as name1,
parent_id as parent_id1
from menu
where parent_id = menu_id;
select
id as id2,
name as name2,
parent_id as parent_id2
from menu;
select
id as id3,
name as name3,
parent_id as parent_id3
from menu;
end $$
-- 將結束標誌符改回 ;
delimiter ;
然後將 mapper 文件的內容修改為:
<resultMap id="MenuMap" type="Menu">
<id column="id1" property="id"/>
<result column="name1" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id1" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" resultSet="menu2" column="id1" foreignColumn="parent_id2">
<id column="id2" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name2" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id2" property="parentId"/>
<collection property="childMenus" ofType="Menu" resultSet="menu3" column="id2" foreignColumn="parent_id3">
<id column="id3" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id"/>
<result column="name3" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="name"/>
<result column="parent_id3" property="parentId"/>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findMenus" parameterType="Map" resultSets="menu1,menu2,menu3" resultMap="MenuMap" statementType="CALLABLE">
{call findMenu(#{menu_id,jdbcType=INTEGER,mode=IN})}
</select>
findMenu 中定義了三條 SQL 語句,第一條的執行邏輯是從 menu 表中查詢出 parent_id 為 menu_id 的菜單,其它兩條的執行邏輯是從 menu 表中查詢出所有的菜單。我們將三條查詢返回的結果集分別表示為 menu1、menu2 和 menu3,然後利用 menu2 和 menu3 中的數據分別填充子菜單和孫子菜單的屬性。
關聯多個結果集 和 嵌套結果映射 一樣,在查詢樹形結構數據時不具備通用性。若菜單表的層級大於 3,那麼我們就需要修改存儲過程和映射關係。
參考資料
MyBatis 官方文檔
Mybatis 中強大的 resultMap



