客戶端: 1.服務端點 2.讀取客戶端已有的圖片數據 3.通過socket輸出流將數據發給服務端 4.讀取服務端反饋信息 5.關閉 獲取Socket對象,new出來,構造參數:String的服務端ip,int的埠號 調用Socket對象的getOutputStream()方法,得到OutputSt ...
客戶端:
1.服務端點
2.讀取客戶端已有的圖片數據
3.通過socket輸出流將數據發給服務端
4.讀取服務端反饋信息
5.關閉
獲取Socket對象,new出來,構造參數:String的服務端ip,int的埠號
調用Socket對象的getOutputStream()方法,得到OutputStream輸出流對象
獲取FileInputStream對象,new出來,構造參數:String的文件路徑
while迴圈調用,條件FileInputStream對象的read()方法,讀取到位元組數組中
迴圈中,調用OutputStream輸出流對象的write()方法,寫入數據,參數:byte[],0,len
調用Socket對象的shutDownOutput()方法,通知服務端寫入完成
調用Socket對象的getInputStream()方法,得到InputStream輸入流對象
調用InputStream輸入流對象的read()方法,讀取,並列印
調用FileInputStream對象的close()方法
調用Socket對象的close()方法
服務端:
正常讀取
解決併發
上面的例子,一次只能有一個客戶端服務,解決併發上傳的問題,使用多線程處理每個來訪的客戶
定義一個類PicThread,實現Runnable介面
定義構造函數,傳遞進來Socket對象
實現run()方法,在try-catch中捕獲異常,正常讀取Socket對象的流
解決文件覆蓋
文件的名稱採用ip+(數字),例如:192.168.1.100(2).jpg
獲取ip 方法,socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress()
第一次進入,文件名192.168.1.100.jpg
第二次進入,判讀文件已存在,文件名變成192.168.1.100(1).jpg
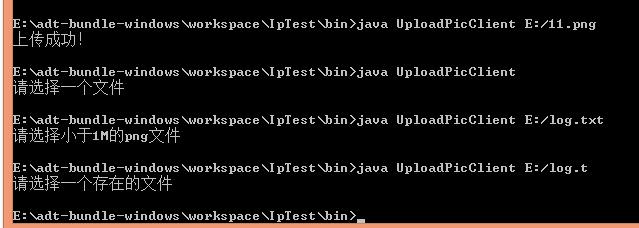
主函數傳值形式並判斷
判斷有一個參數 arg.length==1
判斷是文件,並且存在 File對象的exists()方法和isFile()方法
判斷文件尾碼,File對象的getName().endsWith(“.jpg”)方法
判斷文件大小,File對象的length()方法
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.UnknownHostException; class UploadPicClient { /** * @param args * @throws IOException * @throws UnknownHostException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //判斷參數 if(args.length!=1){ System.out.println("請選擇一個文件"); return; } File file=new File(args[0]); if(!file.exists()||!file.isFile()){ System.out.println("請選擇一個存在的文件"); return; } if(!file.getName().endsWith(".png")||file.length()>(1024*1024)){ System.out.println("請選擇小於1M的png文件"); return; } Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10001); OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); // 輸出 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:/11.png"); byte[] b = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; while ((len = fileInputStream.read(b)) != -1) { out.write(b, 0, len); } // 通知服務端 socket.shutdownOutput(); // 接收反饋 InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] res = new byte[1024]; len = inputStream.read(res); System.out.println(new String(res, 0, len)); out.close(); socket.close(); } } /** * 多線程上傳 * @author taoshihan * */ class UploadPicServerThread implements Runnable { private Socket socket; public UploadPicServerThread(Socket s) { this.socket = s; } @Override public void run() { // 讀取 InputStream is; try { is = socket.getInputStream(); byte[] res = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; // 解決文件覆蓋 String ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress(); int fileNum = 1; File file = new File(ip + ".png"); while (file.exists()) { file = new File(ip + "(" + (fileNum++) + ").png"); } FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file); while ((len = is.read(res)) != -1) { fos.write(res, 0, len); } // 反饋 OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream(); os.write("上傳成功!".getBytes()); is.close(); os.close(); fos.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } // 服務端 public class UploadPicServer { /** * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(10001); while (true) { Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); new Thread(new UploadPicServerThread(socket)).start(); } } }