前言 上一篇【.Net Core微服務入門全紀錄(四)——Ocelot-API網關(上)】已經完成了Ocelot網關的基本搭建,實現了服務入口的統一。當然,這隻是API網關的一個最基本功能,它的進階功能還有很多很多。 服務發現 首先需要解決的就是服務發現的問題,服務發現的優點之前講過,就不說了。 上 ...
前言
上一篇【.Net Core微服務入門全紀錄(四)——Ocelot-API網關(上)】已經完成了Ocelot網關的基本搭建,實現了服務入口的統一。當然,這隻是API網關的一個最基本功能,它的進階功能還有很多很多。
服務發現
首先需要解決的就是服務發現的問題,服務發現的優點之前講過,就不說了。
上一篇中我們的服務地址都是寫在ocelot.json配置文件里,現在我們需要結合之前的Consul來實現服務發現。
- 改造代碼:
首先NuGet安裝Ocelot.Provider.Consul:
修改Startup.cs:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
//添加ocelot服務
services.AddOcelot()
.AddConsul();//添加consul支持
}
修改ocelot.json配置:
{
"Routes": [
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "ProductService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
}
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "OrderService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
}
}
],
"GlobalConfiguration": {
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:9070",
"ServiceDiscoveryProvider": {
"Scheme": "http",
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 8500,
"Type": "Consul"
}
}
}
這個配置應該很好理解,就是把我們上次的DownstreamHostAndPorts節點去掉了,然後增加了ServiceDiscoveryProvider服務發現相關配置。
註意,Ocelot除了支持Consul服務發現以外,還有Eureka也可以,Eureka也是一個類似的註冊中心。
好了,代碼修改就差不多了,下麵運行程式測試一下:
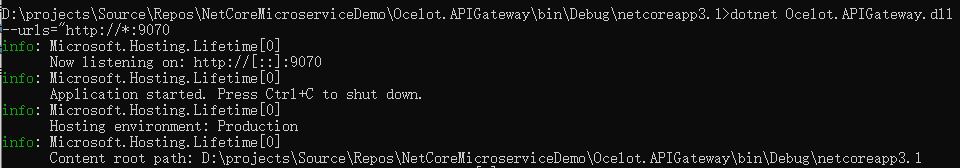

客戶端正常運行。
至此我們就實現了服務註冊與發現和api網關的基本功能。接下來就要提到:服務治理
服務治理
其實服務治理也沒有一個非常明確的定義。它的作用簡單來說,就是幫助我們更好的管理服務,提升服務的可用性。——緩存,限流,熔斷,鏈路追蹤 等等。。。都屬於常用的服務治理手段。
之前講的負載均衡,服務發現也可以算是服務治理。
- 緩存:
在Ocelot中啟用緩存,需要NuGet安裝一下Ocelot.Cache.CacheManager:
修改Startup.cs中的ConfigureServices()方法:
//添加ocelot服務
services.AddOcelot()
//添加consul支持
.AddConsul()
//添加緩存
.AddCacheManager(x =>
{
x.WithDictionaryHandle();
});
修改ocelot.json配置文件:
{
"Routes": [
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "ProductService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
},
"FileCacheOptions": {
"TtlSeconds": 5,
"Region": "regionname"
}
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "OrderService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
},
"FileCacheOptions": {
"TtlSeconds": 5,
"Region": "regionname"
}
}
],
"GlobalConfiguration": {
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:9070",
"ServiceDiscoveryProvider": {
"Scheme": "http",
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 8500,
"Type": "Consul"
}
}
}
在Routes路由配置中增加了FileCacheOptions。TtlSeconds代表緩存的過期時間,Region代表緩衝區名稱,這個我們目前用不到。
好了,代碼修改完需要編譯重啟一下網關項目,然後打開客戶端網站測試一下:
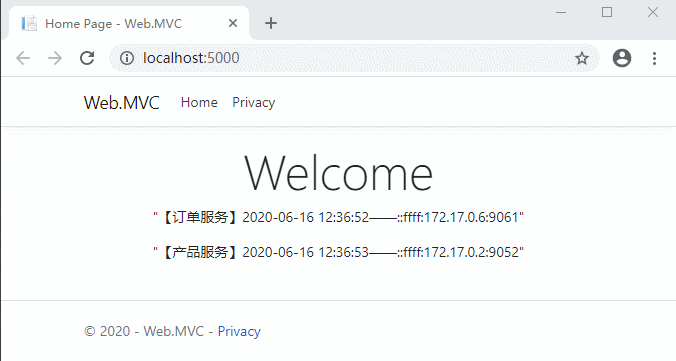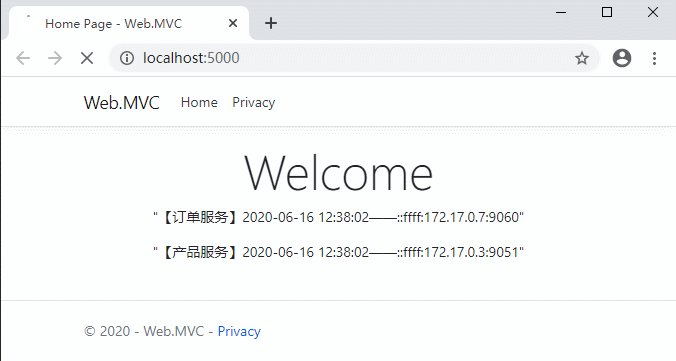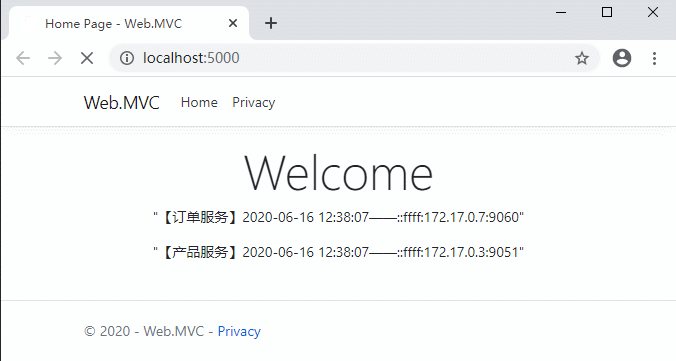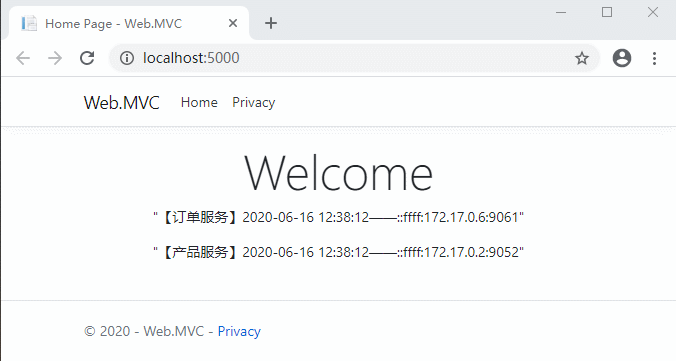
可以看到,5秒之內的請求都是同樣的緩存數據。Ocelot也支持自定義緩存。
- 限流:
限流就是限制客戶端一定時間內的請求次數。
繼續修改配置:
{
"Routes": [
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/products",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "ProductService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
},
"FileCacheOptions": {
"TtlSeconds": 5,
"Region": "regionname"
},
"RateLimitOptions": {
"ClientWhitelist": [ "SuperClient" ],
"EnableRateLimiting": true,
"Period": "5s",
"PeriodTimespan": 2,
"Limit": 1
}
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/orders",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ],
"ServiceName": "OrderService",
"LoadBalancerOptions": {
"Type": "RoundRobin"
},
"FileCacheOptions": {
"TtlSeconds": 5,
"Region": "regionname"
},
"RateLimitOptions": {
"ClientWhitelist": [ "SuperClient" ],
"EnableRateLimiting": true,
"Period": "5s",
"PeriodTimespan": 2,
"Limit": 2
}
}
],
"GlobalConfiguration": {
"BaseUrl": "http://localhost:9070",
"ServiceDiscoveryProvider": {
"Scheme": "http",
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 8500,
"Type": "Consul"
},
"RateLimitOptions": {
"DisableRateLimitHeaders": false,
"QuotaExceededMessage": "too many requests...",
"HttpStatusCode": 999,
"ClientIdHeader": "Test"
}
}
}
在Routes路由配置中增加了RateLimitOptions。ClientWhitelist代表客戶端白名單,在白名單中的客戶端可以不受限流的影響;EnableRateLimiting代表是否限流;Period代表限流的單位時間,例如1s,5m,1h,1d等;PeriodTimespan代表客戶端達到請求上限多少秒後可以重試;Limit代表客戶端在定義的時間內可以發出的最大請求數。
在GlobalConfiguration配置中也增加了RateLimitOptions。DisableRateLimitHeaders代表是否禁用X-Rate-Limit和Retry-After標頭(請求達到上限時response header中的限制數和多少秒後能重試);QuotaExceededMessage:代表請求達到上限時返回給客戶端的消息;HttpStatusCode:代表請求達到上限時返回給客戶端的HTTP狀態代碼。ClientIdHeader可以允許自定義用於標識客戶端的標頭。預設情況下為“ ClientId”。
最重要的就是Period,PeriodTimespan,Limit這幾個配置。
重新編譯啟動看一下效果:
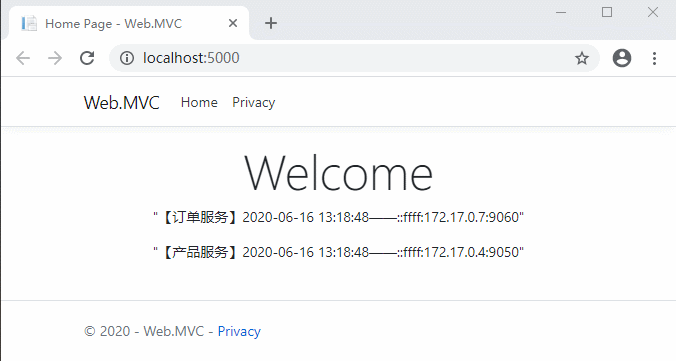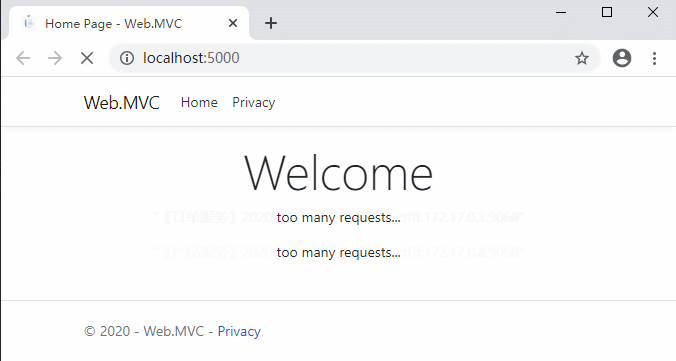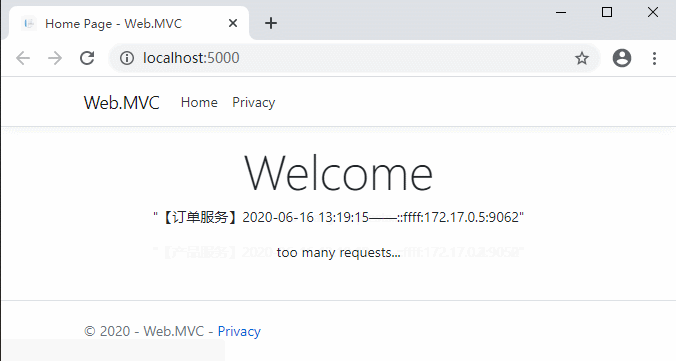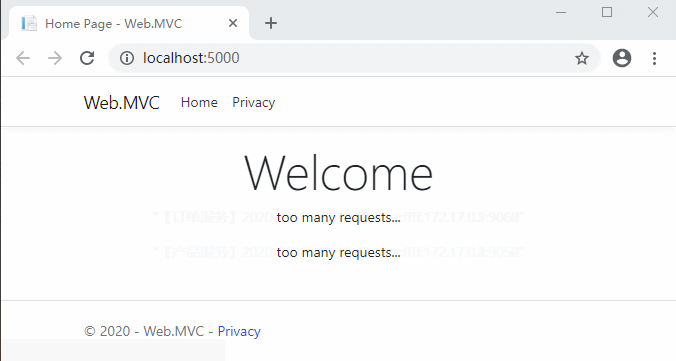
- 超時/熔斷
超時很好理解,就是網關請求服務時可容忍的最長響應時間。熔斷的意思就是當請求某個服務的異常次數達到一定量時,那麼網關在一定時間內就不再對這個服務發起請求了,直接熔斷。
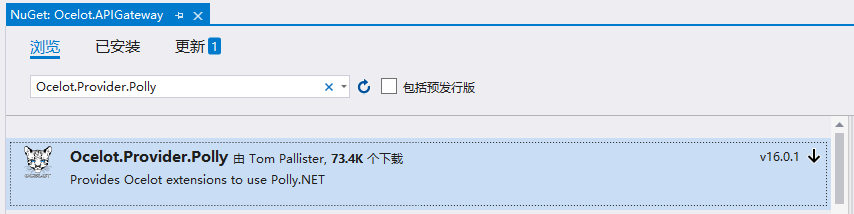
Ocelot中啟用 超時/熔斷 需要NuGet安裝一下Ocelot.Provider.Polly:
修改Startup.cs中的ConfigureServices()方法:
//添加ocelot服務
services.AddOcelot()
//添加consul支持
.AddConsul()
//添加緩存
.AddCacheManager(x =>
{
x.WithDictionaryHandle();
})
//添加Polly
.AddPolly();
同樣的在ocelot.json路由配置中增加QoSOptions:
"QoSOptions": {
"ExceptionsAllowedBeforeBreaking": 3,
"DurationOfBreak": 10000,
"TimeoutValue": 5000
}
ExceptionsAllowedBeforeBreaking代表發生錯誤的次數,DurationOfBreak代表熔斷時間,TimeoutValue代表超時時間。
以上的配置意思就是當服務發生3次錯誤時,那麼就熔斷10秒,期間客戶端的請求直接返回錯誤,10秒之後恢復。
這個不太好模擬,就不演示了,應該也挺好理解的。
。。。。。。
關於服務治理的學問還有很多,不繼續了。。。就到此為止吧。
想要更深入瞭解Ocelot的,請看官網:https://ocelot.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
或者看源碼:https://github.com/ThreeMammals/Ocelot
下一篇準備說一下:事件匯流排。
代碼放在:https://github.com/xiajingren/NetCoreMicroserviceDemo
未完待續...



