資源下載: "https://github.com/mengning/mykernel" 實驗內容: 1、配置實驗環境,完成Linux內核編譯。 2、對系統源碼進行修改,基於mykernel 2.0實現一個簡單的操作系統內核。 3、簡要分析操作系統內核核心功能及運行工作機制。 實驗環境: VMWar ...
資源下載:https://github.com/mengning/mykernel
實驗內容:
1、配置實驗環境,完成Linux內核編譯。
2、對系統源碼進行修改,基於mykernel 2.0實現一個簡單的操作系統內核。
3、簡要分析操作系統內核核心功能及運行工作機制。
實驗環境:
VMWare虛擬機下的Ubuntu18.04.4,實驗採用的內核版本為linux-5.4.34。
1 內核編譯
1.1 準備工作
1.1.1 修改鏡像源地址
為了節省資源下載時間,使用國內鏡像源。
cd /etc/apt/
sudo cp sources.list sources.list.bk
sudo gedit sources.list
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic main multiverse restricted universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-updates main multiverse restricted universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-security main multiverse restricted universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-proposed main multiverse restricted universe
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu bionic-backports main multiverse restricted universe
將sources.list修改保存後,更新apt源。
sudo apt-get update
1.1.2 添加hosts映射
新增GitHub資源功能變數名稱與對應IP的映射。
sudo vi /etc/hosts
151.101.76.133 raw.githubusercontent.com
1.1.3 安裝axel
多線程下載工具,用於下載Linux內核。
sudo apt install axel
1.2 下載內核補丁
wget https://raw.github.com/mengning/mykernel/master/mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch
補丁文件如下,根據diff對比,主要做了以下改動:
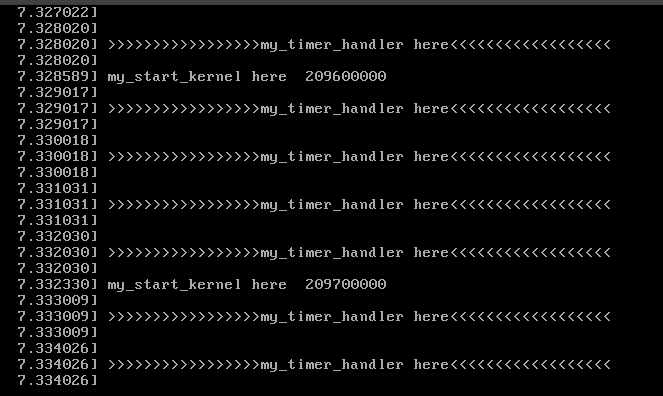
- 在時鐘中斷時調用自定義的my_timer_handler函數,列印輸出>>>>>>>my_timer_handler here<<<<<<<<
- 在start_kernel.h與timer.h中分別聲明my_start_kernel與my_timer_handler函數
- 在main.c中調用my_start_kernel函數
- 在Makefile中新增mykernel的編譯路徑
- 創建mykernel的Makefile文件
- 編寫myinterrupt.c與mymain.c文件,mymain.c中模擬系統運行,每100000次迴圈輸出一次
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/kernel/time.c linux-5.4.34-mykernel/arch/x86/kernel/time.c
--- linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/kernel/time.c 2020-04-21 15:05:05.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/arch/x86/kernel/time.c 2020-04-25 21:58:16.436717811 +0800
@@ -16,6 +16,7 @@
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/i8253.h>
#include <linux/time.h>
+#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/export.h>
#include <asm/vsyscall.h>
@@ -59,6 +60,7 @@
static irqreturn_t timer_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id)
{
global_clock_event->event_handler(global_clock_event);
+ my_timer_handler();
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/include/linux/start_kernel.h linux-5.4.34-mykernel/include/linux/start_kernel.h
--- linux-5.4.34/include/linux/start_kernel.h 2020-04-21 15:05:05.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/include/linux/start_kernel.h 2020-04-25 22:00:17.304717811 +0800
@@ -9,6 +9,7 @@
up something else. */
extern asmlinkage void __init start_kernel(void);
+extern void __init my_start_kernel(void);
extern void __init arch_call_rest_init(void);
extern void __ref rest_init(void);
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/include/linux/timer.h linux-5.4.34-mykernel/include/linux/timer.h
--- linux-5.4.34/include/linux/timer.h 2020-04-21 15:05:05.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/include/linux/timer.h 2020-04-25 21:56:45.064717811 +0800
@@ -193,6 +193,8 @@
extern void init_timers(void);
extern void run_local_timers(void);
+extern void my_timer_handler(void);
+
struct hrtimer;
extern enum hrtimer_restart it_real_fn(struct hrtimer *);
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/init/main.c linux-5.4.34-mykernel/init/main.c
--- linux-5.4.34/init/main.c 2020-04-21 15:05:05.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/init/main.c 2020-04-25 22:01:13.476717811 +0800
@@ -781,6 +781,7 @@
arch_post_acpi_subsys_init();
sfi_init_late();
+ my_start_kernel();
/* Do the rest non-__init'ed, we're now alive */
arch_call_rest_init();
}
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/Makefile linux-5.4.34-mykernel/Makefile
--- linux-5.4.34/Makefile 2020-04-21 15:05:05.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/Makefile 2020-04-25 22:02:47.144717811 +0800
@@ -1012,7 +1012,7 @@
export MODORDER := $(extmod-prefix)modules.order
ifeq ($(KBUILD_EXTMOD),)
-core-y += kernel/ certs/ mm/ fs/ ipc/ security/ crypto/ block/
+core-y += kernel/ certs/ mm/ fs/ ipc/ security/ crypto/ block/ mykernel/
vmlinux-dirs := $(patsubst %/,%,$(filter %/, $(init-y) $(init-m) \
$(core-y) $(core-m) $(drivers-y) $(drivers-m) \
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/mykernel/Makefile linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/Makefile
--- linux-5.4.34/mykernel/Makefile 1970-01-01 08:00:00.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/Makefile 2020-04-25 17:14:13.537908421 +0800
@@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
+#
+# Makefile for the linux mykernel.
+#
+
+obj-y = mymain.o myinterrupt.o
+
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/mykernel/myinterrupt.c linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/myinterrupt.c
--- linux-5.4.34/mykernel/myinterrupt.c 1970-01-01 08:00:00.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/myinterrupt.c 2020-04-25 19:09:50.612555999 +0800
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+/*
+ * linux/mykernel/myinterrupt.c
+ *
+ * Kernel internal my_timer_handler
+ *
+ * Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
+ *
+ */
+#include <linux/kernel_stat.h>
+#include <linux/export.h>
+#include <linux/interrupt.h>
+#include <linux/percpu.h>
+#include <linux/init.h>
+#include <linux/mm.h>
+#include <linux/swap.h>
+#include <linux/pid_namespace.h>
+#include <linux/notifier.h>
+#include <linux/thread_info.h>
+#include <linux/time.h>
+#include <linux/jiffies.h>
+#include <linux/posix-timers.h>
+#include <linux/cpu.h>
+#include <linux/syscalls.h>
+#include <linux/delay.h>
+#include <linux/tick.h>
+#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
+#include <linux/irq_work.h>
+#include <linux/sched.h>
+#include <linux/sched/sysctl.h>
+#include <linux/slab.h>
+
+#include <asm/uaccess.h>
+#include <asm/unistd.h>
+#include <asm/div64.h>
+#include <asm/timex.h>
+#include <asm/io.h>
+
+/*
+ * Called by timer interrupt.
+ */
+void my_timer_handler(void)
+{
+ pr_notice("\n>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>my_timer_handler here<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<<\n\n");
+}
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/mykernel/mymain.c linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/mymain.c
--- linux-5.4.34/mykernel/mymain.c 1970-01-01 08:00:00.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/mymain.c 2020-04-25 19:10:27.635058000 +0800
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+/*
+ * linux/mykernel/mymain.c
+ *
+ * Kernel internal my_start_kernel
+ *
+ * Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
+ *
+ */
+#include <linux/types.h>
+#include <linux/module.h>
+#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
+#include <linux/kernel.h>
+#include <linux/syscalls.h>
+#include <linux/stackprotector.h>
+#include <linux/string.h>
+#include <linux/ctype.h>
+#include <linux/delay.h>
+#include <linux/ioport.h>
+#include <linux/init.h>
+#include <linux/initrd.h>
+#include <linux/acpi.h>
+#include <linux/tty.h>
+#include <linux/percpu.h>
+#include <linux/kmod.h>
+#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
+#include <linux/kernel_stat.h>
+#include <linux/start_kernel.h>
+#include <linux/security.h>
+#include <linux/smp.h>
+#include <linux/profile.h>
+#include <linux/rcupdate.h>
+#include <linux/moduleparam.h>
+#include <linux/kallsyms.h>
+#include <linux/writeback.h>
+#include <linux/cpu.h>
+#include <linux/cpuset.h>
+#include <linux/cgroup.h>
+#include <linux/efi.h>
+#include <linux/tick.h>
+#include <linux/interrupt.h>
+#include <linux/taskstats_kern.h>
+#include <linux/delayacct.h>
+#include <linux/unistd.h>
+#include <linux/rmap.h>
+#include <linux/mempolicy.h>
+#include <linux/key.h>
+#include <linux/buffer_head.h>
+#include <linux/debug_locks.h>
+#include <linux/debugobjects.h>
+#include <linux/lockdep.h>
+#include <linux/kmemleak.h>
+#include <linux/pid_namespace.h>
+#include <linux/device.h>
+#include <linux/kthread.h>
+#include <linux/sched.h>
+#include <linux/signal.h>
+#include <linux/idr.h>
+#include <linux/kgdb.h>
+#include <linux/ftrace.h>
+#include <linux/async.h>
+#include <linux/sfi.h>
+#include <linux/shmem_fs.h>
+#include <linux/slab.h>
+#include <linux/perf_event.h>
+#include <linux/file.h>
+#include <linux/ptrace.h>
+#include <linux/blkdev.h>
+#include <linux/elevator.h>
+
+#include <asm/io.h>
+#include <asm/bugs.h>
+#include <asm/setup.h>
+#include <asm/sections.h>
+#include <asm/cacheflush.h>
+
+#ifdef CONFIG_X86_LOCAL_APIC
+#include <asm/smp.h>
+#endif
+
+
+void __init my_start_kernel(void)
+{
+ int i = 0;
+ while(1)
+ {
+ i++;
+ if(i%100000 == 0)
+ pr_notice("my_start_kernel here %d \n",i);
+
+ }
+}
diff -Naur linux-5.4.34/mykernel/README.md linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/README.md
--- linux-5.4.34/mykernel/README.md 1970-01-01 08:00:00.000000000 +0800
+++ linux-5.4.34-mykernel/mykernel/README.md 2020-04-25 22:18:46.512717811 +0800
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+mykernel 2.0
+==========
+Develop your own OS kernel by reusing Linux infrastructure, based on x86-64/Linux Kernel 5.4.34.
+
+## Set up mykernel 2.0 in Ubuntu 18.04
+
+```
+sudo apt install build-essential
+sudo apt install axel
+sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU
+sudo apt install libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
+wget https://raw.github.com/mengning/mykernel/master/mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.3.34.patch
+axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
+xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
+tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar
+cd linux-5.4.34
+patch -p1 < ../mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.3.34.patch
+make defconfig # Default configuration is based on 'x86_64_defconfig'
+make -j$(nproc)
+qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
+```
1.3 下載內核
sudo axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz
tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar
1.4 安裝補丁
cd linux-5.4.34
sudo apt install patch
patch -p1 < ../mykernel-2.0_for_linux-5.4.34.patch
1.5 編譯內核
在虛擬機環境下,如果物理機支持超線程,可以配置虛擬機為雙核四線程。
編譯時間大致四五分鐘左右,如果虛擬機預設配置單核單線程,使用defconfig需要較長的編譯時間。
sudo apt install build-essential libncurses-dev bison flex libssl-dev libelf-dev
make defconfig
make -j$(nproc)
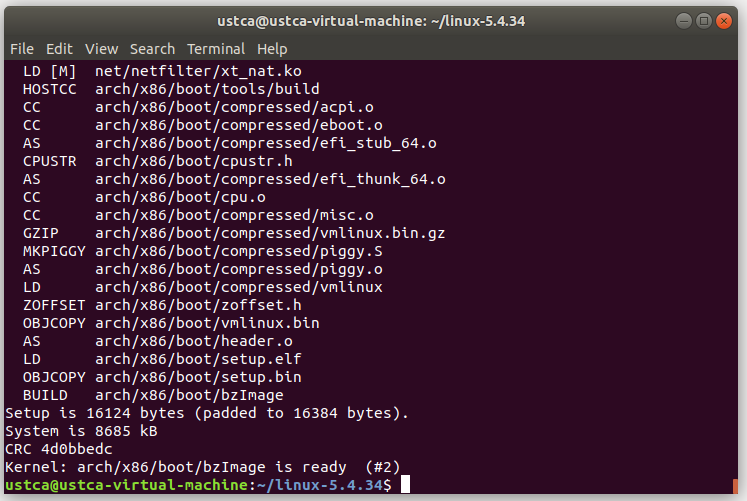
1.6 安裝QEMU模擬器
此處QEMU用於模擬硬體設備,通過模擬一臺獨立運行操作系統的虛擬機,運行編譯後的系統。
sudo apt install qemu # install QEMU
qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage
至此,Linux內核編譯完成,大致的配置流程為:
- 下載內核補丁
- 下載系統內核
- 通過給系統打補丁後編譯運行,觀察內核運行與中斷的輸出
2 修改內核
首先,在mykernel目錄下創建mypcb.h頭文件:
-
Thread結構體模擬指令指針與堆棧指針
-
PCB結構體實現進程式控制制塊,主要包含進程句柄,狀態,棧,線程信息,進程函數等,next以鏈表形式鏈接進程
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4
#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*2
struct Thread {
unsigned long ip;
unsigned long sp;
};
typedef struct PCB{
int pid;
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
unsigned long stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];
struct Thread thread;
unsigned long task_entry;
struct PCB *next;
}tPCB;
void my_schedule(void);
之後創建myinterrupt.c文件,實現中斷效果以及進程間的切換:
#include "mypcb.h"
extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
extern tPCB * my_current_task;
extern volatile int my_need_sched;
volatile int time_count = 0;
/*
* Called by timer interrupt.
* it runs in the name of current running process,
* so it use kernel stack of current running process
*/
void my_timer_handler(void)
{
if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<\n");
my_need_sched = 1;
}
time_count ++ ;
return;
}
void my_schedule(void)
{
tPCB * next;
tPCB * prev;
if(my_current_task == NULL
|| my_current_task->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<\n");
/* schedule */
next = my_current_task->next;
prev = my_current_task;
if(next->state == 0)
{
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<\n",prev->pid,next->pid);
/* switch to next process */
asm volatile(
"pushq %%rbp\n\t"
"movq %%rsp,%0\n\t"
"movq %2,%%rsp\n\t"
"movq $1f,%1\n\t"
"pushq %3\n\t"
"ret\n\t"
"1:\t"
"popq %%rbp\n\t"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
return;
}
最後在mymain.c中,根據0號進程fork出其他進程,形成進程的環狀調用:
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
/*fork more process */
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)(&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]);
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movq %1,%%rsp\n\t"
"pushq %1\n\t"
"pushq %0\n\t"
"ret\n\t"
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp)
);
}
int i = 0;
void my_process(void)
{
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -\n",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +\n",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}
以上代碼的核心在於兩段內嵌彙編代碼,mymain.c與myinterrupt.c中分別實現了0號進程的啟動與進程間切換:
asm volatile(
"movq %1,%%rsp\n\t" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to rsp */
"pushq %1\n\t" /* push rbp */
"pushq %0\n\t" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret\n\t" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to rip */
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
mymain.c中將0號進程棧頂信息存入rsp寄存器,通過將當前進程rbp與指令指針壓棧,再借用ret指令返回0號進程ip指向的my_process函數執行。
asm volatile(
"pushq %%rbp\n\t" /* save rbp of prev */
"movq %%rsp,%0\n\t" /* save rsp of prev */
"movq %2,%%rsp\n\t" /* restore rsp of next */
"movq $1f,%1\n\t" /* save rip of prev */
"pushq %3\n\t"
"ret\n\t" /* restore rip of next */
"1:\t" /* next process start here */
"popq %%rbp\n\t"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
myinterrupt.c中先將當前的rbp壓棧,然後保存當前進程的rsp信息,完成後將其更新為下一個進程的rsp。
之後將即將運行的進程IP入棧,通過ret指令將下一個進程的IP送入rip寄存器。
最後將切換後的進程堆棧基地址從堆棧中恢復到rbp寄存器中。

3 核心功能
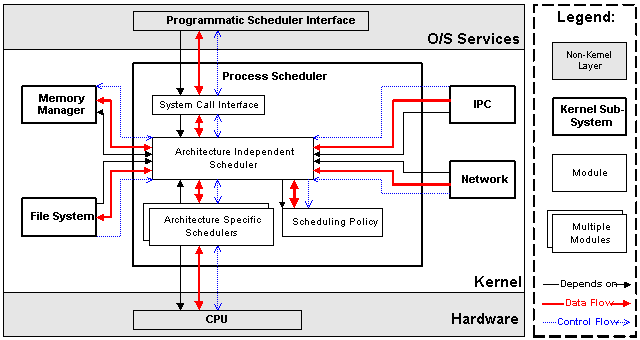
Linux操作系統主要有以下核心功能:
-
進程管理
負責管理CPU資源,以便讓各個進程可以以儘量公平的方式訪問CPU。
-
記憶體管理
負責管理Memory(記憶體)資源,以便讓各個進程可以安全地共用機器的記憶體資源。
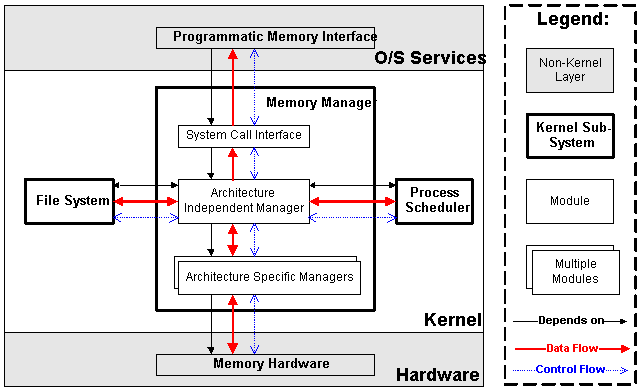
-
文件系統
Linux內核將不同功能的外部設備,抽象為統一的文件操作介面(open、close、read、write等)。

-
網路管理
負責管理系統的網路設備,並實現各類網路標準。
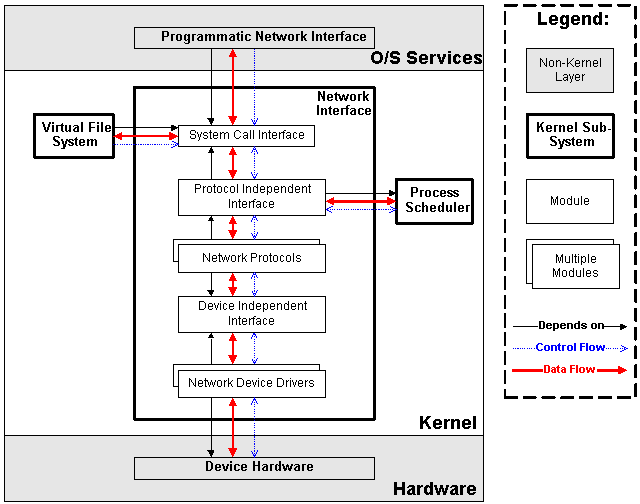
-
硬體驅動
將系統操作映射到物理設備,除了處理器,記憶體等個別實體外,一般設備控制操作都由定址設備相關的代碼進行。
-
進程間通信
不管理硬體,只負責Linux系統中進程之間的通信。



