基於JDK1.7 HashMap源碼分析 概述 HashMap是存放鍵值對的集合,數據結構如下: 1. table被稱為桶,大小(capacity)始終為2的冪,當發生擴容時,map容量擴大為兩倍 2. HashMap採用拉鏈法解決Hash衝突,發生衝突時,新元素採用頭插法插入到對應桶的鏈表中 Ha ...
基於JDK1.7 HashMap源碼分析
概述
HashMap是存放鍵值對的集合,數據結構如下:
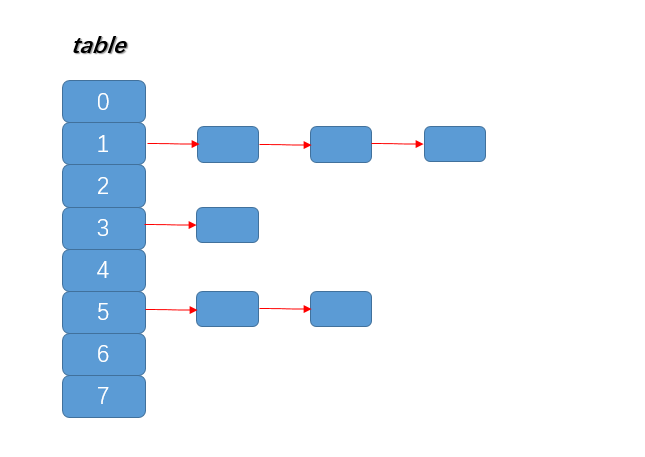
- table被稱為桶,大小(capacity)始終為2的冪,當發生擴容時,map容量擴大為兩倍
- HashMap採用拉鏈法解決Hash衝突,發生衝突時,新元素採用頭插法插入到對應桶的鏈表中
HashMap有幾個重要欄位:
- size:HashMap鍵值對的數量
- capacity:桶數量,即table.length,預設16
- loadFactor:負載因數,度量負載程度,基於時間和空間的權衡,預設0.75
- threshold:閾值,當
size>=threshold將發生擴容,threshold=capacity * loadFactor。
JDK1.7 源碼分析
屬性
/**
* 預設初始容量 (必須是2的冪)
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
/**
* 最大容量
*/
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
/**
* 預設負載因數
*/
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
/**
* 空表
*/
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {};
/**
* hash table
*/
transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
/**
* 鍵值對數目
*/
transient int size;
/**
* 閾值 (等於capacity * load factor).
*/
int threshold;
/**
* 負載因數
*/
final float loadFactor;
/**
* HashMap 結構性變化次數
* 用於快速失敗
*/
transient int modCount;
static final int ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD_DEFAULT = Integer.MAX_VALUE;構造函數
/**
* 構造函數
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = initialCapacity;
init();
}
/**
* 構造函數,預設負載因數
*/
public HashMap(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* 構造函數,預設初始容量和負載因數
*/
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
/**
* 構造函數,通過map構造
*/
public HashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this(Math.max((int) (m.size() / DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR) + 1,
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY), DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
//初始化table
inflateTable(threshold);
//賦值到新map
putAllForCreate(m);
}Hash函數
Hash函數是獲取對象處理後的hash值,為了讓hash值散列更加均勻,減少碰撞,
擾動函數(Hash函數)對hashCode進行一些位運算。
/**
* 擾動函數(減少碰撞幾率)
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}確定桶下標
確定桶下標的常用方式:hash % table.length,為了提高運行效率,
用位運算替代模運算。
能夠這樣做的前提,table.length必須是2的冪,這也是table的長度始終是2的冪的原因之一。
/**
* 確定桶下標
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// length必須是2的冪
return h & (length-1);
}Put操作
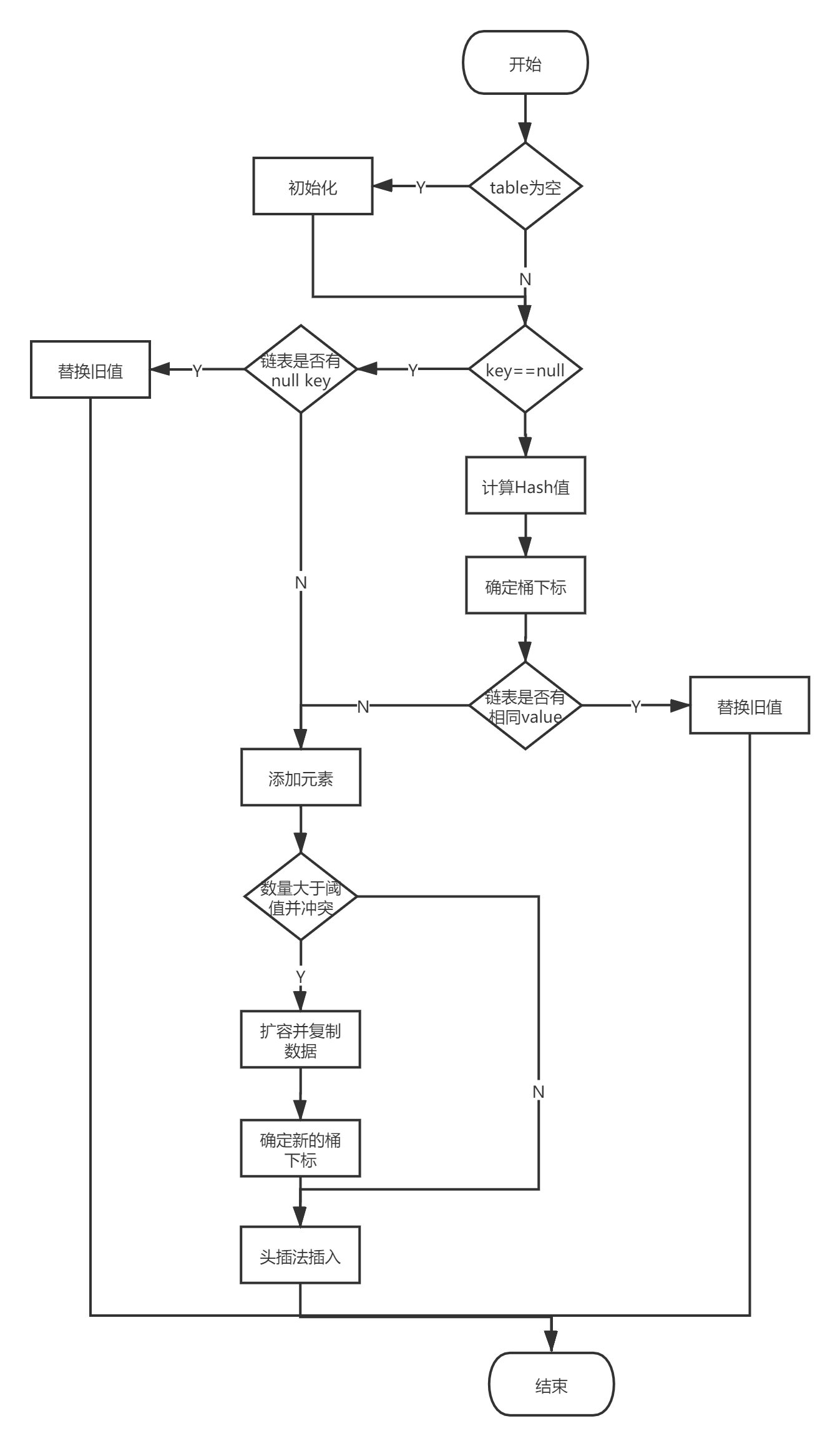
put
註意HashMap的值比較方法:e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))
public V put(K key, V value) {
//空數組,則分配記憶體空間(延遲初始化)
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//null鍵處理
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//若key已經存在,則替換
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//比較值是否相同
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//key不存在,則新增
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
inflateTable
HashMap的空間分配不是在構造函數中完成的,而是採用延遲初始化的方式,當第一個元素put時,才會進行空間分配。
private void inflateTable(int toSize) {
// Find a power of 2 >= toSize
int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);
threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//分配空間
table = new Entry[capacity];
initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity);
}putForNullKey
HashMap與HashTable的區別其中一點便是,前者key value都可以為null,後者都不能為null。
為null的鍵存放在table[0]中,即第一個桶。
/**
* null鍵插入
*/
private V putForNullKey(V value) {
/**
* null鍵存放在table[0]中(table[0]中不全是null鍵)
*/
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
//計數增加
modCount++;
//添加Entry
addEntry(0, null, value, 0);
return null;
}擴容
當向HashMap添加一個不存在的key時(即size將增大),添加之前擴容檢查。
擴容觸發條件為:數量達到閾值並且發生Hash衝突。
擴容本質上,新建一個數組,使用頭插法將舊map的元素拷貝到新map中。
addEntry
添加鍵值對時,檢驗是否需要擴容。擴容的條件:數量達到閾值並且發生Hash衝突
/**
* 添加Entry
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//擴容條件:size大於閾值並且發生碰撞
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
//容量擴為2倍
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
//確定新桶下標
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}resize
當擴容時:
- 容量已經達到最大值,僅調整閾值
- 容量未達到最大值,擴大table空間,並將舊map數據添加到新map中
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
//當容量達到最大時,僅調整閾值
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//擴容
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
//數據複製
transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity));
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}transfer
實際上,擴容本質是新建一個數組,然後在把數據複製過去,複製過程中,元素需要重新定位桶標
所以,多次擴容對性能影響很大
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {
while(null != e) {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}createEntry
從Entry的構造函數中next = n;可以看出元素插入鏈表使用的頭插法。
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//table下標中第一個元素
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
/**
* 構造方法中 next = e; 可見 使用的頭插法插入到鏈表中
*/
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}get操作
/**
* 獲取值
* 返回null有兩種可能:1.不存在對應的鍵值對;2.存在key,但值為null
* 可以通過 {@link #containsKey containsKey} 進行區分
*/
public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
//獲取key為null的值
return getForNullKey();
Entry<K,V> entry = getEntry(key);
return null == entry ? null : entry.getValue();
}
private V getForNullKey() {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
//可見,null的key存放在table[0]中,即第一個桶中
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) {
if (e.key == null)
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : hash(key);
//確定桶下標後,遍歷鏈表
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
//判斷key是否相等。先比較的hash值,再比較的地址,最後比較equals
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
}
return null;
}



