1.1.變數替換 變數替換的六種形式 實例:非貪婪和貪婪的區別 從頭部刪除 從尾部刪除 字元串替換,把bin替換成大寫的BIN,單斜線和雙斜線的區別 1.2.字元串處理 計算字元串長度 方法一 方法二 string有空格,則必須加雙引號 實例 獲取子串在字元串中的索引位置 實例 會把子串分割成一個一 ...
1.1.變數替換
變數替換的六種形式

實例:非貪婪和貪婪的區別
從頭部刪除
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var_1="i love you,do you love me" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var_1 i love you,do you love me [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1=${var_1#*ov} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var1 e you,do you love me [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var2=${var_1##*ov} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var2 e me [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
從尾部刪除
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var_1="i love you,do you love me" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var_1 i love you,do you love me [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var3=${var_1%ov*} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var3 i love you,do you l [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var4=${var_1%%ov*} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var4 i l [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
字元串替換,把bin替換成大寫的BIN,單斜線和雙斜線的區別
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var5=${PATH/bin/BIN} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var5 /usr/local/sBIN:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var6=${PATH//bin//BIN} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var6 /usr/local/s/BIN:/usr/local//BIN:/usr/s/BIN:/usr//BIN:/root//BIN [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
1.2.字元串處理
計算字元串長度
方法一
${#string}
方法二
string有空格,則必須加雙引號
expr length "$string"
實例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello world" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=${#var1} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len 11 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len2=`expr length "$var1"` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len2 11 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
獲取子串在字元串中的索引位置
expr index $string $substring
實例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="quickstart is a app" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index=`expr index "$var1" start` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index 6 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index2=`expr index "$var1" uniq` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index2 1 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index3=`expr index "$var1" cnk` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index3 4 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
會把子串分割成一個一個字元,index是最先找到的那個字元的位置。
計運算元串長度
expr match $string substr
實例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="quickstart is a app" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" quic` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len 4 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" app` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len 0 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" quic.*` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len 19 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
必須從開頭匹配才可以
抽取子串
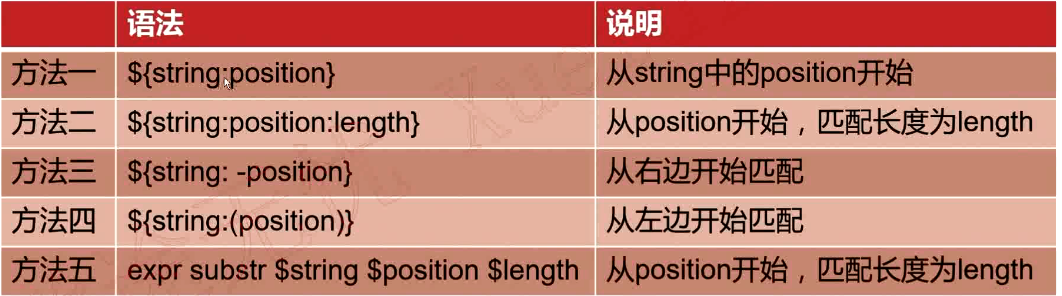
實例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="kafka hadoop yarn mapreduce" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub1=${var1:10} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub1 op yarn mapreduce [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub2=${var1:10:5} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub2 op ya [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub3=${var1: -5} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub3 educe [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub4=${var1:(-6)} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub4 reduce [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub5=${var1: -5:3} [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub5 edu [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub6=`expr substr "$var1" 10 5` [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub6 oop y [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
註意:使用expr索引是從1開始計算,使用${string:position},索引從0開始計算。
1.3.字元串處理完整腳本

思路分析
1.將不同的功能模塊劃分,並編寫函數 function print_tips function len_of_string function del_hadoop function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first function rep_hadoop_maapreduce_all 2.實現第一步所定義的功能函數 3.程式主流程的設計
vim example.sh
#!/bin/bash string="Bigdata process framework is Hadoop,Hadoop is an open source project" function print_tips { echo "******************************" echo "(1)列印string長度" echo "(2)刪除字元串中所有的Hadoop" echo "(3)替換第一個Hadoop為Mapreduce" echo "(4)替換全部Hadoop為Mapreduce" echo "*******************************" } function len_of_string { echo "${#string}" } function del_hadoop { echo "${string//Hadoop/}" } function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first { echo "${string/Hadoop/Mapreduce}" } function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_all { echo "${string//Hadoop/Mapreduce}" } while true do echo "[string=$string]" echo print_tips read -p "Pls input your choice(1|2|3|4|q|Q): " choice case $choice in 1) len_of_string ;; 2) del_hadoop ;; 3) rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first ;; 4) rep_hadoop_mapreduce_all ;; q|Q) exit ;; *) echo "Error,input only in {1|2|3|4|q|Q|}" ;; esac done
sh example.sh

1.4.命令替換
語法格式
方法一:
`command`
方法二:
$(command)
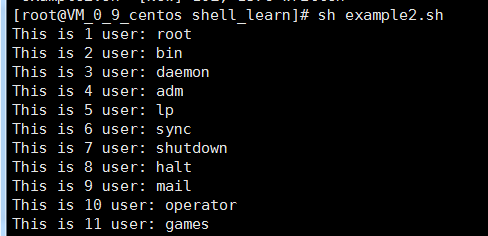
實例一:獲取系統所有的用戶並輸出
cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1
vim example2.sh
#!/bin/bash # index=1 for user in `cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1` do echo "This is $index user: $user" index=$(($index+1)) done
結果
實例二:根據當前當前時間計算今年和明年
$(());兩個括弧主要用來進行整數運算
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date Wed Jun 26 21:58:04 CST 2019 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date +%Y 2019 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This is $(date +%Y) year" This is 2019 year [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This is $(($(date +%Y) + 1)) year" This is 2020 year [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
實例三:根據當前時間獲取今年還剩下多少星期和已經過了多少星期
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date +%j 177 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This yaer have passed $(date +%j) days" This yaer have passed 177 days [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This yaer have passed $(($(date +%j)/7)) weeks" This yaer have passed 25 weeks [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "今年還剩下$(((365 - $(date +%j))/7))星期" 今年還剩下26星期 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
實例四:判斷nginx進程是否存在,若不存在則自動拉起該進程
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx root 6658 1 0 22:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx nginx 6659 6658 0 22:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 6891 501 0 22:35 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l 2 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# systemctl stop nginx [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l 0 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sh example3.sh [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l 2 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
vim example3.sh
如果nginx的進程個數為0,則拉起該進程
#!/bin.bash # nginx_process_num=$(ps -ef | grep nginx | grep -v grep | wc -l) if [ $nginx_process_num -eq 0 ];then systemctl start nginx fi
1.5.有類型變數
declare和typeset命令
- declare和typeset命令兩者等價
- declare和typeset命令都是用來定義變數類型的
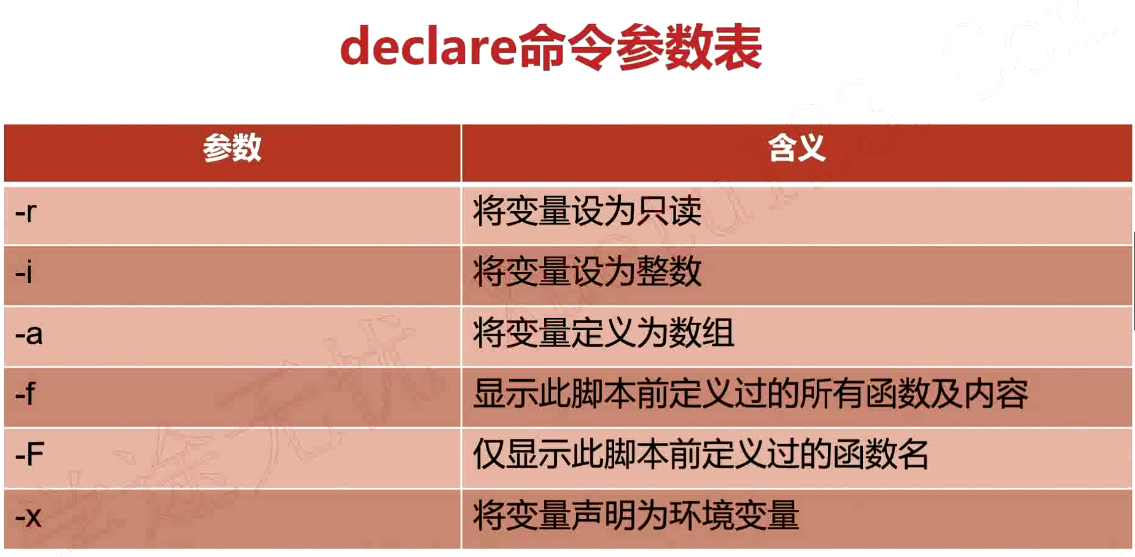
取消申明的變數
declare +r declare +i declare +a declare +x
實例一:-r 將變數設為只讀
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello world" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello python" [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var1 hello python [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -r var1 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello go" -bash: var1: readonly variable [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
實例二:-i 將變數設為整數
shell中如果不聲明,預設當做字元串處理
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num1=10 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=$num1+20 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $num2 10+20 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -i num2 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=$num1+20 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $num2 30 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
實例三:-a 將變數定義為數組
定義數組
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -a array [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# array=("jones" "mike" "kobe" "jordan")
輸出數組所有的內容
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${array[@]} jones mike kobe jordan
第一個元素
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${array[0]} jones
數組長度
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${#array[@]} 4
刪除元素
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# unset array
1.6.Bash數學運算之expr
語法格式

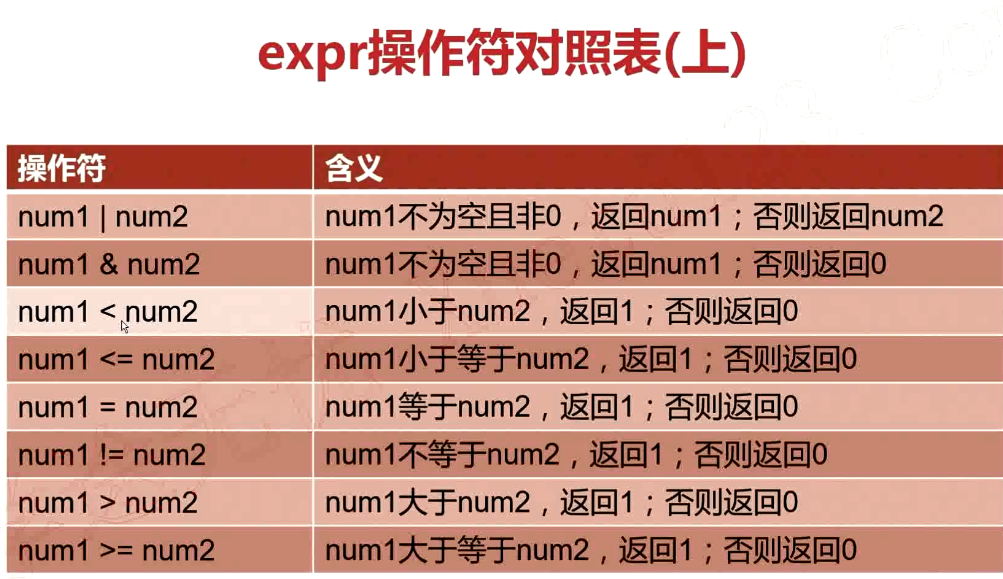
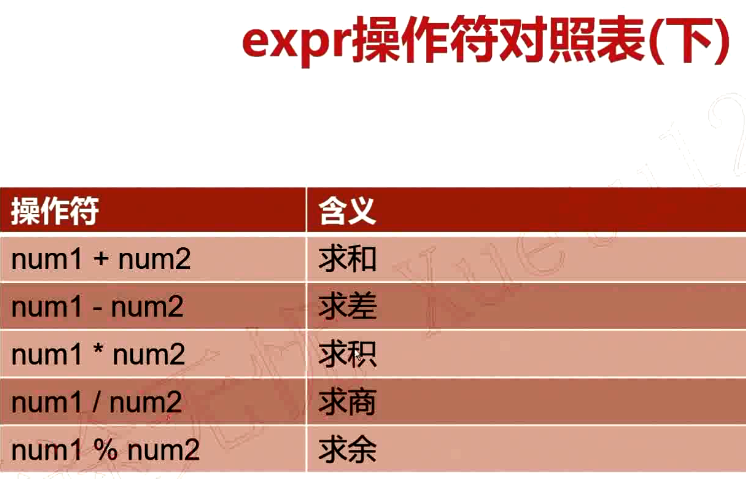
需要加轉義字元“\”
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num1=30 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=40 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \> $num2 0 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \< $num2 1 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 + $num2 70 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 - $num2 -10 [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 * $num2 expr: syntax error [root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \* $num2 1200
實例:輸入一個正整數num,然後計算1+2+3+....+num的值,必須判斷num是否為正整數,不符合重新輸入
vim num.sh



